
Phorbol esters are a class of chemical compounds found in a variety of plants, particularly in the families Euphorbiaceae and Thymelaeaceae. [1] [2] Chemically, they are ester derivatives of the tetracyclic diterpenoid phorbol.

Phorbol esters are a class of chemical compounds found in a variety of plants, particularly in the families Euphorbiaceae and Thymelaeaceae. [1] [2] Chemically, they are ester derivatives of the tetracyclic diterpenoid phorbol.
Protein kinase C (PKC) is a phorbol ester receptor. [2] [3] Phorbol esters can stimulate PKC in a similar way to diglycerides. [2] [3]
Phorbol esters are known for their ability to promote tumors. [2] In particular, 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA) is used as a biomedical research tool in models of carcinogenesis. [4] [5]
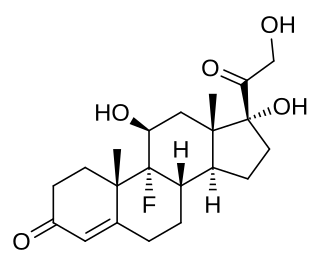
Fludrocortisone, sold under the brand name Florinef, among others, is a corticosteroid used to treat adrenogenital syndrome, postural hypotension, and adrenal insufficiency. In adrenal insufficiency, it is generally taken together with hydrocortisone. Fludrocortisone is taken by mouth and is most commonly used in its acetate form.
In cell biology, Protein kinase C, commonly abbreviated to PKC (EC 2.7.11.13), is a family of protein kinase enzymes that are involved in controlling the function of other proteins through the phosphorylation of hydroxyl groups of serine and threonine amino acid residues on these proteins, or a member of this family. PKC enzymes in turn are activated by signals such as increases in the concentration of diacylglycerol (DAG) or calcium ions (Ca2+). Hence PKC enzymes play important roles in several signal transduction cascades.
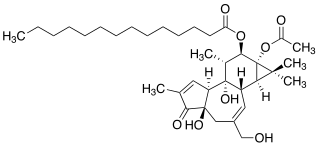
12-O-Tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA), also commonly known as tetradecanoylphorbol acetate, tetradecanoyl phorbol acetate, and phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) is a diester of phorbol. It is a potent tumor promoter often employed in biomedical research to activate the signal transduction enzyme protein kinase C (PKC). The effects of TPA on PKC result from its similarity to one of the natural activators of classic PKC isoforms, diacylglycerol. TPA is a small molecule drug.

Estradiol acetate (EA), sold under the brand names Femtrace, Femring, and Menoring, is an estrogen medication which is used in hormone therapy for the treatment of menopausal symptoms in women. It is taken by mouth once daily or given as a vaginal ring once every three months.
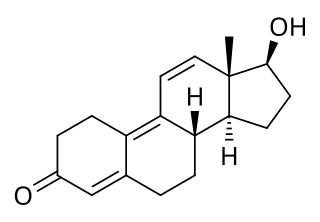
Trenbolone is an androgen and anabolic steroid (AAS) of the nandrolone group which itself was never marketed. Trenbolone ester prodrugs, including trenbolone acetate and trenbolone hexahydrobenzylcarbonate, are or have been marketed for veterinary and clinical use. Trenbolone acetate is used in veterinary medicine in livestock to increase muscle growth and appetite, while trenbolone hexahydrobenzylcarbonate was formerly used clinically in humans but is now no longer marketed. In addition, although it is not approved for clinical or veterinary use, trenbolone enanthate is sometimes sold on the black market under the nickname Trenabol.

Phorbol is a natural, plant-derived organic compound. It is a member of the tigliane family of diterpenes. Phorbol was first isolated in 1934 as the hydrolysis product of croton oil, which is derived from the seeds of the purging croton, Croton tiglium. The structure of phorbol was determined in 1967. Various esters of phorbol have important biological properties, the most notable of which is the capacity to act as tumor promoters through activation of protein kinase C. They mimic diacylglycerols, glycerol derivatives in which two hydroxyl groups have reacted with fatty acids to form esters. The most common and potent phorbol ester is 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA), also called phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate (PMA), which is used as a biomedical research tool in contexts such as models of carcinogenesis.

Gestonorone caproate, also known as gestronol hexanoate or norhydroxyprogesterone caproate and sold under the brand names Depostat and Primostat, is a progestin medication which is used in the treatment of enlarged prostate and cancer of the endometrium. It is given by injection into muscle typically once a week.

Motilin receptor is a G protein-coupled receptor that binds motilin. It was first cloned in 1999 by Merck Laboratories. and scientists have since been searching for compounds to modify its behavior.

Retinoic acid-induced protein 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GPRC5A gene. This gene and its encoded mRNA was first identified as a phorbol ester-induced gene, and named Phorbol Ester Induced Gen 1 (PEIG-1); two years later it was rediscovered as a retinoic acid-inducible gene, and named Retinoic Acid-Inducible Gene 1 (RAIG1). Its encoded protein was later named Retinoic acid-induced protein 3.

Protein kinase C eta type is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PRKCH gene.

Phorbol 12,13-dibutyrate (PDBu) is a phorbol ester which is one of the constituents of croton oil. As an activator of protein kinase C, it is a weak tumor promoter compared to 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate.

Tigilanol tiglate, sold under the brand name Stelfonta is a medication used to treat dogs with non-metastatic, skin-based (cutaneous) mast cell tumors (MCTs). The FDA is also approving Stelfonta to treat non-metastatic MCTs located under the dog's skin (subcutaneous), in particular areas of a dog's leg. Stelfonta is injected directly into the MCT. Stelfonta works by activating a protein that spreads throughout the treated tumor, which disintegrates tumor cells.

A diglyceride, or diacylglycerol (DAG), is a glyceride consisting of two fatty acid chains covalently bonded to a glycerol molecule through ester linkages. Two possible forms exist, 1,2-diacylglycerols and 1,3-diacylglycerols. DAGs can act as surfactants and are commonly used as emulsifiers in processed foods. DAG-enriched oil has been investigated extensively as a fat substitute due to its ability to suppress the accumulation of body fat; with total annual sales of approximately USD 200 million in Japan since its introduction in the late 1990s till 2009.

Estradiol undecylate, also known as estradiol undecanoate and formerly sold under the brand names Delestrec and Progynon Depot 100 among others, is an estrogen medication which has been used in the treatment of prostate cancer in men. It has also been used as a part of hormone therapy for transgender women. Although estradiol undecylate has been used in the past, it was discontinued and hence is no longer available. The medication has been given by injection into muscle usually once a month.

Mezerein is a toxic diterpene ester found in the sap of Daphne mezereum and related plants. Plants of the genera Euphorbiaceae and Thymelaeaceae possess a wide variety of different phorbol esters, which share the capacity of mimicking diacylglycerol (DAG) and thus activating different isoforms of protein kinase C. Mezerein was first isolated in 1975. It has antileukemic properties in mice, but it is also defined as a weak promoter of skin cancers in the same species. All parts of the plants contain an acrid and irritant sap that contains mezerein, thought to be the principal poison. The sap is especially prevalent in the bark and berries.

Edogestrone, or edogesterone, also known as 17α-acetoxy-3,3-ethylenedioxy-6-methylpregn-5-en-20-one, is a steroidal progestin and antiandrogen of the 17α-hydroxyprogesterone group which was synthesized in 1964 but was never marketed. Similarly to the structurally related steroid cyproterone acetate, edogestrone binds directly to the androgen receptor and antagonizes it, displacing androgens like testosterone from the receptor, though not as potently as cyproterone acetate. The drug has also been found to suppress androgen production, likely via progesterone receptor activation-mediated antigonadotropic activity.

Clogestone acetate (USAN), also known as chlormadinol acetate or as 3β,17α-diacetoxy-6-chloropregna-4,6-diene-20-one, is a steroidal progestin which was investigated as a progestin-only contraceptive and postcoital contraceptive but was never marketed. It is the diacetate ester of clogestone, which, similarly was never marketed. Clogestone acetate produces chlormadinone acetate as an active metabolite.

Amadinone (INN), also known as 19-norchlormadinone, is a steroidal progestin of the 19-norprogesterone and 17α-hydroxyprogesterone groups that was synthesized and characterized in 1968 but was never marketed. It has antigonadotropic properties, and for this reason, is a functional antiandrogen. An acetate ester, amadinone acetate, also exists, but similarly was never marketed.
Karen L. Leach is an American biochemist with extensive drug discovery experience in large pharmaceutical research laboratories. Her expertise in molecular pharmacology, signal transduction and protein kinases, has been used to establish mechanisms of toxicity for therapeutics such as the novel antibiotic linezolid (Zyvox).