 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
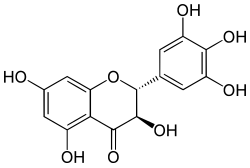
| IUPAC name (2R,3R)-3,3′,4′,5,5′,7-Hexahydroxyflavan-4-one | |
| Systematic IUPAC name (2R,3R)-3,5,7-Trihydroxy-2-(3,4,5-trihydroxy)-2,3-dihydro-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one | |
| Other names Dihydromyricetin, Ampeloptin,(+)-Ampelopsin,(+)-Dihydromyricetin | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H12O8 | |
| Molar mass | 320.253 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Ampelopsin, also known as dihydromyricetin and DHM, when used as an herbal medicine, is a flavanonol, a type of flavonoid. It is extracted from the Japanese raisin tree and found in Ampelopsis species japonica, megalophylla, and grossedentata; Cercidiphyllum japonicum ; Hovenia dulcis ; Rhododendron cinnabarinum ; some Pinus species; and some Cedrus species, [1] as well as in Salix sachalinensis . [2]
Contents
Hovenia dulcis has been used in traditional Japanese, Chinese, and Korean medicines to treat fever, parasitic infection, as a laxative, and a treatment of liver diseases, and as a hangover treatment. [3] Methods have been developed to extract ampelopsin on a larger scale, and laboratory research has been conducted with the compound to see if it might be useful as a drug in any of the conditions for which the parent plant has been traditionally used. [3]