 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
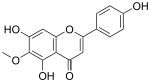
| IUPAC name 4′,5,7-Trihydroxy-6-methoxyflavone | |
| Systematic IUPAC name 5,7-Dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-6-methoxy-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.229.713 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C16H12O6 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Hispidulin is a naturally occurring flavone with potential antiepileptic activity in rats and gerbils. [1] [2] It is found in plants including Grindelia argentina , Arrabidaea chica , Saussurea involucrate , Crossostephium chinense , Artemisia , and Salvia . [3]