
The noble gases are the naturally occurring members of group 18 of the periodic table: helium (He), neon (Ne), argon (Ar), krypton (Kr), xenon (Xe), and radon (Rn). Under standard conditions, these elements are odorless, colorless, monatomic gases with very low chemical reactivity and cryogenic boiling points.
Nerve agents, sometimes also called nerve gases, are a class of organic chemicals that disrupt the mechanisms by which nerves transfer messages to organs. The disruption is caused by the blocking of acetylcholinesterase (AChE), an enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter. Nerve agents are irreversible acetylcholinesterase inhibitors used as poison.

Xenon is a chemical element; it has symbol Xe and atomic number 54. It is a dense, colorless, odorless noble gas found in Earth's atmosphere in trace amounts. Although generally unreactive, it can undergo a few chemical reactions such as the formation of xenon hexafluoroplatinate, the first noble gas compound to be synthesized.

Hydrogen cyanide is a chemical compound with the formula HCN and structural formula H−C≡N. It is a highly toxic and flammable liquid that boils slightly above room temperature, at 25.6 °C (78.1 °F). HCN is produced on an industrial scale and is a highly valued precursor to many chemical compounds ranging from polymers to pharmaceuticals. Large-scale applications are for the production of potassium cyanide and adiponitrile, used in mining and plastics, respectively. It is more toxic than solid cyanide compounds due to its volatile nature. A solution of hydrogen cyanide in water, represented as HCN, is called hydrocyanic acid. The salts of the cyanide anion are known as cyanides.

Mustard gas or sulfur mustard is any of the several chemical compounds that contain the chemical structure S(CH2CH2Cl)2. In the wider sense, compounds with the substituent S(CH2CH2X)2 and N(CH2CH2X)3 are known as sulfur mustards and nitrogen mustards, respectively, where X = Cl or Br. Such compounds are potent alkylating agents, which can interfere with several biological processes. Also known as mustard agents, this family of compounds are infamous cytotoxins and blister agents with a long history of use as chemical weapons. The name mustard gas is technically incorrect: the substances, when dispersed, are often not gases but a fine mist of liquid droplets. Sulfur mustards are viscous liquids at room temperature and have an odor resembling mustard plants, garlic, or horseradish, hence the name. When pure, they are colorless, but when used in impure forms, such as in warfare, they are usually yellow-brown. Mustard gases form blisters on exposed skin and in the lungs, often resulting in prolonged illness ending in death. The typical mustard gas is the organosulfur compound bis(2-chloroethyl) sulfide.
Incapacitating agent is a chemical or biological agent which renders a person unable to harm themselves or others, regardless of consciousness.

Soman is an extremely toxic chemical substance. It is a nerve agent, interfering with normal functioning of the mammalian nervous system by inhibiting the enzyme cholinesterase. It is an inhibitor of both acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase. As a chemical weapon, it is classified as a weapon of mass destruction by the United Nations according to UN Resolution 687. Its production is strictly controlled, and stockpiling is outlawed by the Chemical Weapons Convention of 1993 where it is classified as a Schedule 1 substance. Soman was the third of the so-called G-series nerve agents to be discovered along with GA (tabun), GB (sarin), and GF (cyclosarin).

The use of toxic chemicals as weapons dates back thousands of years, but the first large-scale use of chemical weapons was during World War I. They were primarily used to demoralize, injure, and kill entrenched defenders, against whom the indiscriminate and generally very slow-moving or static nature of gas clouds would be most effective. The types of weapons employed ranged from disabling chemicals, such as tear gas, to lethal agents like phosgene, chlorine, and mustard gas. These chemical weapons caused medical problems. This chemical warfare was a major component of the first global war and first total war of the 20th century. The killing capacity of gas was profound, with about 90,000 fatalities from a total of 1.3 million casualties caused by gas attacks. Gas was unlike most other weapons of the period because it was possible to develop countermeasures, such as gas masks. In the later stages of the war, as the use of gas increased, its overall effectiveness diminished. The widespread use of these agents of chemical warfare, and wartime advances in the composition of high explosives, gave rise to an occasionally expressed view of World War I as "the chemist's war" and also the era where weapons of mass destruction were created.

The compound 2-chlorobenzalmalononitrile (also called o-chlorobenzylidene malononitrile; chemical formula: C10H5ClN2), a cyanocarbon, is the defining component of the lachrymatory agent commonly referred to as CS gas, which is used as a riot control agent.

Lewisite (L) (A-243) is an organoarsenic compound. It was once manufactured in the U.S., Japan, Germany and the Soviet Union for use as a chemical weapon, acting as a vesicant and lung irritant. Although the substance is colorless and odorless in its pure form, impure samples of lewisite are a yellow, brown, violet-black, green, or amber oily liquid with a distinctive odor that has been described as similar to geraniums.

Arsine (IUPAC name: arsane) is an inorganic compound with the formula AsH3. This flammable, pyrophoric, and highly toxic pnictogen hydride gas is one of the simplest compounds of arsenic. Despite its lethality, it finds some applications in the semiconductor industry and for the synthesis of organoarsenic compounds. The term arsine is commonly used to describe a class of organoarsenic compounds of the formula AsH3−xRx, where R = aryl or alkyl. For example, As(C6H5)3, called triphenylarsine, is referred to as "an arsine".

Tear gas, also known as a lachrymatory agent or lachrymator, sometimes colloquially known as "mace" after the early commercial self-defense spray, is a chemical weapon that stimulates the nerves of the lacrimal gland in the eye to produce tears. In addition, it can cause severe eye and respiratory pain, skin irritation, bleeding, and blindness. Common lachrymators both currently and formerly used as tear gas include pepper spray, PAVA spray (nonivamide), CS gas, CR gas, CN gas, bromoacetone, xylyl bromide and Mace.

Saxitoxin (STX) is a potent neurotoxin and the best-known paralytic shellfish toxin (PST). Ingestion of saxitoxin by humans, usually by consumption of shellfish contaminated by toxic algal blooms, is responsible for the illness known as paralytic shellfish poisoning (PSP).

Acrolein is the simplest unsaturated aldehyde. It is a colorless liquid with a foul and acrid aroma. The smell of burnt fat is caused by glycerol in the burning fat breaking down into acrolein. It is produced industrially from propene and mainly used as a biocide and a building block to other chemical compounds, such as the amino acid methionine.

Chlormethine, also known as mechlorethamine, mustine, HN2, and embikhin (эмбихин), is a nitrogen mustard sold under the brand name Mustargen among others. It is the prototype of alkylating agents, a group of anticancer chemotherapeutic drugs. It works by binding to DNA, crosslinking two strands and preventing cell duplication. It binds to the N7 nitrogen on the DNA base guanine. As the chemical is a blister agent, its use is strongly restricted within the Chemical Weapons Convention where it is classified as a Schedule 1 substance.
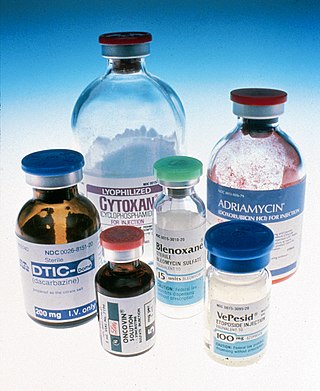
The era of cancer chemotherapy began in the 1940s with the first use of nitrogen mustards and folic acid antagonist drugs. The targeted therapy revolution has arrived, but many of the principles and limitations of chemotherapy discovered by the early researchers still apply.

Nitrogen mustards (NMs) are cytotoxic organic compounds with the bis(2-chloroethyl)amino ((ClC2H4)2NR) functional group. Although originally produced as chemical warfare agents, they were the first chemotherapeutic agents for treatment of cancer. Nitrogen mustards are nonspecific DNA alkylating agents.
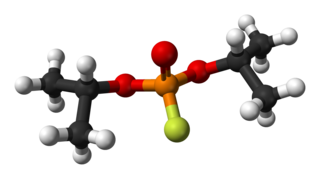
Diisopropyl fluorophosphate (DFP) or Isoflurophate is an oily, colorless liquid with the chemical formula C6H14FO3P. It is used in medicine and as an organophosphorus insecticide. It is stable, but undergoes hydrolysis when subjected to moisture.
A chemical weapon (CW) is a specialized munition that uses chemicals formulated to inflict death or harm on humans. According to the Organisation for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW), this can be any chemical compound intended as a weapon "or its precursor that can cause death, injury, temporary incapacitation or sensory irritation through its chemical action. Munitions or other delivery devices designed to deliver chemical weapons, whether filled or unfilled, are also considered weapons themselves."

A-234 is an organophosphate nerve agent. It was developed in the Soviet Union under the FOLIANT program and is one of the group of compounds referred to as Novichok agents that were revealed by Vil Mirzayanov. In March 2018 the Russian ambassador to the UK, Alexander Yakovenko, claimed to have been informed by British authorities that A-234 had been identified as the agent used in the poisoning of Sergei and Yulia Skripal. Vladimir Uglev, one of the inventors of the Novichok series of compounds, said he was "99 percent sure that it was A-234" in relation to the 2018 Amesbury poisonings, noting its unusually high persistence in the environment.


















