
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) are a class of drugs that inhibit the activity of one or both monoamine oxidase enzymes: monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A) and monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B). They are best known as effective antidepressants, especially for treatment-resistant depression and atypical depression. They are also used to treat panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, Parkinson's disease, and several other disorders.

Monoamine neurotransmitters are neurotransmitters and neuromodulators that contain one amino group connected to an aromatic ring by a two-carbon chain (such as -CH2-CH2-). Examples are dopamine, norepinephrine and serotonin.

Phenethylamine (PEA) is an organic compound, natural monoamine alkaloid, and trace amine, which acts as a central nervous system stimulant in humans. In the brain, phenethylamine regulates monoamine neurotransmission by binding to trace amine-associated receptor 1 (TAAR1) and inhibiting vesicular monoamine transporter 2 (VMAT2) in monoamine neurons. To a lesser extent, it also acts as a neurotransmitter in the human central nervous system. In mammals, phenethylamine is produced from the amino acid L-phenylalanine by the enzyme aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase via enzymatic decarboxylation. In addition to its presence in mammals, phenethylamine is found in many other organisms and foods, such as chocolate, especially after microbial fermentation.

Monoamine transporters (MATs) are proteins that function as integral plasma-membrane transporters to regulate concentrations of extracellular monoamine neurotransmitters. The three major classes are serotonin transporters (SERTs), dopamine transporters (DATs), and norepinephrine transporters (NETs) and are responsible for the reuptake of their associated amine neurotransmitters. MATs are located just outside the synaptic cleft (peri-synaptically), transporting monoamine transmitter overflow from the synaptic cleft back to the cytoplasm of the pre-synaptic neuron. MAT regulation generally occurs through protein phosphorylation and post-translational modification. Due to their significance in neuronal signaling, MATs are commonly associated with drugs used to treat mental disorders as well as recreational drugs. Compounds targeting MATs range from medications such as the wide variety of tricyclic antidepressants, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors such as fluoxetine (Prozac) to stimulant medications such as methylphenidate (Ritalin) and amphetamine in its many forms and derivatives methamphetamine (Desoxyn) and lisdexamfetamine (Vyvanse). Furthermore, drugs such as MDMA and natural alkaloids such as cocaine exert their effects in part by their interaction with MATs, by blocking the transporters from mopping up dopamine, serotonin, and other neurotransmitters from the synapse.
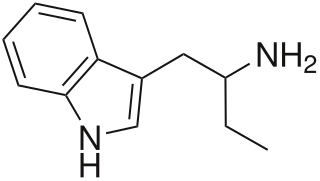
α-Ethyltryptamine, also known as etryptamine, is an entactogen and stimulant drug of the tryptamine family. It was originally developed and marketed as an antidepressant under the brand name Monase by Upjohn in the 1960s before being withdrawn due to toxicity.

Isocarboxazid is a non-selective, irreversible monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) of the hydrazine class used as an antidepressant. Along with phenelzine and tranylcypromine, it is one of only three classical MAOIs still available for clinical use in the treatment of psychiatric disorders in the United States, though it is not as commonly employed in comparison to the others.

Trace amines are an endogenous group of trace amine-associated receptor 1 (TAAR1) agonists – and hence, monoaminergic neuromodulators – that are structurally and metabolically related to classical monoamine neurotransmitters. Compared to the classical monoamines, they are present in trace concentrations. They are distributed heterogeneously throughout the mammalian brain and peripheral nervous tissues and exhibit high rates of metabolism. Although they can be synthesized within parent monoamine neurotransmitter systems, there is evidence that suggests that some of them may comprise their own independent neurotransmitter systems.

Rasagiline, sold under the brand name Azilect among others, is a medication which is used in the treatment of Parkinson's disease. It is used as a monotherapy to treat symptoms in early Parkinson's disease or as an adjunct therapy in more advanced cases. The drug is taken by mouth.

Pargyline, sold under the brand name Eutonyl among others, is a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) medication which has been used to treat hypertension but is no longer marketed. It has also been studied as an antidepressant, but was never licensed for use in the treatment of depression. The drug is taken by mouth.

N-Methylphenethylamine (NMPEA) is a naturally occurring trace amine neuromodulator in humans that is derived from the trace amine, phenethylamine (PEA). It has been detected in human urine and is produced by phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase with phenethylamine as a substrate, which significantly increases PEA's effects. PEA breaks down into phenylacetaldehyde which is further broken down into phenylacetic acid by monoamine oxidase. When this is inhibited by monoamine oxidase inhibitors, it allows more of the PEA to be metabolized into nymphetamine (NMPEA) and not wasted on the weaker inactive metabolites.

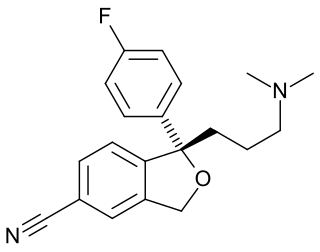
(–)-Benzofuranylpropylaminopentane is an experimental drug related to selegiline which acts as a monoaminergic activity enhancer (MAE). It is orally active in animals.

Monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MAOB gene.

Trace amine-associated receptor 1 (TAAR1) is a trace amine-associated receptor (TAAR) protein that in humans is encoded by the TAAR1 gene. TAAR1 is an intracellular amine-activated Gs-coupled and Gq-coupled G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) that is primarily expressed in several peripheral organs and cells, astrocytes, and in the intracellular milieu within the presynaptic plasma membrane of monoamine neurons in the central nervous system (CNS). TAAR1 was discovered in 2001 by two independent groups of investigators, Borowski et al. and Bunzow et al. TAAR1 is one of six functional human trace amine-associated receptors, which are so named for their ability to bind endogenous amines that occur in tissues at trace concentrations. TAAR1 plays a significant role in regulating neurotransmission in dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin neurons in the CNS; it also affects immune system and neuroimmune system function through different mechanisms.
Reuptake inhibitors (RIs) are a type of reuptake modulators. It is a drug that inhibits the plasmalemmal transporter-mediated reuptake of a neurotransmitter from the synapse into the pre-synaptic neuron. This leads to an increase in extracellular concentrations of the neurotransmitter and an increase in neurotransmission. Various drugs exert their psychological and physiological effects through reuptake inhibition, including many antidepressants and psychostimulants.
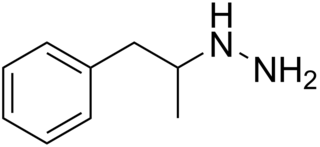
Pheniprazine, formerly sold under the brand names Catron and Cavodil, is an irreversible and non-selective monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) of the hydrazine group that was used as an antidepressant to treat depression in the 1960s. It was also used in the treatment of angina pectoris and schizophrenia. Pheniprazine has been largely discontinued due to toxicity concerns such as jaundice, amblyopia, and optic neuritis.

para-Chloroamphetamine (PCA), also known as 4-chloroamphetamine (4-CA), is a substituted amphetamine and monoamine releaser similar to MDMA, but with substantially higher activity as a monoaminergic neurotoxin, thought to be due to the unrestrained release of both serotonin and dopamine by a metabolite. It is used as a neurotoxin by neurobiologists to selectively kill serotonergic neurons for research purposes, in the same way that 6-hydroxydopamine is used to kill dopaminergic neurons.

A monoamine releasing agent (MRA), or simply monoamine releaser, is a drug that induces the release of a monoamine neurotransmitter from the presynaptic neuron into the synapse, leading to an increase in the extracellular concentrations of the neurotransmitter. Many drugs induce their effects in the body and/or brain via the release of monoamine neurotransmitters, e.g., trace amines, many substituted amphetamines, and related compounds.
A serotonin releasing agent (SRA) is a type of drug that induces the release of serotonin into the neuronal synaptic cleft. A selective serotonin releasing agent (SSRA) is an SRA with less significant or no efficacy in producing neurotransmitter efflux at other types of monoamine neurons, including dopamine and norepinephrine neurons.

Mofegiline (MDL-72,974) is a selective, irreversible inhibitor of monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B) and semicarbazide-sensitive amine oxidase (SSAO) which was under investigation for the treatment of Parkinson's disease and Alzheimer's disease, but was never marketed.
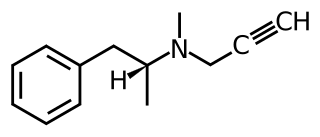
Monoaminergic activity enhancers (MAE), also known as catecholaminergic/serotonergic activity enhancers (CAE/SAE), are a class of drugs that enhance the action potential-evoked release of monoamine neurotransmitters in the nervous system. MAEs are distinct from monoamine releasing agents (MRAs) like amphetamine and fenfluramine in that they do not induce the release of monoamines from synaptic vesicles but rather potentiate only nerve impulse propagation-mediated monoamine release. That is, MAEs increase the amounts of monoamine neurotransmitters released by neurons per electrical impulse.



















