Monoamine transporters (MATs) are proteins that function as integral plasma-membrane transporters to regulate concentrations of extracellular monoamine neurotransmitters. The three major classes are serotonin transporters (SERTs), dopamine transporters (DATs), and norepinephrine transporters (NETs) and are responsible for the reuptake of their associated amine neurotransmitters. MATs are located just outside the synaptic cleft (peri-synaptically), transporting monoamine transmitter overflow from the synaptic cleft back to the cytoplasm of the pre-synaptic neuron. MAT regulation generally occurs through protein phosphorylation and post-translational modification. Due to their significance in neuronal signaling, MATs are commonly associated with drugs used to treat mental disorders as well as recreational drugs. Compounds targeting MATs range from medications such as the wide variety of tricyclic antidepressants, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors such as fluoxetine (Prozac) to stimulant medications such as methylphenidate (Ritalin) and amphetamine in its many forms and derivatives methamphetamine (Desoxyn) and lisdexamfetamine (Vyvanse). Furthermore, drugs such as MDMA and natural alkaloids such as cocaine exert their effects in part by their interaction with MATs, by blocking the transporters from mopping up dopamine, serotonin, and other neurotransmitters from the synapse.

Lithium aluminium hydride, commonly abbreviated to LAH, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Li[AlH4] or LiAlH4. It is a white solid, discovered by Finholt, Bond and Schlesinger in 1947. This compound is used as a reducing agent in organic synthesis, especially for the reduction of esters, carboxylic acids, and amides. The solid is dangerously reactive toward water, releasing gaseous hydrogen (H2). Some related derivatives have been discussed for hydrogen storage.

Serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) are a class of antidepressant medications used to treat major depressive disorder (MDD), anxiety disorders, social phobia, chronic neuropathic pain, fibromyalgia syndrome (FMS), and menopausal symptoms. Off-label uses include treatments for attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD). SNRIs are monoamine reuptake inhibitors; specifically, they inhibit the reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine. These neurotransmitters are thought to play an important role in mood regulation. SNRIs can be contrasted with the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (NRIs), which act upon single neurotransmitters.
A dopamine reuptake inhibitor (DRI) is a class of drug which acts as a reuptake inhibitor of the monoamine neurotransmitter dopamine by blocking the action of the dopamine transporter (DAT). Reuptake inhibition is achieved when extracellular dopamine not absorbed by the postsynaptic neuron is blocked from re-entering the presynaptic neuron. This results in increased extracellular concentrations of dopamine and increase in dopaminergic neurotransmission.

Nomifensine, sold under the brand names Merital and Alival, is a norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor (NDRI), i.e. a drug that increases the amount of synaptic norepinephrine and dopamine available to receptors by blocking the dopamine and norepinephrine reuptake transporters. This is a mechanism of action shared by some recreational drugs like cocaine and the medication tametraline (see DRI). Research showed that the (S)-isomer is responsible for activity.

Alaproclate is a drug that was being developed as an antidepressant by the Swedish pharmaceutical company Astra AB in the 1970s.

Indatraline hydrochloride is an antidepressive agent and non-selective monoamine transporter inhibitor that blocks the reuptake of dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin with similar efficacy to cocaine. This compound may be used to treat cocaine addictions as its effects have a slower onset and a longer duration than those of cocaine. Lu 19-005 has been shown to block the action of methamphetamine and MDMA in laboratory experiments.

Indalpine, sold under the brand name Upstène, is a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) that was briefly marketed as an antidepressant for treatment of depression. It was marketed in France and a few other European countries.

Nisoxetine, originally synthesized in the Lilly research laboratories during the early 1970s, is a potent and selective inhibitor for the reuptake of norepinephrine (noradrenaline) into synapses. It currently has no clinical applications in humans, although it was originally researched as an antidepressant. Nisoxetine is now widely used in scientific research as a standard selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor. It has been used to research obesity and energy balance, and exerts some local analgesia effects.
Reuptake inhibitors (RIs) are a type of reuptake modulators. It is a drug that inhibits the plasmalemmal transporter-mediated reuptake of a neurotransmitter from the synapse into the pre-synaptic neuron. This leads to an increase in extracellular concentrations of the neurotransmitter and an increase in neurotransmission. Various drugs exert their psychological and physiological effects through reuptake inhibition, including many antidepressants and psychostimulants.

Diclofensine (Ro 8-4650) was developed by Hoffmann-La Roche in the 1970s in the search for a new antidepressant. It was found that the (S)-isomer was responsible for activity. Diclofensine is a stimulant drug which acts as a triple monoamine reuptake inhibitor, primarily inhibiting the reuptake of dopamine and norepinephrine, with affinities (Ki) of 16.8 nM, 15.7 nM, and 51 nM for DAT, NET, and SERT (dopamine, norepinephrine and serotonin transporters), respectively. It was found to be an effective antidepressant in human trials, with relatively few side effects, but was ultimately dropped from clinical development, possibly due to concerns about its abuse potential.

Tandamine is a selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor with a tricyclic structure. It was developed in the 1970s as an antidepressant but was never commercialized. Tandamine is analogous to pirandamine, which, instead, acts as a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI).

Talsupram is a selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (NRI) which was investigated as an antidepressant in the 1960s and 1970s but was never marketed. Along with talopram, it is structurally related to the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) citalopram.

Mepiprazole is an anxiolytic drug of the phenylpiperazine group with additional antidepressant properties that is marketed in Spain. It acts as a 5-HT2A and α1-adrenergic receptor antagonist and inhibits the reuptake and induces the release of serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine to varying extents, and has been described as a serotonin antagonist and reuptake inhibitor (SARI). Controlled clinical trials of mepiprazole in patients with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) were also carried out and suggested some benefits of the drug in relieving symptoms of IBS in some patients. Similarly to other phenylpiperazines like trazodone, nefazodone, and etoperidone, mepiprazole produces mCPP as an active metabolite.
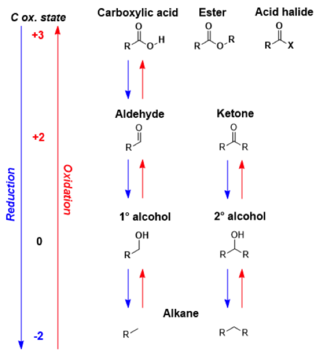
In organic chemistry, carbonyl reduction is the conversion of any carbonyl group, usually to an alcohol. It is a common transformation that is practiced in many ways. Ketones, aldehydes, carboxylic acids, esters, amides, and acid halides - some of the most pervasive functional groups, -comprise carbonyl compounds. Carboxylic acids, esters, and acid halides can be reduced to either aldehydes or a step further to primary alcohols, depending on the strength of the reducing agent. Aldehydes and ketones can be reduced respectively to primary and secondary alcohols. In deoxygenation, the alcohol group can be further reduced and removed altogether by replacement with H.
Reductions with hydrosilanes are methods used for hydrogenation and hydrogenolysis of organic compounds. The approach is a subset of ionic hydrogenation. In this particular method, the substrate is treated with a hydrosilane and auxiliary reagent, often a strong acid, resulting in formal transfer of hydride from silicon to carbon. This style of reduction with hydrosilanes enjoys diverse if specialized applications.

Teniloxazine, also known as sufoxazine and sulfoxazine, is a drug which is marketed in Japan. Though initially investigated as a neuroprotective and nootropic agent for the treatment of cerebrovascular insufficiency in the 1980s, it was ultimately developed and approved as an antidepressant instead. It acts as a potent norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor, with fair selectivity over the serotonin and dopamine transporters, and also behaves as an antagonist of the 5-HT2A receptor.
A monoamine reuptake inhibitor (MRI) is a drug that acts as a reuptake inhibitor of one or more of the three major monoamine neurotransmitters serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine by blocking the action of one or more of the respective monoamine transporters (MATs), which include the serotonin transporter (SERT), norepinephrine transporter (NET), and dopamine transporter (DAT). This in turn results in an increase in the synaptic concentrations of one or more of these neurotransmitters and therefore an increase in monoaminergic neurotransmission.
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, or serotonin-specific re-uptake inhibitor (SSRIs), are a class of chemical compounds that have application as antidepressants and in the treatment of depression and other psychiatric disorders. SSRIs are therapeutically useful in the treatment of panic disorder (PD), posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), social anxiety disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD), and anorexia. There is also clinical evidence of the value of SSRIs in the treatment of the symptoms of schizophrenia and their ability to prevent cardiovascular diseases.

Dazepinil, classified as a tricyclic antidepressant, is a pharmacological compound that has never been approved for medical use. Its mechanism of action involves inhibiting the reuptake of norepinephrine and serotonin at the synaptic cleft, thereby enhancing neurotransmitter availability in the brain.