
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) are a class of drugs that inhibit the activity of one or both monoamine oxidase enzymes: monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A) and monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B). They are best known as effective antidepressants, especially for treatment-resistant depression and atypical depression. They are also used to treat panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, Parkinson's disease, and several other disorders.

Monoamine neurotransmitters are neurotransmitters and neuromodulators that contain one amino group connected to an aromatic ring by a two-carbon chain (such as -CH2-CH2-). Examples are dopamine, norepinephrine and serotonin.

Phenelzine, sold under the brand name Nardil among others, is a non-selective and irreversible monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) of the hydrazine family which is primarily used as an antidepressant and anxiolytic to treat depression and anxiety. Along with tranylcypromine and isocarboxazid, phenelzine is one of the few non-selective and irreversible MAOIs still in widespread clinical use.

Phenethylamine (PEA) is an organic compound, natural monoamine alkaloid, and trace amine, which acts as a central nervous system stimulant in humans. In the brain, phenethylamine regulates monoamine neurotransmission by binding to trace amine-associated receptor 1 (TAAR1) and inhibiting vesicular monoamine transporter 2 (VMAT2) in monoamine neurons. To a lesser extent, it also acts as a neurotransmitter in the human central nervous system. In mammals, phenethylamine is produced from the amino acid L-phenylalanine by the enzyme aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase via enzymatic decarboxylation. In addition to its presence in mammals, phenethylamine is found in many other organisms and foods, such as chocolate, especially after microbial fermentation.
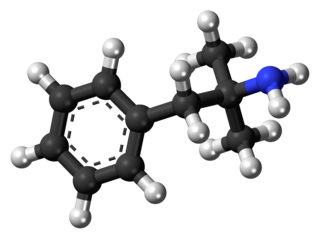
Phentermine, sold under the brand name Adipex-P among others, is a medication used together with diet and exercise to treat obesity. It is available by itself or as the combination phentermine/topiramate. Phentermine is taken by mouth.
A serotonin–norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor (SNDRI), also known as a triple reuptake inhibitor (TRI), is a type of drug that acts as a combined reuptake inhibitor of the monoamine neurotransmitters serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine. It does this by concomitantly inhibiting the serotonin transporter (SERT), norepinephrine transporter (NET), and dopamine transporter (DAT), respectively. Inhibition of the reuptake of these neurotransmitters increases their extracellular concentrations and, therefore, results in an increase in serotonergic, adrenergic, and dopaminergic neurotransmission. The naturally-occurring and potent SNDRI cocaine is widely used recreationally and often illegally for the euphoric effects it produces.

Tesofensine (NS2330) is a serotonin–noradrenaline–dopamine reuptake inhibitor from the phenyltropane family of drugs, which is being developed for the treatment of obesity. Tesofensine was originally developed by a Danish biotechnology company, NeuroSearch, who transferred the rights to Saniona in 2014.

BTS 74,398 is a centrally acting stimulant drug which was developed for the treatment of Parkinson's disease. It inhibits the synaptic reuptake of dopamine, serotonin and noradrenaline, making it a triple reuptake inhibitor. It was effective in animal models of Parkinson's disease, but was unsuccessful in human trials.

A monoamine releasing agent (MRA), or simply monoamine releaser, is a drug that induces the release of one or more monoamine neurotransmitters from the presynaptic neuron into the synapse, leading to an increase in the extracellular concentrations of the neurotransmitters and hence enhanced signaling by those neurotransmitters. The monoamine neurotransmitters include serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine; MRAs can induce the release of one or more of these neurotransmitters.
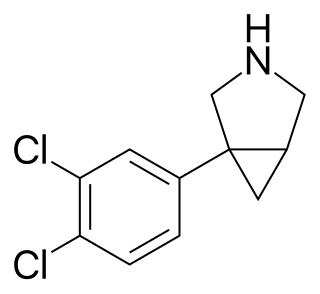
DOV 216,303 is an experimental antidepressant drug originally developed by DOV Pharmaceutical and was licensed to Merck & Co. in 2004; Merck and DOV terminated their relationship in December 2006.
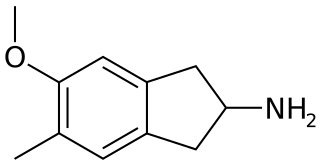
5-Methoxy-6-methyl-2-aminoindane (MMAI) is a drug of the 2-aminoindane group developed in the 1990s by a team led by David E. Nichols at Purdue University. It acts as a less neurotoxic and highly selective serotonin releasing agent (SSRA) and produces entactogenic effects in humans. It has been sold as a designer drug and research chemical online since 2010.

A norepinephrine releasing agent (NRA), also known as an adrenergic releasing agent, is a catecholaminergic type of drug that induces the release of norepinephrine (noradrenaline) and epinephrine (adrenaline) from the pre-synaptic neuron into the synapse. This in turn leads to increased extracellular concentrations of norepinephrine and epinephrine therefore an increase in adrenergic neurotransmission.

The plasma membrane monoamine transporter (PMAT) is a low-affinity monoamine transporter protein which in humans is encoded by the SLC29A4 gene. It is known alternatively as the human equilibrative nucleoside transporter-4 (hENT4). It was discovered in 2004 and has been identified as a potential alternate target for treating various conditions.

3-Methoxyamphetamine (3-MA), also known as meta-methoxyamphetamine (MMA), is a monoamine releasing agent (MRA) of the amphetamine family. It is a positional isomer of para-methoxyamphetamine.

Almoxatone (MD-780,236) is a selective and reversible inhibitor of MAO-B. It was patented as an antidepressant and antiparkinsonian agent but was never marketed.

Thiopropamine is a stimulant drug which is an analogue of amphetamine where the phenyl ring has been replaced by thiophene. It has similar stimulant effects to amphetamine but with around one third the potency. The N-methyl and thiophen-3-yl analogues are also known and are somewhat more potent, though still generally weaker than the corresponding amphetamines.
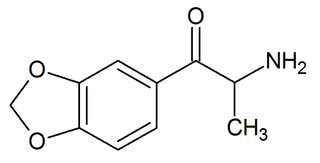
3,4-Methylenedioxycathinone is an empathogen and stimulant of the phenethylamine, amphetamine, and cathinone classes and the β-keto analogue of MDA.

GSK1360707F is a potent and selective triple reuptake inhibitor. It is chemically related to amitifadine and NS-2359 (GSK-372,475). Until recently, it was under development for the treatment of major depressive disorder; its development was put on hold for strategic reasons.
A monoamine reuptake inhibitor (MRI) is a drug that acts as a reuptake inhibitor of one or more of the three major monoamine neurotransmitters serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine by blocking the action of one or more of the respective monoamine transporters (MATs), which include the serotonin transporter (SERT), norepinephrine transporter (NET), and dopamine transporter (DAT). This in turn results in an increase in the synaptic concentrations of one or more of these neurotransmitters and therefore an increase in monoaminergic neurotransmission.

Methamnetamine is a triple monoamine releasing agent and N-methyl analog of the non-neurotoxic experimental drug naphthylaminopropane and the naphthalene analog of methamphetamine. It has been sold online as a designer drug.


















