
γ-Aminobutyric acid, or GABA, is the chief inhibitory neurotransmitter in the developmentally mature mammalian central nervous system. Its principal role is reducing neuronal excitability throughout the nervous system.

Desflurane (1,2,2,2-tetrafluoroethyl difluoromethyl ether) is a highly fluorinated methyl ethyl ether used for maintenance of general anesthesia. Like halothane, enflurane, and isoflurane, it is a racemic mixture of (R) and (S) optical isomers (enantiomers). Together with sevoflurane, it is gradually replacing isoflurane for human use, except in economically undeveloped areas, where its high cost precludes its use. It has the most rapid onset and offset of the volatile anesthetic drugs used for general anesthesia due to its low solubility in blood.

Enflurane is a halogenated ether. Developed by Ross Terrell in 1963, it was first used clinically in 1966. It was increasingly used for inhalational anesthesia during the 1970s and 1980s but is no longer in common use.

The GABAA receptor (GABAAR) is an ionotropic receptor and ligand-gated ion channel. Its endogenous ligand is γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA), the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. Accurate regulation of GABAergic transmission through appropriate developmental processes, specificity to neural cell types, and responsiveness to activity is crucial for the proper functioning of nearly all aspects of the central nervous system (CNS). Upon opening, the GABAA receptor on the postsynaptic cell is selectively permeable to chloride ions (Cl−) and, to a lesser extent, bicarbonate ions (HCO3−).

Neurosteroids, also known as neuroactive steroids, are endogenous or exogenous steroids that rapidly alter neuronal excitability through interaction with ligand-gated ion channels and other cell surface receptors. The term neurosteroid was coined by the French physiologist Étienne-Émile Baulieu and refers to steroids synthesized in the brain. The term, neuroactive steroid refers to steroids that can be synthesized in the brain, or are synthesized by an endocrine gland, that then reach the brain through the bloodstream and have effects on brain function. The term neuroactive steroids was first coined in 1992 by Steven Paul and Robert Purdy. In addition to their actions on neuronal membrane receptors, some of these steroids may also exert effects on gene expression via nuclear steroid hormone receptors. Neurosteroids have a wide range of potential clinical applications from sedation to treatment of epilepsy and traumatic brain injury. Ganaxolone, a synthetic analog of the endogenous neurosteroid allopregnanolone, is under investigation for the treatment of epilepsy.

Etiocholanolone, also known as 5β-androsterone, as well as 3α-hydroxy-5β-androstan-17-one or etiocholan-3α-ol-17-one, is an etiocholane (5β-androstane) steroid as well as an endogenous 17-ketosteroid that is produced from the metabolism of testosterone. It causes fever, immunostimulation, and leukocytosis, and is used to evaluate adrenal cortex function, bone marrow performance, and in neoplastic disease to stimulate the immune system. Etiocholanolone is also known to be an inhibitory androstane neurosteroid, acting as a positive allosteric modulator of the GABAA receptor, and possesses anticonvulsant effects. The unnatural enantiomer of etiocholanolone is more potent as a positive allosteric modulator of GABAA receptors and as an anticonvulsant than the natural form.

Allopregnanolone is a naturally occurring neurosteroid which is made in the body from the hormone progesterone. As a medication, allopregnanolone is referred to as brexanolone, sold under the brand name Zulresso, and used to treat postpartum depression. It is given by injection into a vein.

Alfaxalone, also known as alphaxalone or alphaxolone and sold under the brand name Alfaxan, is a neuroactive steroid and general anesthetic which is used currently in veterinary practice as an induction agent for anesthesia and as an injectable anesthetic. Though it is more expensive than other induction agents, it often preferred due to the lack of depressive effects on the cardiovascular system. The most common side effect seen in current veterinary practice is respiratory depression when Alfaxan is administered concurrently with other sedative and anesthetic drugs; when premedications aren't given, veterinary patients also become agitated and hypersensitive when waking up.
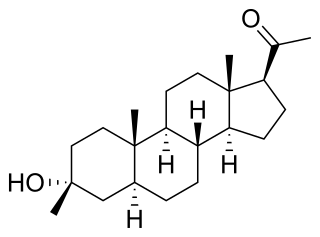
Ganaxolone, sold under the brand name Ztalmy, is a medication used to treat seizures in people with cyclin-dependent kinase-like 5 (CDKL5) deficiency disorder. Ganaxolone is a neuroactive steroid gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) A receptor positive modulator.
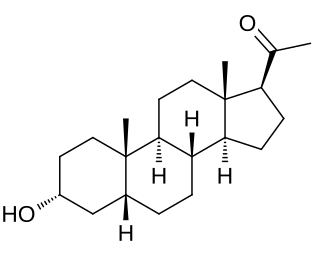
Pregnanolone, also known as eltanolone, is an endogenous inhibitory neurosteroid which is produced in the body from progesterone. It is closely related to allopregnanolone, which has similar properties.
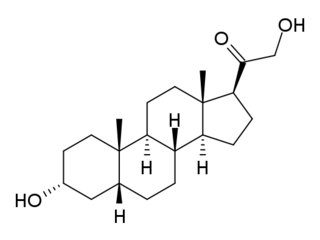
Tetrahydrodeoxycorticosterone, also referred to as allotetrahydrocorticosterone, is an endogenous neurosteroid. It is synthesized from the adrenal hormone deoxycorticosterone by the action of two enzymes, 5α-reductase type I and 3α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase. THDOC is a potent positive allosteric modulator of the GABAA receptor, and has sedative, anxiolytic and anticonvulsant effects. Changes in the normal levels of this steroid particularly during pregnancy and menstruation may be involved in some types of epilepsy and premenstrual syndrome, as well as stress, anxiety and depression.
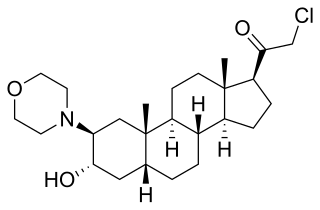
ORG-20599 is a synthetic neuroactive steroid, with sedative effects resulting from its action as a GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulator and, at higher concentrations, agonist. It was developed for use as an anaesthetic agent but was never marketed for this purpose, although it is still used in scientific research.

Pregnenolone sulfate is an endogenous excitatory neurosteroid that is synthesized from pregnenolone. It is known to have cognitive and memory-enhancing, antidepressant, anxiogenic, and proconvulsant effects.

ORG-21465 is a synthetic neuroactive steroid, with sedative effects resulting from its action as a GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulator. It is similar to related drugs such as ORG-20599, and was similarly developed as an improved alternative to other sedative steroids such as althesin and allopregnanolone, which despite its superior properties in some respects has not proved to offer enough advantages to be accepted into clinical use.

In pharmacology, GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulators, also known as GABAkines or GABAA receptor potentiators, are positive allosteric modulator (PAM) molecules that increase the activity of the GABAA receptor protein in the vertebrate central nervous system.

Epipregnanolone, also known as 3β-hydroxy-5β-pregnan-20-one, 3β,5β-tetrahydroprogesterone, or 3β,5β-THP, is an endogenous neurosteroid. It acts as a negative allosteric modulator of the GABAA receptor and reverses the effects of potentiators like allopregnanolone. Epipregnanolone is biosynthesized from progesterone by the actions of 5β-reductase and 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase, with 5β-dihydroprogesterone as the intermediate in this two-step transformation.

5β-Dihydroprogesterone is an endogenous neurosteroid and an intermediate in the biosynthesis of pregnanolone and epipregnanolone from progesterone. It is synthesized from progesterone by the enzyme 5β-reductase.

Pregnenolone succinate is a synthetic pregnane steroid and an ester of pregnenolone which is described as a glucocorticoid and anti-inflammatory drug and has been patented and marketed as a topical medication in the form of a cream for the treatment of allergic, pruritic, and inflammatory dermatitis. It has also been described as a non-hormonal sterol, having neurosteroid activity, and forming a progesterone analogue via dehydrogenation.

Posovolone is a synthetic neurosteroid which was under development as a sedative/hypnotic medication for the treatment of insomnia. It is orally active and acts as a GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulator. In animals, posovolone shows anticonvulsant, anxiolytic-like, ataxic, and sleep-promoting effects and appeared to produce effects similar to those of pregnanolone. Development of the agent was started by 1999 and appears to have been discontinued by 2007. In 2021, an INN was registered for posovolone with the descriptor of "antidepressant". Posovolone was originally developed by Purdue Pharma.



















