In chemistry, a hydrate is a substance that contains water or its constituent elements. The chemical state of the water varies widely between different classes of hydrates, some of which were so labeled before their chemical structure was understood.
In slang, a Mickey Finn is a drink laced with a psychoactive drug or incapacitating agent given to someone without their knowledge, with intent to incapacitate them. Serving someone a "Mickey" is most commonly referred to as "slipping someone a mickey".

Chloral hydrate is a geminal diol with the formula C
2H
3Cl
3O
2. It is a colorless solid. It has limited use as a sedative and hypnotic pharmaceutical drug. It is also a useful laboratory chemical reagent and precursor. It is derived from chloral (trichloroacetaldehyde) by the addition of one equivalent of water.
An elixir is a sweet liquid used for medical purposes, to be taken orally and intended to cure one's illness. When used as a pharmaceutical preparation, an elixir contains at least one active ingredient designed to be taken orally.
ATC code N05Psycholeptics is a therapeutic subgroup of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System, a system of alphanumeric codes developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) for the classification of drugs and other medical products. Subgroup N05 is part of the anatomical group N Nervous system.
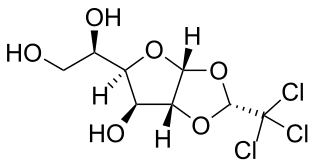
Chloralose is an avicide, and a rodenticide used to kill mice in temperatures below 15 °C. It is also widely used in neuroscience and veterinary medicine as an anesthetic and sedative.
Amidrine, Midrin, Nodolor, Duradrin, IDA, Migquin, Migrin-A, Migrazone or Epidrine is a combination drug consisting of paracetamol, dichloralphenazone and isometheptene used to treat migraines and severe, refractory headaches.
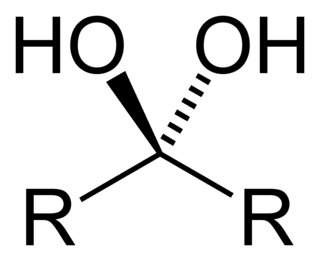
A geminal diol is any organic compound having two hydroxyl functional groups (-OH) bound to the same carbon atom. Geminal diols are a subclass of the diols, which in turn are a special class of alcohols. Most of the geminal diols are considered unstable.
Chloral, also known as trichloroacetaldehyde or trichloroethanal, is the organic compound with the formula Cl3CCHO. This aldehyde is a colourless oily liquid that is soluble in a wide range of solvents. It reacts with water to form chloral hydrate, a once widely used sedative and hypnotic substance.
2,2,2-Trichloroethanol is the chemical compound with formula Cl
3C−CH
2OH. Its molecule can be described as that of ethanol, with the three hydrogen atoms at position 2 replaced by chlorine atoms. It is a clear flammable liquid at room temperature, colorless when pure but often with a light yellow color.
Dichloralphenazone is a 1:2 mixture of antipyrine with chloral hydrate. In combination with paracetamol and isometheptene, it is the active ingredient of medications for migraine and tension headaches, including Epidrin and Midrin. Performance impairments are common with this drug and caution is advised, for example when driving motor vehicles. Additional uses of dichloralphenazone include sedation for the treatment of short-term insomnia, although there are probably better drug choices for the treatment of insomnia.
Melzer's reagent is a chemical reagent used by mycologists to assist with the identification of fungi.
Chloral hydrate/magnesium sulfate/pentobarbital sodium, brand name Equithesin, is a combination anesthetic agent used as a general anesthetic in horses. It is administered intravenously to effect. For many years, it was the most commonly used injectable anesthetic in horses. Newer anesthetic agents such as injectable barbiturates, alpha-2 agonists, cyclohexylamines, and inhalants gradually replaced Equithesin. The drug has been off the market and unavailable for decades.

Synthol is a liquid medical product brand available in France since 1920, though the nature of the product has changed through the brand's history.
Chlorobutanol (trichloro-2-methyl-2-propanol) is a preservative, sedative, hypnotic and weak local anesthetic similar in nature to chloral hydrate. It has antibacterial and antifungal properties. Chlorobutanol is typically used at a concentration of 0.5% where it lends long term stability to multi-ingredient formulations. However, it retains antimicrobial activity at 0.05% in water. Chlorobutanol has been used in anesthesia and euthanasia of invertebrates and fishes. It is a white, volatile solid with a menthol-like odor.

N-Acetylglycinamide is a glycine derivative.

Petrichloral is a sedative and hypnotic chloral hydrate prodrug. It is a Schedule IV drug in the USA.

Amfecloral (INN), also known as amphecloral (USAN), is a stimulant drug of the phenethylamine and amphetamine chemical classes that was used as an appetite suppressant under the trade name Acutran, but is now no longer marketed. It was classified as an anorectic drug with little to no stimulant activity in a 1970 review. The British Pharmacopoeia Commission approved the name in 1970. The raw ingredients used in manufacturing it were d-amphetamine and chloral hydrate.

Chloral betaine, also known as cloral betaine (INN), is a sedative-hypnotic drug. It was introduced by Mead Johnson in the United States in 1963. It is a betaine complex with chloral hydrate, which acts as an extended-acting formulation of chloral hydrate which is then metabolized into trichloroethanol, which is responsible for most or all of its effects.

2,2,2-Tribromoethanol, often called just tribromoethanol, is a chemical compound with formula Br
3C−CH
2OH. Its molecule can be described as that of ethanol, with the three hydrogen atoms in position 2 replaced by bromine. It is a white crystalline solid, soluble in water and other solvents, that absorbs strongly in the UV below 290 nm.









