| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name 1,1,3,3,3-Pentafluoro-2-(trifluoromethyl)prop-1-ene | |||
| Other names Perfluoroisobutene, Perfluoroisobutylene, Octafluoroisobutylene, Octafluoro-sec-butene, PFIB | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.108.743 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
PubChem CID | |||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
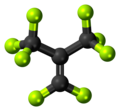
| C4F8 | |||
| Molar mass | 200.030 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | colorless gas | ||
| Density | 8.2 g/l | ||
| Melting point | −130 °C (−202 °F; 143 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 7.0 °C (44.6 °F; 280.1 K) | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
  | |||
| Danger | |||
| H330, H370 | |||
| P260, P264, P270, P271, P284, P304+P340, P307+P311, P310, P320, P321, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
Perfluoroisobutene (PFIB) is the perfluorocarbon with the formula (CF3)2C=CF2. Classified as a perfluoroalkene, it is the fluorinated counterpart of the hydrocarbon isobutene. This colorless gas is notable for its high toxicity. [1]