 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
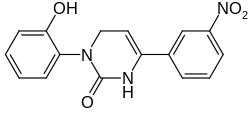
| Preferred IUPAC name 3-(2-Hydroxyphenyl)-6-(3-nitrophenyl)-3,4-dihydropyrimidin-2(1H)-one | |
| Other names 1-(2-Hydroxyphenyl)-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-3,6-dihydropyrimidin-2-one AG-3-5 | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.164.593 |
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C16H13N3O4 | |
| Molar mass | 311.29 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Icilin (AG-3-5) is a synthetic super-agonist of the transient receptor potential M8 (TRPM8) ion channel. Although structurally not related to menthol, it produces an extreme sensation of cold, both in humans and animals. It is almost 200 times more potent than menthol, and 2.5 times more efficacious. [1] Despite their similar effects, icilin activates the TRPM8 receptor in a different way than menthol does. [2] Icilin has been shown to be effective in the treatment of pruritus in an experimental model of itch. [3] It is now used as a research tool for the study of TRP channels, although despite its high potency it is less selective for TRPM8 over other related ion channels than are other compounds such as WS-12.