 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
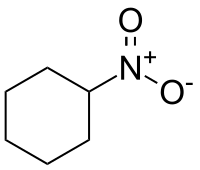
| IUPAC name Nitrocyclohexane | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.013.050 |
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H11NO2 | |
| Molar mass | 129.159 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.061 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −34 °C (−29 °F; 239 K) |
| Boiling point | 205.8 °C (402.4 °F; 478.9 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Nitrocyclohexane is an organic compound with the molecular formula C6H11NO2. It is a colorless liquid, but degraded samples appear pale yellow. It once was produced commercially as a precursor to caprolactam. [1]