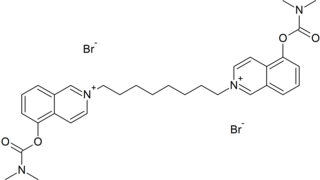Citric acid is an organic compound with the skeletal formula HOC(CO2H)(CH2CO2H)2. It is a colorless weak organic acid. It occurs naturally in citrus fruits. In biochemistry, it is an intermediate in the citric acid cycle, which occurs in the metabolism of all aerobic organisms.

Trichlorosilane (TCS) is an inorganic compound with the formula HCl3Si. It is a colourless, volatile liquid. Purified trichlorosilane is the principal precursor to ultrapure silicon in the semiconductor industry. In water, it rapidly decomposes to produce a siloxane polymer while giving off hydrochloric acid. Because of its reactivity and wide availability, it is frequently used in the synthesis of silicon-containing organic compounds.
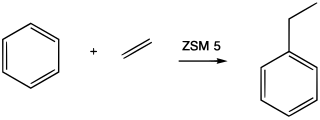
Alkylation is a chemical reaction that entails transfer of an alkyl group. The alkyl group may be transferred as an alkyl carbocation, a free radical, a carbanion, or a carbene. Alkylating agents are reagents for effecting alkylation. Alkyl groups can also be removed in a process known as dealkylation. Alkylating agents are often classified according to their nucleophilic or electrophilic character. In oil refining contexts, alkylation refers to a particular alkylation of isobutane with olefins. For upgrading of petroleum, alkylation produces a premium blending stock for gasoline. In medicine, alkylation of DNA is used in chemotherapy to damage the DNA of cancer cells. Alkylation is accomplished with the class of drugs called alkylating antineoplastic agents.

Nitrobenzene is an aromatic nitro compound and the simplest of the nitrobenzenes, with the chemical formula C6H5NO2. It is a water-insoluble pale yellow oil with an almond-like odor. It freezes to give greenish-yellow crystals. It is produced on a large scale from benzene as a precursor to aniline. In the laboratory, it is occasionally used as a solvent, especially for electrophilic reagents.
Semisynthesis, or partial chemical synthesis, is a type of chemical synthesis that uses chemical compounds isolated from natural sources as the starting materials to produce novel compounds with distinct chemical and medicinal properties. The novel compounds generally have a high molecular weight or a complex molecular structure, more so than those produced by total synthesis from simple starting materials. Semisynthesis is a means of preparing many medicines more cheaply than by total synthesis since fewer chemical steps are necessary.
Tin(IV) chloride, also known as tin tetrachloride or stannic chloride, is an inorganic compound of tin and chlorine with the formula SnCl4. It is a colorless hygroscopic liquid, which fumes on contact with air. It is used as a precursor to other tin compounds. It was first discovered by Andreas Libavius (1550–1616) and was known as spiritus fumans libavii.
1,8-Diazabicyclo[5.4.0]undec-7-ene, or more commonly DBU, is a chemical compound and belongs to the class of amidine compounds. It is used in organic synthesis as a catalyst, a complexing ligand, and a non-nucleophilic base.

Peroxymonosulfuric acid, H
2SO
5, is also known as persulfuric acid, peroxysulfuric acid, or Caro's acid. In this acid, the S(VI) center adopts its characteristic tetrahedral geometry; the connectivity is indicated by the formula HO–O–S(O)2–OH. It is one of the strongest oxidants known (E0 = +2.51 V) and is highly explosive.
Calcium hypochlorite is an inorganic compound with chemical formula Ca(ClO)2, also written as Ca(OCl)2. It is a white solid, although commercial samples appear yellow. It strongly smells of chlorine, owing to its slow decomposition in moist air. This compound is relatively stable as a solid and solution and has greater available chlorine than sodium hypochlorite. "Pure" samples have 99.2% active chlorine. Given common industrial purity, an active chlorine content of 65-70% is typical. It is the main active ingredient of commercial products called bleaching powder, used for water treatment and as a bleaching agent.

Pimelic acid is the organic compound with the formula HO2C(CH2)5CO2H. Pimelic acid is one CH
2 unit longer than a related dicarboxylic acid, adipic acid, a precursor to many polyesters and polyamides. However compared to adipic acid, pimelic acid is relatively small in importance industrially. Derivatives of pimelic acid are involved in the biosynthesis of the amino acid lysine and the vitamin biotin.

1,4-Benzoquinone, commonly known as para-quinone, is a chemical compound with the formula C6H4O2. In a pure state, it forms bright-yellow crystals with a characteristic irritating odor, resembling that of chlorine, bleach, and hot plastic or formaldehyde. This six-membered ring compound is the oxidized derivative of 1,4-hydroquinone. The molecule is multifunctional: it exhibits properties of a ketone, being able to form oximes; an oxidant, forming the dihydroxy derivative; and an alkene, undergoing addition reactions, especially those typical for α,β-unsaturated ketones. 1,4-Benzoquinone is sensitive toward both strong mineral acids and alkali, which cause condensation and decomposition of the compound.

Polyester is a category of polymers that contain one or two ester linkages in every repeat unit of their main chain. As a specific material, it most commonly refers to a type called polyethylene terephthalate (PET). Polyesters include naturally occurring chemicals, such as in plants and insects, as well as synthetics such as polybutyrate. Natural polyesters and a few synthetic ones are biodegradable, but most synthetic polyesters are not. Synthetic polyesters are used extensively in clothing.

Pinacolone (3,3-dimethyl-2-butanone) is an important ketone in organic chemistry. It is a colorless liquid with a slight peppermint or camphor odor. It is a precursor to triazolylpinacolone in the synthesis of the fungicide triadimefon and in synthesis of the herbicide metribuzin. The molecule is an unsymmetrical ketone. The α-methyl group can participate in condensation reactions. The carbonyl group can undergo the usual reactions. It is a Schedule 3 compound under the Chemical Weapons Convention 1993, due to being related to pinacolyl alcohol, which is used in the production of soman. It is also a controlled export in Australia Group member states.

Basketane is a polycyclic alkane with the chemical formula C10H12. The name is taken from its structural similarity to a basket shape. Basketane was first synthesized in 1966, independently by Masamune and Dauben and Whalen. A patent application published in 1988 used basketane, which is a hydrocarbon, as a source material in doping thin diamond layers because of the molecule's high vapor pressure, carbon ring structure, and fewer hydrogen-to-carbon bond ratio.
Dan Ioan Popescu is a Romanian businessman and politician. A chemical engineer, he served between 2001 and 2003 as Minister of Industry and between 2003 and 2004 as Minister of Economy, both in the Adrian Năstase cabinet. He is married and has one child.

4-Methylcyclohexanemethanol (MCHM, systematic name 4-methylcyclohexylmethanol) is an organic compound with the formula CH3C6H10CH2OH. Classified as a saturated higher alicyclic primary alcohol. Both cis and trans isomers exist, depending on the relative positions of the methyl (CH3) and hydroxymethyl (CH2OH) groups on the cyclohexane ring. Commercial samples of MCHM consists of a mixture of these isomers as well as other components that vary with the supplier.

4-Fluorobromobenzene is a mixed aryl halide (aryl fluoride and aryl bromide) with the formula C6H4BrF. It is a derivative of benzene, with a bromine atom bonded para to a fluorine atom. It has uses as a precursor to some pharmaceuticals, as an agrochemical intermediate, and in organic synthesis. It is a colorless liquid of low acute toxicity.

EA-3990 is a deadly carbamate nerve agent. It is lethal because it inhibits acetylcholinesterase. Inhibition causes an overly high accumulation of acetylcholine between the nerve and muscle cells. This paralyzes the muscles by preventing their relaxation. The paralyzed muscles include the muscles used for breathing.
Octamethylene-bis(5-dimethylcarbamoxyisoquinolinium bromide) (4-673-745-01) is an extremely potent carbamate nerve agent. It works by inhibiting acetylcholinesterase, causing acetylcholine to accumulate. Since the agent molecule is positively charged, it does not cross the blood brain barrier very well.
1,9-Dibromononane is a chemical compound used in the synthesis of the carbamate nerve agent EA-4056. It can be obtained by the hydrobromination of cyclononene with sulfuric acid and catalysts, analogous to the synthesis of 1,8-dibromooctane.