
3,4-Methylenedioxyamphetamine is an empathogen-entactogen, psychostimulant, and psychedelic drug of the amphetamine family that is encountered mainly as a recreational drug. In its pharmacology, MDA is a serotonin–norepinephrine–dopamine releasing agent (SNDRA). In most countries, the drug is a controlled substance and its possession and sale are illegal.

Catechin is a flavan-3-ol, a type of secondary metabolite providing antioxidant roles in plants. It belongs to the subgroup of polyphenols called flavonoids.
GABAB receptors (GABABR) are G-protein coupled receptors for gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), therefore making them metabotropic receptors, that are linked via G-proteins to potassium channels. The changing potassium concentrations hyperpolarize the cell at the end of an action potential. The reversal potential of the GABAB-mediated IPSP is −100 mV, which is much more hyperpolarized than the GABAA IPSP. GABAB receptors are found in the central nervous system and the autonomic division of the peripheral nervous system.
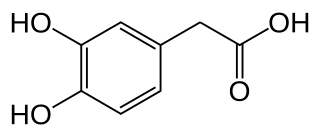
3,4-Dihydroxyphenylacetic acid (DOPAC) is a metabolite of the neurotransmitter dopamine. Dopamine can be metabolized into one of three substances. One such substance is DOPAC. Another is 3-methoxytyramine (3-MT). Both of these substances are degraded to form homovanillic acid (HVA). Both degradations involve the enzymes monoamine oxidase (MAO) and catechol-O-methyl transferase (COMT), albeit in reverse order: MAO catalyzes dopamine to DOPAC, and COMT catalyzes DOPAC to HVA; whereas COMT catalyzes dopamine to 3-MT and MAO catalyzes 3-MT to HVA. The third metabolic end-product of dopamine is norepinephrine (noradrenaline).
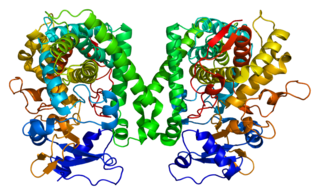
Cytochrome P4502C8 (CYP2C8) is a member of the cytochrome P450 mixed-function oxidase system involved in the metabolism of xenobiotics in the body. Cytochrome P4502C8 also possesses epoxygenase activity, i.e. it metabolizes long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids, e.g. arachidonic acid, eicosapentaenoic acid, docosahexaenoic acid, and linoleic acid to their biologically active epoxides.

Vanillylmandelic acid (VMA) is a chemical intermediate in the synthesis of artificial vanilla flavorings and is an end-stage metabolite of the catecholamines. It is produced via intermediary metabolites.
Doma or DOMA may refer to:

Normetanephrine, also called normetadrenaline, is a metabolite of norepinephrine created by action of catechol-O-methyl transferase on norepinephrine. It is excreted in the urine and found in certain tissues. It is a marker for catecholamine-secreting tumors such as pheochromocytoma.

1,3-Benzodioxolylbutanamine is an entactogenic drug of the phenethylamine chemical class. It is the α-ethyl analog of MDPEA and MDA and the methylenedioxy analogue of α-ethylphenethylamine.
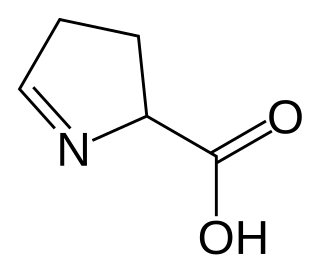
1-Pyrroline-5-carboxylic acid is a cyclic imino acid. Its conjugate base and anion is 1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate (P5C). In solution, P5C is in spontaneous equilibrium with glutamate-5-semialdhyde (GSA).
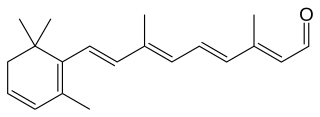
Dehydroretinal (3,4-dehydroretinal) is a derivative metabolite of retinal belonging to the group of vitamin A2 as a retinaldehyde form, besides the endogenously present 3,4-dehydroretinol and 3,4-dehydroretinoic acid.

3-Methoxy-4-hydroxyphenylglycol is a metabolite of norepinephrine degradation. In the brain, it is the principal norepinephrine metabolite. It is released into the blood and cerebrospinal fluid, and a blood sample of it may therefore be an indication of recent sympathetic nervous system activity.

Protocatechuic acid (PCA) is a dihydroxybenzoic acid, a type of phenolic acid. It is a major metabolite of antioxidant polyphenols found in green tea. It has mixed effects on normal and cancer cells in in vitro and in vivo studies. It is produced commercially from vanillin.
Metabolic intermediates are molecules that are the precursors or metabolites of biologically significant molecules.

3,4-Dihydroxyphenylacetaldehyde (DOPAL), also known as dopamine aldehyde, is a metabolite of the monoamine neurotransmitter dopamine formed by monoamine oxidase (MAO).
The molecular formula C8H8O5 (molar mass: 184.14 g/mol, exact mass: 184.0372 u) may refer to:

Phenolic acids or phenolcarboxylic acids are phenolic compounds and types of aromatic acid compounds. Included in that class are substances containing a phenolic ring and an organic carboxylic acid function. Two important naturally occurring types of phenolic acids are hydroxybenzoic acids and hydroxycinnamic acids, which are derived from non-phenolic molecules of benzoic and cinnamic acid, respectively.

N,N-Dimethyldopamine (DMDA) is an organic compound belonging to the phenethylamine family. It is related structurally to the alkaloid epinine (N-methyldopamine) and to the major neurotransmitter dopamine (of which it is the N,N-dimethylated analog). Because of its structural relationship to dopamine, DMDA has been the subject of a number of pharmacological investigations. DMDA has been detected in Acacia rigidula.
Substituted piperazines are a class of chemical compounds based on a piperazine core. Some are used as recreational drugs and some are used in scientific research.

3,4-Dihydroxyphenylglycolaldehyde (DOPEGAL), also known as 3,4-dihydroxymandelaldehyde (DHMAL) as well as norepinephrine aldehyde or epinephrine aldehyde, is a metabolite of the monoamine neurotransmitters norepinephrine and epinephrine. DOPEGAL is a noradrenergic neurotoxin.
















