
A general anaesthetic is a drug that brings about a reversible loss of consciousness. These drugs are generally administered by an anaesthetist/anesthesiologist to induce or maintain general anaesthesia to facilitate surgery.

The GABAA receptor (GABAAR) is an ionotropic receptor and ligand-gated ion channel. Its endogenous ligand is γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA), the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. Upon opening, the GABAA receptor on the postsynaptic cell is selectively permeable to chloride ions (Cl−) and, to a lesser extent, bicarbonate ions (HCO3−). Depending on the membrane potential and the ionic concentration difference, this can result in ionic fluxes across the pore. If the membrane potential is higher than the equilibrium potential (also known as the reversal potential) for chloride ions, when the receptor is activated Cl− will flow into the cell. This causes an inhibitory effect on neurotransmission by diminishing the chance of a successful action potential occurring at the postsynaptic cell. The reversal potential of the GABAA-mediated inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP) in normal solution is −70 mV, contrasting the GABAB IPSP (-100 mV).
Neurosteroids, also known as neuroactive steroids, are endogenous or exogenous steroids that rapidly alter neuronal excitability through interaction with ligand-gated ion channels and other cell surface receptors. The term neurosteroid was coined by the French physiologist Étienne-Émile Baulieu and refers to steroids synthesized in the brain. The term, neuroactive steroid refers to steroids that can be synthesized in the brain, or are synthesized by an endocrine gland, that then reach the brain through the bloodstream and have effects on brain function. The term neuroactive steroids was first coined in 1992 by Steven Paul and Robert Purdy. In addition to their actions on neuronal membrane receptors, some of these steroids may also exert effects on gene expression via nuclear steroid hormone receptors. Neurosteroids have a wide range of potential clinical applications from sedation to treatment of epilepsy and traumatic brain injury. Ganaxolone, a synthetic analog of the endogenous neurosteroid allopregnanolone, is under investigation for the treatment of epilepsy.
Alfaxolone/alfadolone (brand names Althesin, Saffan is a short acting intravenous anaesthetic agent. It was withdrawn from the market due to severe drug reactions. It is composed of a 3:1 mixture of alfaxalone and alfadolone, two neurosteroids.

Allopregnanolone is a naturally occurring neurosteroid which is made in the body from the hormone progesterone. As a medication, allopregnanolone is referred to as brexanolone, sold under the brand name Zulresso, and used to treat postpartum depression. It is given by injection into a vein.

Minaxolone (CCI-12923) is a neuroactive steroid which was developed as a general anesthetic but was withdrawn before registration due to toxicity seen with long-term administration in rats, and hence was never marketed. It is a positive allosteric modulator of the GABAA receptor, as well as, less potently, a positive allosteric modulator of the glycine receptor.

Alfaxalone, also known as alphaxalone or alphaxolone and sold under the brand name Alfaxan, is a neuroactive steroid and general anesthetic which is used currently in veterinary practice as an induction agent for anesthesia and as an injectable anesthetic. Though it is more expensive than other induction agents, it often preferred due to the lack of depressive effects on the cardiovascular system. The most common side effect seen in current veterinary practice is respiratory depression when Alfaxan is administered concurrently with other sedative and anesthetic drugs; when premedications aren't given, veterinary patients also become agitated and hypersensitive when waking up.

A GABA receptor agonist is a drug that is an agonist for one or more of the GABA receptors, producing typically sedative effects, and may also cause other effects such as anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, and muscle relaxant effects. There are three receptors of the gamma-aminobutyric acid. The two receptors GABA-α and GABA-ρ are ion channels that are permeable to chloride ions which reduces neuronal excitability. The GABA-β receptor belongs to the class of G-Protein coupled receptors that inhibit adenylyl cyclase, therefore leading to decreased cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP). GABA-α and GABA-ρ receptors produce sedative and hypnotic effects and have anti-convulsion properties. GABA-β receptors also produce sedative effects. Furthermore, they lead to changes in gene transcription.

Fospropofol (INN), often used as the disodium salt is an intravenous sedative-hypnotic agent. It is currently approved for use in sedation of adult patients undergoing diagnostic or therapeutic procedures such as endoscopy.
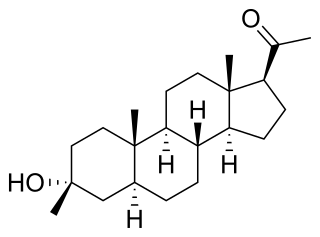
Ganaxolone, sold under the brand name Ztalmy, is a medication used to treat seizures in people with cyclin-dependent kinase-like 5 (CDKL5) deficiency disorder (CDD).
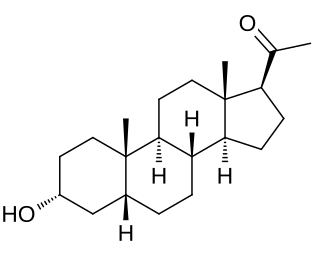
Pregnanolone, also known as eltanolone, is an endogenous inhibitory neurosteroid which is produced in the body from progesterone. It is closely related to allopregnanolone, which has similar properties.
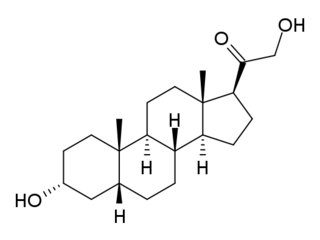
Tetrahydrodeoxycorticosterone, also referred to as allotetrahydrocorticosterone, is an endogenous neurosteroid. It is synthesized from the adrenal hormone deoxycorticosterone by the action of two enzymes, 5α-reductase type I and 3α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase. THDOC is a potent positive allosteric modulator of the GABAA receptor, and has sedative, anxiolytic and anticonvulsant effects. Changes in the normal levels of this steroid particularly during pregnancy and menstruation may be involved in some types of epilepsy and premenstrual syndrome, as well as stress, anxiety and depression.

17-Phenylandrostenol (17-PA), or (3α,5α)-17-phenylandrost-16-en-3-ol, is a steroid drug which binds to GABAA receptors. It acts as an antagonist against the sedative effects of neuroactive steroids, but has little effect when administered by itself, and does not block the effects of benzodiazepines or barbiturates.

ORG-21465 is a synthetic neuroactive steroid, with sedative effects resulting from its action as a GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulator. It is similar to related drugs such as ORG-20599, and was similarly developed as an improved alternative to other sedative steroids such as althesin and allopregnanolone, which despite its superior properties in some respects has not proved to offer enough advantages to be accepted into clinical use.

ORG-25435 is a synthetic drug developed by Organon International, which acts as a GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulator, and produces sedative effects. It has been researched for use as an intravenous anesthetic agent, with positive results in initial trials, although negative side effects like hypotension and tachycardia, as well as unpredictable pharmacokinetics at higher doses, have meant it has ultimately not been adopted for medical use.

In pharmacology, GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulators, also known as GABAkines or GABAA receptor potentiators, are positive allosteric modulator (PAM) molecules that increase the activity of the GABAA receptor protein in the vertebrate central nervous system.
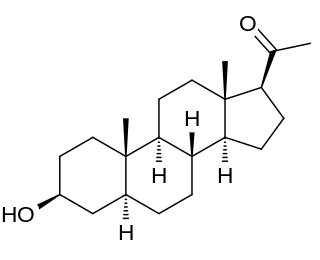
Isopregnanolone, also known as isoallopregnanolone and epiallopregnanolone, as well as sepranolone (INN), and as 3β-hydroxy-5α-pregnan-20-one or 3β,5α-tetrahydroprogesterone (3β,5α-THP), is an endogenous neurosteroid and a natural 3β-epimer of allopregnanolone. It has been reported to act as a subunit-selective negative allosteric modulator of the GABAA receptor, and antagonizes in animals and humans some but not all of the GABAA receptor-mediated effects of allopregnanolone, such as anesthesia, sedation, and reduced saccadic eye movements, but not learning impairment. Isopregnanolone has no hormonal effects and appears to have no effect on the GABAA receptor by itself; it selectively antagonizes allopregnanolone and does not affect the effects of other types of GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulators such as benzodiazepines or barbiturates.

5β-Dihydroprogesterone is an endogenous neurosteroid and an intermediate in the biosynthesis of pregnanolone and epipregnanolone from progesterone. It is synthesized from progesterone by the enzyme 5β-reductase.

Posovolone is a synthetic neurosteroid which was under development as a sedative/hypnotic medication for the treatment of insomnia. It is orally active and acts as a GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulator. In animals, posovolone shows anticonvulsant, anxiolytic-like, ataxic, and sleep-promoting effects and appeared to produce effects similar to those of pregnanolone. Development of the agent was started by 1999 and appears to have been discontinued by 2007. In 2021, an INN was registered for posovolone with the descriptor of "antidepressant". Posovolone was originally developed by Purdue Pharma.

















