 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
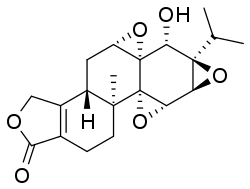
| Preferred IUPAC name (3bS,4aS,5aS,6R,6aR,7aS,7bS,8aS,9bS)-6-Hydroxy-8b-methyl-6a-(propan-2-yl)-3b,4,4a,5a,6,6a,7a,7b,8a,8b,9,10-dodecahydrotris(oxireno)[2′,3′:4b,5;2′′,3′′:6,7;2′′′,3′′′:8a,9]phenanthro[1,2-c]furan-1(3H)-one | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.208.723 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C20H24O6 | |
| Molar mass | 360.406 g·mol−1 |
| 0.017 mg/mL [1] | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Triptolide is a diterpenoid epoxide which is produced by the thunder god vine, Tripterygium wilfordii . It has in vitro and in vivo activities against mouse models of polycystic kidney disease [2] and pancreatic cancer, but its physical properties [3] and severe toxicity [4] limit its therapeutic potential. Consequently, a synthetic water-soluble prodrug, minnelide, is being studied clinically instead. [3] [5]
Contents
Triptolide is a component of ContraPest, a contraceptive pest control liquid used to reduce rat populations in the United States.
