
Ammonium iodide is the inorganic compound with the formula NH4I. A white solid. It is an ionic compound, although impure samples appear yellow. This salt consists of ammonium cation and an iodide anion. It can be prepared by the action of hydroiodic acid on ammonia. It is easily soluble in water, from which it crystallizes in cubes. It is also soluble in ethanol. Ammonium iodide in aqueous solutions are observed as acidic and display elevated vapor pressures at high temperatures

Cumene (isopropylbenzene) is an organic compound that contains a benzene ring with an isopropyl substituent. It is a constituent of crude oil and refined fuels. It is a flammable colorless liquid that has a boiling point of 152 °C. Nearly all the cumene that is produced as a pure compound on an industrial scale is converted to cumene hydroperoxide, which is an intermediate in the synthesis of other industrially important chemicals, primarily phenol and acetone.

Citronellol, or dihydrogeraniol, is a natural acyclic monoterpenoid. Both enantiomers occur in nature. (+)-Citronellol, which is found in citronella oils, including Cymbopogon nardus (50%), is the more common isomer. (−)-Citronellol is widespread, but particularly abundant in the oils of rose (18–55%) and Pelargonium geraniums.

Agricultural chemistry is the chemistry, especially organic chemistry and biochemistry, as they relate to agriculture. Agricultural chemistry embraces the structures and chemical reactions relevant in the production, protection, and use of crops and livestock. Its applied science and technology aspects are directed towards increasing yields and improving quality, which comes with multiple advantages and disadvantages.

Titanium(III) fluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula TiF3. A violet, paramagnetic solid, it is one of two titanium fluorides, the other being titanium tetrafluoride. It adopts a defect perovskite-like structure such that each Ti center has octahedral coordination geometry, and each fluoride ligand is doubly bridging.

Molten salt is salt which is solid at standard temperature and pressure but liquified due to elevated temperature. A salt that is liquid even at standard temperature and pressure is usually called a room-temperature ionic liquid, and molten salts are technically a class of ionic liquids.
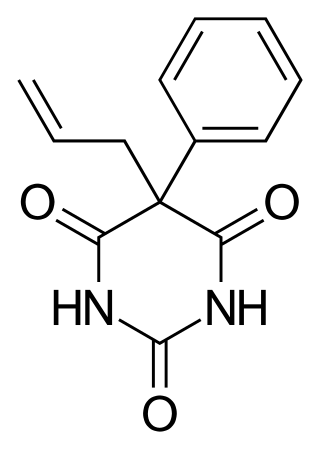
Alphenal, also known as 5-allyl-5-phenylbarbituric acid, is a barbiturate derivative developed in the 1920s. It has primarily anticonvulsant properties, and was used occasionally for the treatment of epilepsy or convulsions, although not as commonly, as better known barbiturates such as phenobarbital.

Cyclopentobarbital sodium is a barbiturate derivative invented in the 1940s. It has sedative and anticonvulsant properties, and was used primarily as an anaesthetic in veterinary medicine. Cyclopal is considered similar in effects to phenobarbital but lasts almost three times as long, and is considered a long-acting barbiturate with a fairly slow onset of action.
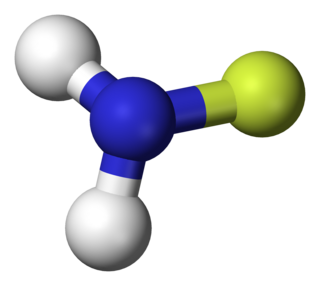
Fluoroamine is a chemical compound with formula NH2F. It is analogous to monochloramine, but seldom studied. It is an unstable gas.

Hexachlorobutadiene, (often abbreviated as "HCBD") Cl2C=C(Cl)C(Cl)=CCl2, is a colorless liquid at room temperature that has an odor similar to that of turpentine. It is a chlorinated aliphatic diene with niche applications but is most commonly used as a solvent for other chlorine-containing compounds. Structurally, it has a 1,3-butadiene core, but fully substituted with chlorine atoms.

Perfluorotripentylamine is a perfluorocarbon. It is used as an electronics coolant, and has a high boiling point. It is colorless, odorless, and insoluble in water. Unlike ordinary amines, perfluoroamines are of low basicity. Perfluorinated amines are components of fluorofluids, used as immersive coolants for supercomputers.

Extraction in chemistry is a separation process consisting of the separation of a substance from a matrix. The distribution of a solute between two phases is an equilibrium condition described by partition theory. This is based on exactly how the analyte moves from the initial solvent into the extracting solvent. The term washing may also be used to refer to an extraction in which impurities are extracted from the solvent containing the desired compound.
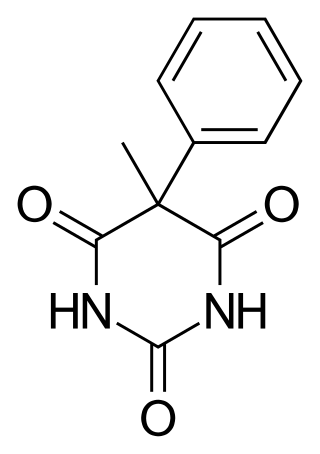
Heptobarbital (Rutonal), also known as phenylmethylbarbituric acid is a barbiturate derivative. It has often been confused with methylphenobarbital because both drugs contain a methylphenyl moiety and are overall very similar in structure.

Buthalital sodium, or buthalitone sodium (BAN), is a barbiturate derivative which was under development as a short-acting anesthetic. However, development was discontinued, perhaps due to its extremely rapid elimination rate, and buthalital sodium was never marketed.

Lithium cyanide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula LiCN. It is a toxic, white coloured, hygroscopic, water-soluble salt that finds only niche uses.

Trimellitic acid (benzene-1,2,4-tricarboxylic acid) is a chemical compound with the molecular formula C6H3(СООН)3. Like the other isomers of benzenetricarboxylic acid, trimellitic acid is a colorless solid. It is prepared by oxidation of 1,2,4-trimethylbenzene.
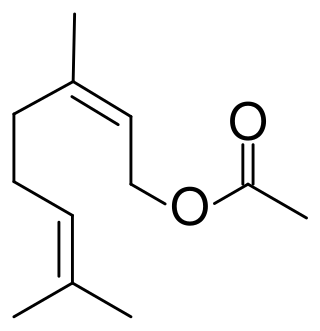
Neryl acetate is a terpenoid found in citrus oils. It is the acetate ester of nerol, an isomer of the more common fragrance geranyl acetate. In flavors and perfumery it is used to impart floral and fruity aromas.

o-Cymene is an organic compound classified as an aromatic hydrocarbon. Its structure consists of a benzene ring ortho-substituted with a methyl group and an isopropyl group. It is a flammable colorless liquid which is nearly insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents.

m-Cymene is an organic compound classified as an aromatic hydrocarbon. Its structure consists of a benzene ring meta-substituted with a methyl group and an isopropyl group. It is a flammable colorless liquid which is nearly insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents.

Hemimellitic acid (benzene-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid) is an organic compound with the molecular formula C6H3(СО2Н)3. Like the other isomers of benzenetricarboxylic acid, hemimellitic acid is a colorless solid. It is prepared by oxidation of 1,2,3-trimethylbenzene.




















