Amphetamine is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant that is used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), narcolepsy, and obesity; it is also used to treat binge eating disorder in the form of its inactive prodrug lisdexamfetamine. Amphetamine was discovered as a chemical in 1887 by Lazăr Edeleanu, and then as a drug in the late 1920s. It exists as two enantiomers: levoamphetamine and dextroamphetamine. Amphetamine properly refers to a specific chemical, the racemic free base, which is equal parts of the two enantiomers in their pure amine forms. The term is frequently used informally to refer to any combination of the enantiomers, or to either of them alone. Historically, it has been used to treat nasal congestion and depression. Amphetamine is also used as an athletic performance enhancer and cognitive enhancer, and recreationally as an aphrodisiac and euphoriant. It is a prescription drug in many countries, and unauthorized possession and distribution of amphetamine are often tightly controlled due to the significant health risks associated with recreational use.

Stimulants are a class of drugs that increase the activity of the brain. They are used for various purposes, such as enhancing alertness, attention, motivation, cognition, mood, and physical performance. Some of the most common stimulants are caffeine, nicotine, amphetamines, cocaine, methylphenidate, and modafinil.
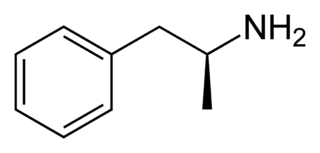
Dextroamphetamine (INN:dexamfetamine) is a potent central nervous system (CNS) stimulant and enantiomer of amphetamine that is prescribed for the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy. It is also used as an athletic performance and cognitive enhancer, and recreationally as an aphrodisiac and euphoriant. Dextroamphetamine is generally regarded as the prototypical stimulant.
Stimulant psychosis is a mental disorder characterized by psychotic symptoms. It involves and typically occurs following an overdose or several day binge on psychostimulants, though one study reported occurrences at regularly prescribed doses in approximately 0.1% of individuals within the first several weeks after starting amphetamine or methylphenidate therapy. Methamphetamine psychosis, or long-term effects of stimulant use in the brain, depend upon genetics and may persist for some time.
Adderall and Mydayis are trade names for a combination drug containing four salts of amphetamine. The mixture is composed of equal parts racemic amphetamine and dextroamphetamine, which produces a (3:1) ratio between dextroamphetamine and levoamphetamine, the two enantiomers of amphetamine. Both enantiomers are stimulants, but differ enough to give Adderall an effects profile distinct from those of racemic amphetamine or dextroamphetamine, which are marketed as Evekeo and Dexedrine/Zenzedi, respectively. Adderall is used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy. It is also used illicitly as an athletic performance enhancer, cognitive enhancer, appetite suppressant, and recreationally as a euphoriant. It is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant of the phenethylamine class.
Phentermine, sold under the brand name Ionamin among others, is a medication used together with diet and exercise to treat obesity. It is taken by mouth for up to a few weeks at a time, after which the benefits subside. It is also available as the combination phentermine/topiramate.
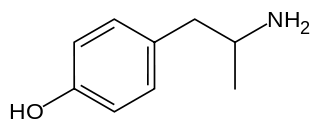
Hydroxyamphetamine, also known as 4-hydroxyamphetamine or norpholedrine and sold under the brand names Paredrine and Paremyd among others, is a sympathomimetic medication used in eye drops to dilate the pupil for eye examinations.

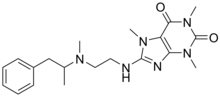
Fenethylline or fenetylline (INN) is a codrug of amphetamine and theophylline and so a mutual prodrug of both. It is also spelled phenethylline; other names for it are amphetaminoethyltheophylline and amfetyline. The drug was marketed for use as a psychostimulant under the brand names Captagon, Biocapton, and Fitton. It is now illegal in most countries and is produced primarily for illicit use. Syria is considered to be the world's largest producer of the drug, accounting for about 80% of the global supply.

Clobenzorex is a stimulant drug of the amphetamine chemical class used as an appetite suppressant. The drug is legally distributed in Mexico under the trade name Asenlix by Aventis.
Ganesha (2,5-dimethoxy-3,4-dimethylamphetamine) is a lesser-known psychedelic drug. It is also a substituted amphetamine. It was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin. In his book PiHKAL, the dosage range is listed as 24–32 mg. The drug is usually taken orally, although other routes such as rectally may also be used. Ganesha is synthesized from 2,5-dimethoxy-3,4-dimethylbenzaldehyde. Ganesha is the amphetamine analog of 2C-G. It is a particularly long lasting drug, with the duration listed in PiHKAL as being 18–24 hours, which might make it undesirable to some users. It is named after the Hindu deity, Ganesha. Very little is known about the dangers or toxicity of ganesha. Effects of ganesha include:

Lisdexamfetamine, sold under the brand names Vyvanse and Elvanse among others, is a stimulant medication that is used to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in children and adults and for moderate-to-severe binge eating disorder in adults. Lisdexamfetamine is taken by mouth. Its effects generally begin within two hours and last for up to 14 hours.

Etilamfetamine is a stimulant drug of the phenethylamine and amphetamine chemical classes. It was invented in the early 20th century and was subsequently used as an anorectic or appetite suppressant in the 1950s, but was not as commonly used as other amphetamines such as amphetamine, methamphetamine, and benzphetamine, and was largely discontinued once newer drugs such as phenmetrazine were introduced. It most likely acts primarily as a dopamine releasing agent. Its activity as a norepinephrine or serotonin releasing agent is not known.

Methamphetamine is a potent central nervous system (CNS) stimulant that is mainly used as a recreational or performance-enhancing drug and less commonly as a second-line treatment for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and obesity. It has also been researched as a potential treatment for traumatic brain injury. Methamphetamine was discovered in 1893 and exists as two enantiomers: levo-methamphetamine and dextro-methamphetamine. Methamphetamine properly refers to a specific chemical substance, the racemic free base, which is an equal mixture of levomethamphetamine and dextromethamphetamine in their pure amine forms, but the hydrochloride salt, commonly called crystal meth, is widely used. Methamphetamine is rarely prescribed over concerns involving its potential for recreational use as an aphrodisiac and euphoriant, among other concerns, as well as the availability of safer substitute drugs with comparable treatment efficacy such as Adderall and Vyvanse. Dextromethamphetamine is a stronger CNS stimulant than levomethamphetamine.

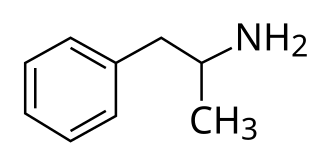
Levoamphetamine is a stimulant medication which is used in the treatment of certain medical conditions. It was previously marketed by itself under the brand name Cydril, but is now available only in combination with dextroamphetamine in varying ratios under brand names like Adderall and Evekeo. The drug is known to increase wakefulness and concentration in association with decreased appetite and fatigue. Pharmaceuticals that contain levoamphetamine are currently indicated and prescribed for the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), obesity, and narcolepsy in some countries. Levoamphetamine is taken by mouth.

Substituted phenethylamines are a chemical class of organic compounds that are based upon the phenethylamine structure; the class is composed of all the derivative compounds of phenethylamine which can be formed by replacing, or substituting, one or more hydrogen atoms in the phenethylamine core structure with substituents.

A norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor (NDRI) is a drug used for the treatment of clinical depression, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), narcolepsy, and the management of Parkinson's disease. The drug acts as a reuptake inhibitor for the neurotransmitters norepinephrine and dopamine by blocking the action of the norepinephrine transporter (NET) and the dopamine transporter (DAT), respectively. This in turn leads to increased extracellular concentrations of both norepinephrine and dopamine and, therefore, an increase in adrenergic and dopaminergic neurotransmission.

3-Fluoroamphetamine is a stimulant drug from the amphetamine family which acts as a monoamine releaser with similar potency to methamphetamine but more selectivity for dopamine and norepinephrine release over serotonin. It is self-administered by mice to a similar extent to related drugs such as 4-fluoroamphetamine and 3-methylamphetamine.
Substituted amphetamines are a class of compounds based upon the amphetamine structure; it includes all derivative compounds which are formed by replacing, or substituting, one or more hydrogen atoms in the amphetamine core structure with substituents. The compounds in this class span a variety of pharmacological subclasses, including stimulants, empathogens, and hallucinogens, among others. Examples of substituted amphetamines are amphetamine (itself), methamphetamine, ephedrine, cathinone, phentermine, mephentermine, tranylcypromine, bupropion, methoxyphenamine, selegiline, amfepramone (diethylpropion), pyrovalerone, MDMA (ecstasy), and DOM (STP).

Amfecloral (INN), also known as amphecloral (USAN), is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant drug of the phenethylamine and amphetamine chemical classes that was used as an appetite suppressant under the brand name Acutran, but is now no longer marketed. It was classified as an anorectic drug with little to no stimulant activity in a 1970 review. The British Pharmacopoeia Commission approved the name in 1970. The raw ingredients used in manufacturing it were dextroamphetamine and chloral hydrate.
Amphetamine and methamphetamine are central nervous system stimulants used to treat a variety of conditions. When used recreationally, they are colloquially known as "speed" or sometimes "crank". Amphetamine was first synthesized in 1887 in Germany by Romanian chemist Lazăr Edeleanu, who named it phenylisopropylamine. Around the same time, Japanese organic chemist Nagai Nagayoshi isolated ephedrine from the Chinese ephedra plant and later developed a method for ephedrine synthesis. Methamphetamine was synthesized from ephedrine in 1893 by Nagayoshi. Neither drug had a pharmacological use until 1934, when Smith, Kline & French began selling amphetamine as an inhaler under the trade name Benzedrine for congestion.