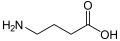
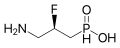
Functions
GABABRs stimulate the opening of K+ channels, specifically GIRKs, which brings the neuron closer to the equilibrium potential of K+. This reduces the frequency of action potentials which reduces neurotransmitter release.[ citation needed ] Thus GABAB receptors are usually considered as inhibitory receptors.
GABAB receptors can also function as an excitatory receptor and facilitate neurotransmitter release via increasing the activity of CaV2.3 channels. [3]
GABAB receptors usually reduces the activity of adenylyl cyclase and Ca2+ channels by using G-proteins with Gi/G0 α subunits. [4]
GABAB receptors are involved in behavioral actions of ethanol, [5] [6] gamma-hydroxybutyric acid (GHB), [7] and possibly in pain. [8] Recent research suggests that these receptors may play an important developmental role. [9]