In toxicology, the median lethal dose, LD50 (abbreviation for "lethal dose, 50%"), LC50 (lethal concentration, 50%) or LCt50 is a toxic unit that measures the lethal dose of a given substance. The value of LD50 for a substance is the dose required to kill half the members of a tested population after a specified test duration. LD50 figures are frequently used as a general indicator of a substance's acute toxicity. A lower LD50 is indicative of higher toxicity.

Strychnine is a highly toxic, colorless, bitter, crystalline alkaloid used as a pesticide, particularly for killing small vertebrates such as birds and rodents. Strychnine, when inhaled, swallowed, or absorbed through the eyes or mouth, causes poisoning which results in muscular convulsions and eventually death through asphyxia. While it is no longer used medicinally, it was used historically in small doses to strengthen muscle contractions, such as a heart and bowel stimulant and performance-enhancing drug. The most common source is from the seeds of the Strychnos nux-vomica tree.
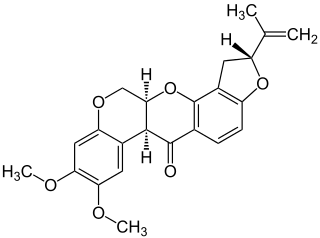
Rotenone is an odorless, colorless, crystalline isoflavone. It occurs naturally in the seeds and stems of several plants, such as the jicama vine, and in the roots of several other members of the Fabaceae. It was the first-described member of the family of chemical compounds known as rotenoids. Rotenone was used in the past as a broad-spectrum insecticide, and is still used as a piscicide to remove alien fish species,
Neurochemistry is the study of chemicals, including neurotransmitters and other molecules such as psychopharmaceuticals and neuropeptides, that control and influence the physiology of the nervous system. This particular field within neuroscience examines how neurochemicals influence the operation of neurons, synapses, and neural networks. Neurochemists analyze the biochemistry and molecular biology of organic compounds in the nervous system, and their roles in such neural processes including cortical plasticity, neurogenesis, and neural differentiation.

Muscimol is one of the principal psychoactive constituents of Amanita muscaria and related species of mushroom. Muscimol is a potent and selective orthosteric agonist for the GABAA receptor and displays sedative-hypnotic, depressant and hallucinogenic psychoactivity. This colorless or white solid is classified as an isoxazole.

Rodenticides are chemicals made and sold for the purpose of killing rodents. While commonly referred to as "rat poison", rodenticides are also used to kill mice, woodchucks, chipmunks, porcupines, nutria, beavers, and voles. Despite the crucial roles that rodents play in nature, there are times when they need to be controlled.

Aldrin is an organochlorine insecticide that was widely used until the 1990s, when it was banned in most countries. Aldrin is a member of the so-called "classic organochlorines" (COC) group of pesticides. COCs enjoyed a very sharp rise in popularity during and after World War II. Other noteworthy examples of COCs include dieldrin and DDT. After research showed that organochlorines can be highly toxic to the ecosystem through bioaccumulation, most were banned from use. Before the ban, it was heavily used as a pesticide to treat seed and soil. Aldrin and related "cyclodiene" pesticides became notorious as persistent organic pollutants.

Theobromine poisoning, also informally called chocolate poisoning or cocoa poisoning, is an overdosage reaction to the xanthine alkaloid theobromine, found in chocolate, tea, cola beverages, and some other foods.

Tetramethylenedisulfotetramine (TETS) is an organic compound used as a rodenticide. It is an odorless, tasteless white powder that is slightly soluble in water, DMSO and acetone, and insoluble in methanol and ethanol. It is a sulfamide derivative. It can be synthesized by reacting sulfamide with formaldehyde solution in acidified water. When crystallized from acetone, it forms cubic crystals with a melting point of 255–260 °C.

Azinphos-methyl (Guthion) is a broad spectrum organophosphate insecticide manufactured by Bayer CropScience, Gowan Co., and Makhteshim Agan. Like other pesticides in this class, it owes its insecticidal properties to the fact that it is an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. It is classified as an extremely hazardous substance in the United States as defined in Section 302 of the U.S. Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act, and is subject to strict reporting requirements by facilities which produce, store, or use it in significant quantities.

Methiocarb is a carbamate pesticide which is used as an insecticide, bird repellent, acaricide and molluscicide since the 1960s. Methiocarb has contact and stomach action on mites and neurotoxic effects on molluscs. Seeds treated with methiocarb also affect birds. Other names for methiocarb are mesurol and mercaptodimethur.

Tutin is a poisonous plant derivative found in New Zealand tutu plants. It acts as a potent antagonist of the glycine receptor, and has powerful convulsant effects. It is used in scientific research into the glycine receptor. It is sometimes associated with outbreaks of toxic honey poisoning when bees feed on honeydew exudate from the sap-sucking passion vine hopper insect, when the vine hoppers have been feeding on the sap of tutu bushes. Toxic honey is a rare event and is more likely to occur when comb honey is eaten directly from a hive that has been harvesting honeydew from passionvine hoppers feeding on tutu plants.

Phenylsilatrane is a convulsant chemical which has been used as a rodenticide. Phenylsilatrane and some of its analogs with 4-substituents of H, CH3, Cl, Br, and CSi(CH3)3 are highly toxic to mice. They have been observed in the laboratory to inhibit the 35S-tert-butylbicyclophosphorothionate (TBPS) binding site (GABA-gated chloride channel) of mouse brain membranes.

2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) is a polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin (sometimes shortened, though inaccurately, to simply 'dioxin') with the chemical formula C12H4Cl4O2. Pure TCDD is a colorless solid with no distinguishable odor at room temperature. It is usually formed as an unwanted product in burning processes of organic materials or as a side product in organic synthesis.

Leptophos (O-(4-bromo-2,5-dichlorophenyl) O-methyl phenylphosphonothioate) belongs to the organophosphates and at room temperature it is a stable white solid. It is also known as Phosvel, Abar and Vcs 506. Leptophos was primarily used as a pesticide and fungicide. for rice, cotton, fruit and vegetables until its use was discontinued in 1975 in USA, but still sold in South-Eastern Asia in 1981.

Tetramethylammonium (TMA) is the simplest quaternary ammonium cation. It has the chemical formula [Me4N]+ and consists of four methyl groups attached to a central nitrogen atom. The cation is isoelectronic with neopentane. It is positively-charged and can only be isolated in association with a counter-ion. Common salts include tetramethylammonium chloride and tetramethylammonium hydroxide. Tetramethylammonium salts are used in chemical synthesis and in pharmacological research. It confers no color to its salts.

TBPS (tert-butylbicyclophosphorothionate) is a bicyclic phosphate convulsant. It is an extremely potent GABA receptor antagonist.

IPTBO is a bicyclic phosphate convulsant. It is an extremely potent GABA receptor antagonist that can cause violent convulsions in mice.

TBPO is an extremely toxic bicyclic phosphate convulsant and GABA receptor antagonist. It is the most toxic bicyclic phosphate known, with an LD50 of 36 μg/kg in mice.

Monocrotaline (MCT) is a pyrrolizidine alkaloid that is present in plants of the Crotalaria genus. These species can synthesise MCT out of amino acids and can cause liver, lung and kidney damage in various organisms. Initial stress factors are released intracellular upon binding of MCT to BMPR2 receptors and elevated MAPK phosphorylation levels are induced, which can cause cancer in Homo sapiens. MCT can be detoxified in rats via oxidation, followed by glutathione-conjugation and hydrolysis.


















