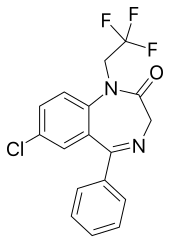
Flurazepam is a drug which is a benzodiazepine derivative. It possesses anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, hypnotic, sedative and skeletal muscle relaxant properties. It produces a metabolite with a long half-life, which may stay in the bloodstream for days. Flurazepam was patented in 1968 and came into medical use the same year. Flurazepam, developed by Roche Pharmaceuticals, was one of the first benzodiazepine hypnotic medications to be marketed.

Nordazepam is a 1,4-benzodiazepine derivative. Like other benzodiazepine derivatives, it has amnesic, anticonvulsant, anxiolytic, muscle relaxant, and sedative properties. However, it is used primarily in the treatment of anxiety disorders. It is an active metabolite of diazepam, chlordiazepoxide, clorazepate, prazepam, pinazepam, and medazepam.

Medazepam is a drug that is a benzodiazepine derivative. It possesses anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, sedative, and skeletal muscle relaxant properties. It is known by the following brand names: Azepamid, Nobrium, Tranquirax, Rudotel, Raporan, Ansilan and Mezapam. Medazepam is a long-acting benzodiazepine drug. The half-life of medazepam is 36–200 hours.
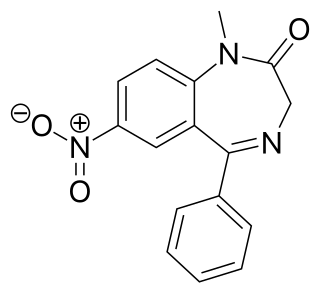
Nimetazepam is an intermediate-acting hypnotic drug which is a benzodiazepine derivative. It was first synthesized by a team at Hoffmann-La Roche in 1964. It possesses powerful hypnotic, anxiolytic, sedative, and skeletal muscle relaxant properties. Nimetazepam is also a particularly potent anticonvulsant. It is marketed in 5 mg tablets known as Erimin, which is the brand name manufactured and marketed by the large Japanese corporation Sumitomo. Japan is the sole manufacturer of nimetazepam in the world. Outside of Japan, Erimin is available in much of East and Southeast Asia and was widely prescribed for the short-term treatment of severe insomnia in patients who have difficulty falling asleep or maintaining sleep. Sumitomo has ceased manufacturing Erimin since November 2015. It is still available as a generic drug or as Lavol.

Pinazepam is a benzodiazepine drug. It possesses anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, sedative and skeletal muscle relaxant properties.

Ketazolam is a drug which is a benzodiazepine derivative. It possesses anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, sedative and skeletal muscle relaxant properties.

Camazepam is a benzodiazepine psychoactive drug, marketed under the brand names Albego, Limpidon and Paxor. It is the dimethyl carbamate ester of temazepam, a metabolite of diazepam. While it possesses anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, skeletal muscle relaxant and hypnotic properties it differs from other benzodiazepines in that its anxiolytic properties are particularly prominent but has comparatively limited anticonvulsant, hypnotic and skeletal muscle relaxant properties.

Ethyl loflazepate is a drug which is a benzodiazepine derivative. It possesses anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, sedative and skeletal muscle relaxant properties. In animal studies it was found to have low toxicity, although in rats evidence of pulmonary phospholipidosis occurred with pulmonary foam cells developing with long-term use of very high doses. Its elimination half-life is 51–103 hours. Its mechanism of action is similar to other benzodiazepines. Ethyl loflazepate also produces an active metabolite which is stronger than the parent compound. Ethyl loflazepate was designed to be a prodrug for descarboxyloflazepate, its active metabolite. It is the active metabolite which is responsible for most of the pharmacological effects rather than ethyl loflazepate. The main metabolites of ethyl loflazepate are descarbethoxyloflazepate, loflazepate and 3-hydroxydescarbethoxyloflazepate. Accumulation of the active metabolites of ethyl loflazepate are not affected by those with kidney failure or impairment. The symptoms of an overdose of ethyl loflazepate include sleepiness, agitation and ataxia. Hypotonia may also occur in severe cases. These symptoms occur much more frequently and severely in children. Death from therapeutic maintenance doses of ethyl loflazepate taken for 2 – 3 weeks has been reported in 3 elderly patients. The cause of death was asphyxia due to benzodiazepine toxicity. High doses of the antidepressant fluvoxamine may potentiate the adverse effects of ethyl loflazepate.

Etizolam is a thienodiazepine derivative which is a benzodiazepine analog. The etizolam molecule differs from a benzodiazepine in that the benzene ring has been replaced by a thiophene ring and triazole ring has been fused, making the drug a thienotriazolodiazepine.
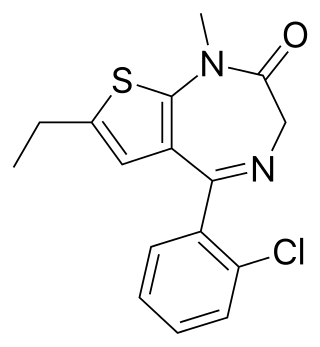
Clotiazepam is a thienodiazepine drug which is a benzodiazepine analog. The clotiazepam molecule differs from benzodiazepines in that the benzene ring has been replaced by a thiophene ring. It possesses anxiolytic, skeletal muscle relaxant, anticonvulsant, sedative properties. Stage 2 NREM sleep is significantly increased by clotiazepam.

Cloxazolam is a benzodiazepine derivative that has anxiolytic, sedative, and anticonvulsant properties. It is not widely used; as of August 2018 it was marketed in Belgium, Luxembourg, Portugal, Brazil, and Japan. In 2019, it has been retired from the Belgian market.

Ethinamate is a short-acting carbamate-derivative sedative-hypnotic medication used to treat insomnia. Regular use leads to drug tolerance, and it is usually not effective for more than 7 days. Prolonged use can lead to dependence.

Chlordiazepoxide, trade name Librium among others, is a sedative and hypnotic medication of the benzodiazepine class; it is used to treat anxiety, insomnia and symptoms of withdrawal from alcohol, benzodiazepines, and other drugs.

Phenazepam is a benzodiazepine drug, first developed in the Soviet Union in 1975, and now produced in Russia and several other countries.

Haloxazolam, is a drug which is a benzodiazepine derivative. It has similar hypnotic properties as the benzodiazepine drugs triazolam, temazepam, and flunitrazepam and as such is indicated for the treatment of insomnia. A study in cats comparing estazolam and haloxazolam found that haloxazolam only affects gamma motor neurons, whereas estazolam affects both alpha and gamma motor neurons.

Oxazolam is a drug that is a benzodiazepine derivative. It has anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, sedative, and skeletal muscle relaxant properties. It is a prodrug for desmethyldiazepam.

Diclazepam (Ro5-3448), also known as chlorodiazepam and 2'-chloro-diazepam, is a benzodiazepine and functional analog of diazepam. It was first synthesized by Leo Sternbach and his team at Hoffman-La Roche in 1960. It is not currently approved for use as a medication, but rather sold as an unscheduled substance. Efficacy and safety have not been tested in humans.

Clonazolam is a drug of the triazolobenzodiazepine (TBZD) class, which are benzodiazepines (BZDs) fused with a triazole ring. Although little research has been done about its effects and metabolism, it is sold online as a designer drug.
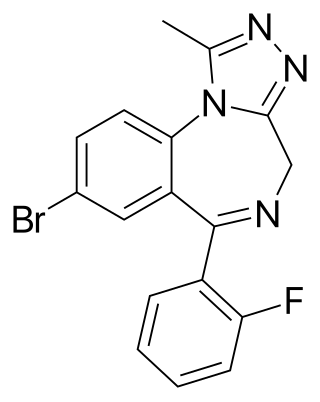
Flubromazolam (JYI-73) is a triazolobenzodiazepine (TBZD), which are benzodiazepine (BZD) derivatives. Flubromazolam is reputed to be highly potent, and concerns have been raised that clonazolam and flubromazolam in particular may pose comparatively higher risks than other designer benzodiazepines, due to their ability to produce strong sedation and amnesia at oral doses of as little as 0.5 mg. Life-threatening adverse reactions have been observed at doses of only 3 mg of flubromazolam.
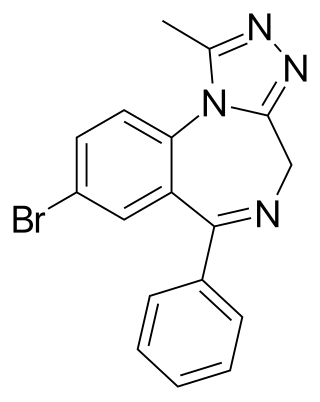
Bromazolam (XLI-268) is a triazolobenzodiazepine (TBZD) which was first synthesised in 1976, but was never marketed. It has subsequently been sold as a designer drug, first being definitively identified by the EMCDDA in Sweden in 2016. It is the bromo instead of chloro analogue of alprazolam and has similar sedative and anxiolytic effects to it and other benzodiazepines. Bromazolam is a non subtype selective agonist at the benzodiazepine site of GABAA receptors, with a binding affinity of 2.81 nM at the α1 subtype, 0.69 nM at α2 and 0.62 nM at α5. The "common" dosage range for users of bromazolam was reported to be 1–2 mg, suggesting its potency is similar to alprazolam.