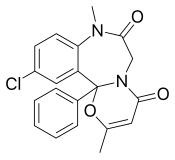
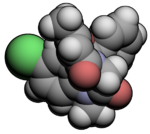
Diazepam, sold under the brand name Valium among others, is a medicine of the benzodiazepine family that acts as an anxiolytic. It is used to treat a range of conditions, including anxiety, seizures, alcohol withdrawal syndrome, muscle spasms, insomnia, and restless legs syndrome. It may also be used to cause memory loss during certain medical procedures. It can be taken orally, as a suppository inserted into the rectum, intramuscularly, intravenously or used as a nasal spray. When injected intravenously, effects begin in one to five minutes and last up to an hour. When taken by mouth, effects begin after 15 to 60 minutes.

Eszopiclone, sold under the brand name Lunesta among others, is a medication used in the treatment of insomnia. Evidence supports slight to moderate benefit up to six months. It is taken by mouth.

Oxazepam is a short-to-intermediate-acting benzodiazepine. Oxazepam is used for the treatment of anxiety, insomnia, and to control symptoms of alcohol withdrawal syndrome.

Nonbenzodiazepines, sometimes referred to colloquially as Z-drugs, are a class of psychoactive, depressant, sedative, hypnotic, anxiolytic drugs that are benzodiazepine-like in uses, such as for treating insomnia and anxiety.
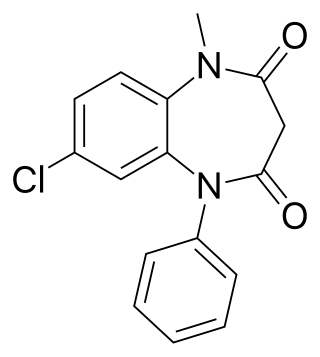
Clobazam, sold under the brand names Frisium, Onfi and others, is a benzodiazepine class medication that was patented in 1968. Clobazam was first synthesized in 1966 and first published in 1969. Clobazam was originally marketed as an anxioselective anxiolytic since 1970, and an anticonvulsant since 1984. The primary drug-development goal was to provide greater anxiolytic, anti-obsessive efficacy with fewer benzodiazepine-related side effects.

Estazolam, sold under the brand name Prosom among others, is a tranquilizer medication of the triazolobenzodiazepine (TBZD) class, which are benzodiazepines (BZDs) fused with a triazole ring. It possesses anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, hypnotic, sedative and skeletal muscle relaxant properties. Estazolam is an intermediate-acting oral benzodiazepine. It is used for short-term treatment of insomnia.

Nordazepam is a 1,4-benzodiazepine derivative. Like other benzodiazepine derivatives, it has amnesic, anticonvulsant, anxiolytic, muscle relaxant, and sedative properties. However, it is used primarily in the treatment of anxiety disorders. It is an active metabolite of diazepam, chlordiazepoxide, clorazepate, prazepam, pinazepam, and medazepam.

Loprazolam (triazulenone) marketed under many brand names is a benzodiazepine medication. It possesses anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, hypnotic, sedative and skeletal muscle relaxant properties. It is licensed and marketed for the short-term treatment of moderately-severe insomnia.

Pinazepam is a benzodiazepine drug. It possesses anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, sedative and skeletal muscle relaxant properties.

Camazepam is a benzodiazepine psychoactive drug, marketed under the brand names Albego, Limpidon and Paxor. It is the dimethyl carbamate ester of temazepam, a metabolite of diazepam. While it possesses anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, skeletal muscle relaxant and hypnotic properties it differs from other benzodiazepines in that its anxiolytic properties are particularly prominent but has comparatively limited anticonvulsant, hypnotic and skeletal muscle relaxant properties.

Ethyl loflazepate is a drug which is a benzodiazepine derivative. It possesses anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, sedative and skeletal muscle relaxant properties. In animal studies it was found to have low toxicity, although in rats evidence of pulmonary phospholipidosis occurred with pulmonary foam cells developing with long-term use of very high doses. Its elimination half-life is 51–103 hours. Its mechanism of action is similar to other benzodiazepines. Ethyl loflazepate also produces an active metabolite which is stronger than the parent compound. Ethyl loflazepate was designed to be a prodrug for descarboxyloflazepate, its active metabolite. It is the active metabolite which is responsible for most of the pharmacological effects rather than ethyl loflazepate. The main metabolites of ethyl loflazepate are descarbethoxyloflazepate, loflazepate and 3-hydroxydescarbethoxyloflazepate. Accumulation of the active metabolites of ethyl loflazepate are not affected by those with kidney failure or impairment. The symptoms of an overdose of ethyl loflazepate include sleepiness, agitation and ataxia. Hypotonia may also occur in severe cases. These symptoms occur much more frequently and severely in children. Death from therapeutic maintenance doses of ethyl loflazepate taken for 2 – 3 weeks has been reported in 3 elderly patients. The cause of death was asphyxia due to benzodiazepine toxicity. High doses of the antidepressant fluvoxamine may potentiate the adverse effects of ethyl loflazepate.

Etizolam is a thienodiazepine derivative which is a benzodiazepine analog. The etizolam molecule differs from a benzodiazepine in that the benzene ring has been replaced by a thiophene ring and triazole ring has been fused, making the drug a thienotriazolodiazepine.

Delorazepam, also known by the synonyms chlordesmethyldiazepam and nordiclazepam, is a drug which is a benzodiazepine and a derivative of desmethyldiazepam. It is marketed in Italy, where it is available under the trade name EN and Dadumir. Delorazepam (chlordesmethyldiazepam) is also an active metabolite of the benzodiazepine drugs diclazepam and cloxazolam. Adverse effects may include hangover type effects, drowsiness, behavioural impairments and short-term memory impairments. Similar to other benzodiazepines delorazepam has anxiolytic, skeletal muscle relaxant, hypnotic and anticonvulsant properties.

Benzoctamine is a drug that possesses sedative and anxiolytic properties. Marketed as Tacitin by Ciba-Geigy, it is different from most sedative drugs because in most clinical trials it does not produce respiratory depression, but actually stimulates the respiratory system. As a result, when compared to other sedative and anxiolytic drugs such as benzodiazepines like diazepam, it is a safer form of tranquilizing. However, when co-administered with other drugs that cause respiratory depression, like morphine, it can cause increased respiratory depression.

Abecarnil (ZK-112,119) is an anxiolytic drug from the β-Carboline family. It is one of a relatively recently developed class of medicines known as the nonbenzodiazepines, which have similar effects to the older benzodiazepine group, but with quite different chemical structures. It is a partial agonist acting selectively at the benzodiazepine site of the GABAA receptor.
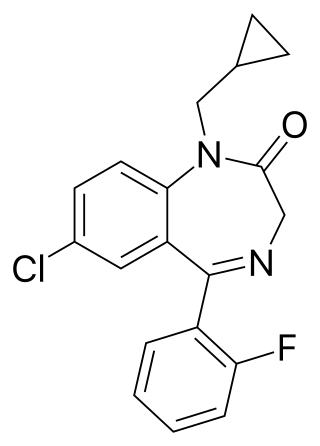
Flutoprazepam (Restas) is a drug which is a benzodiazepine. It was patented in Japan by Sumitomo in 1972 and its medical use remains mostly confined to that country. Its muscle relaxant properties are approximately equivalent to those of diazepam - however, it has more powerful sedative, hypnotic, anxiolytic and anticonvulsant effects and is around four times more potent by weight compared to diazepam. It is longer acting than diazepam due to its long-acting active metabolites, which contribute significantly to its effects. Its principal active metabolite is n-desalkylflurazepam, also known as norflurazepam, which is also a principal metabolite of flurazepam.

Metaclazepam is a drug which is a benzodiazepine derivative. It is a relatively selective anxiolytic with less sedative or muscle relaxant properties than other benzodiazepines such as diazepam or bromazepam. It has an active metabolite N-desmethylmetaclazepam, which is the main metabolite of metaclazepam. There is no significant difference in metabolism between younger and older individuals.

Pipequaline (INN) is an anxiolytic drug that was never marketed. It possesses a novel chemical structure that is not closely related to other drugs of this type. The drug has a similar pharmacological profile to the benzodiazepine family of drugs, but with mainly anxiolytic properties and very little sedative, amnestic or anticonvulsant effects, and so is classified as a nonbenzodiazepine anxiolytic.

Premazepam is a Pyrrolodiazepine class of drug. It is a partial agonist of benzodiazepine receptors and was shown in 1984 to possess both anxiolytic and sedative properties in humans but was never marketed.

Diclazepam (Ro5-3448), also known as chlorodiazepam and 2'-chloro-diazepam, is a benzodiazepine and functional analog of diazepam. It was first synthesized by Leo Sternbach and his team at Hoffman-La Roche in 1960. It is not currently approved for use as a medication, but rather sold as an unscheduled substance. Efficacy and safety have not been tested in humans.