In chemistry, halogenation is a chemical reaction which introduces of one or more halogens into a chemical compound. Halide-containing compounds are pervasive, making this type of transformation important, e.g. in the production of polymers, drugs. This kind of conversion is in fact so common that a comprehensive overview is challenging. This article mainly deals with halogenation using elemental halogens. Halides are also commonly introduced using salts of the halides and halogen acids. Many specialized reagents exist for and introducing halogens into diverse substrates, e.g. thionyl chloride.

Titanium tetrachloride is the inorganic compound with the formula TiCl4. It is an important intermediate in the production of titanium metal and the pigment titanium dioxide. TiCl4 is a volatile liquid. Upon contact with humid air, it forms thick clouds of titanium dioxide and hydrochloric acid, a reaction that was formerly exploited for use in smoke machines. It is sometimes referred to as "tickle" or "tickle 4", as a phonetic representation of the symbols of its molecular formula.
Boron trifluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula BF3. This pungent, colourless, and toxic gas forms white fumes in moist air. It is a useful Lewis acid and a versatile building block for other boron compounds.

Trimethylaluminium is one of the simplest examples of an organoaluminium compound. Despite its name it has the formula Al2(CH3)6 (abbreviated as Al2Me6 or TMA), as it exists as a dimer. This colorless liquid is pyrophoric. It is an industrially important compound, closely related to triethylaluminium.

Triphenylphosphine (IUPAC name: triphenylphosphane) is a common organophosphorus compound with the formula P(C6H5)3 and often abbreviated to PPh3 or Ph3P. It is versatile compound that is widely used as a reagent in organic synthesis and as a ligand for transition metal complexes, including ones that serve as catalysts in organometallic chemistry. PPh3 exists as relatively air stable, colorless crystals at room temperature. It dissolves in non-polar organic solvents such as benzene and diethyl ether.
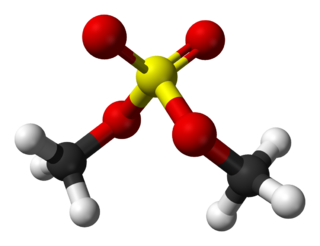
Dimethyl sulfate (DMS) is a chemical compound with formula (CH3O)2SO2. As the diester of methanol and sulfuric acid, its formula is often written as (CH3)2SO4 or Me2SO4, where CH3 or Me is methyl. Me2SO4 is mainly used as a methylating agent in organic synthesis.

Cadmium selenide is an inorganic compound with the formula CdSe. It is a black to red-black solid that is classified as a II-VI semiconductor of the n-type. It is a pigment, but applications are declining because of environmental concerns.

Iron pentacarbonyl, also known as iron carbonyl, is the compound with formula Fe(CO)5. Under standard conditions Fe(CO)5 is a free-flowing, straw-colored liquid with a pungent odour. Older samples appear darker. This compound is a common precursor to diverse iron compounds, including many that are useful in small scale organic synthesis.
Boron trichloride is the inorganic compound with the formula BCl3. This colorless gas is a reagent in organic synthesis. It is highly reactive towards water.
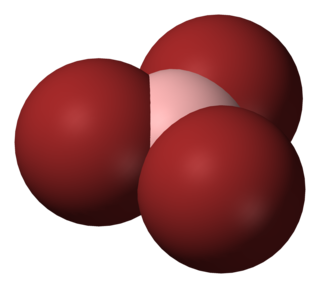
Boron tribromide, BBr3, is a colorless, fuming liquid compound containing boron and bromine. Commercial samples usually are amber to red/brown, due to weak bromine contamination. It is decomposed by water and alcohols.

Vanadium oxytrichloride is the inorganic compound with the formula VOCl3. This yellow distillable liquid hydrolyzes readily in air. It is an oxidizing agent. It is used as a reagent in organic synthesis. Samples often appear red or orange owing to an impurity of vanadium tetrachloride.
Vanadium tetrachloride is the inorganic compound with the formula VCl4. This reddish-brown liquid serves as a useful reagent for the preparation of other vanadium compounds.
Indium(III) sulfide (Indium sesquisulfide, Indium sulfide (2:3), Indium (3+) sulfide) is the inorganic compound with the formula In2S3.

Organocadmium chemistry describes the physical properties, synthesis, reactions, and use of organocadmium compounds, which are organometallic compounds containing a carbon to cadmium chemical bond. Cadmium shares group 12 with zinc and mercury and their corresponding chemistries have much in common. The synthetic utility of organocadmium compounds is limited.

Copper(I) bromide is the chemical compound with the formula CuBr. This diamagnetic solid adopts a polymeric structure akin to that for zinc sulfide. The compound is widely used in the synthesis of organic compounds and as a lasing medium in copper bromide lasers.
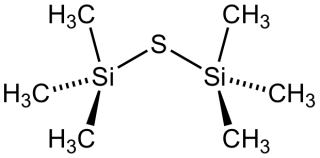
Bis(trimethylsilyl) sulfide is the chemical compound with the formula ((CH3)3Si)2S. Often abbreviated (tms)2S, this colourless, vile-smelling liquid is a useful aprotic source of "S2−" in chemical synthesis.
Organoarsenic chemistry is the chemistry of compounds containing a chemical bond between arsenic and carbon. A few organoarsenic compounds, also called "organoarsenicals," are produced industrially with uses as insecticides, herbicides, and fungicides. In general these applications are declining in step with growing concerns about their impact on the environment and human health. The parent compounds are arsane and arsenic acid. Despite their toxicity, organoarsenic biomolecules are well known.
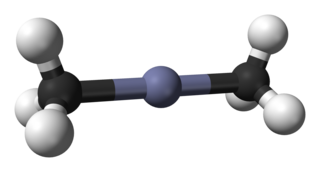
Dimethylzinc, also known as zinc methyl, DMZ, or DMZn, is an organozinc compound with the chemical formula Zn(CH3)2. It belongs to the large series of similar compounds such as diethylzinc.

Nickel(II) bromide is the name for the inorganic compounds with the chemical formula NiBr2(H2O)x. The value of x can be 0 for the anhydrous material, as well as 2, 3, or 6 for the three known hydrate forms. The anhydrous material is a yellow-brown solid which dissolves in water to give blue-green hexahydrate (see picture).

Trimethylborane (TMB) is a toxic, pyrophoric gas with the formula B(CH3)3 (which can also be written as Me3B, with Me representing methyl).


















