
Pesticides are substances that are meant to control pests. This includes herbicide, insecticide, nematicide, molluscicide, piscicide, avicide, rodenticide, bactericide, insect repellent, animal repellent, microbicide, fungicide, and lampricide. The most common of these are herbicides which account for approximately 80% of all pesticide use. Most pesticides are intended to serve as plant protection products, which in general, protect plants from weeds, fungi, or insects. As an example, the fungus Alternaria solani is used to combat the aquatic weed Salvinia.

Pesticide resistance describes the decreased susceptibility of a pest population to a pesticide that was previously effective at controlling the pest. Pest species evolve pesticide resistance via natural selection: the most resistant specimens survive and pass on their acquired heritable changes traits to their offspring. If a pest has resistance then the pesticide lacks efficacy – efficacy and resistance are inversely related.

Warfarin, sold under the brand name Coumadin among others, is a medication that is used as an anticoagulant. It is commonly used to prevent blood clots such as deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism, and to prevent stroke in people who have atrial fibrillation, valvular heart disease, or artificial heart valves. Less commonly, it is used following ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction and orthopedic surgery. It is generally taken by mouth, but may also be used intravenously.

Rodenticides are chemicals made and sold for the purpose of killing rodents. While commonly referred to as "rat poison", rodenticides are also used to kill mice, squirrels, woodchucks, chipmunks, porcupines, nutria, beavers, and voles. Despite the crucial roles that rodents play in nature, there are times when they need to be controlled.
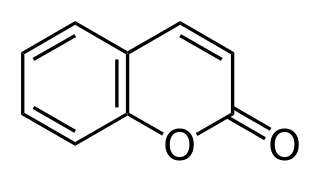
Coumarin or 2H-chromen-2-one is an aromatic organic chemical compound with formula C9H6O2. Its molecule can be described as a benzene molecule with two adjacent hydrogen atoms replaced by a lactone-like chain −(CH)=(CH)−(C=O)−O−, forming a second six-membered heterocycle that shares two carbons with the benzene ring. It can be placed in the benzopyrone chemical class and considered as a lactone.

An agrochemical or agrichemical, a contraction of agricultural chemical, is a chemical product used in industrial agriculture. Agrichemical refers to biocides and synthetic fertilizers. It may also include hormones and other chemical growth agents.

The Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA) is a United States federal law that set up the basic U.S. system of pesticide regulation to protect applicators, consumers, and the environment. It is administered and regulated by the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the appropriate environmental agencies of the respective states. FIFRA has undergone several important amendments since its inception. A significant revision in 1972 by the Federal Environmental Pesticide Control Act (FEPCA) and several others have expanded EPA's present authority to oversee the sales and use of pesticides with emphasis on the preservation of human health and protection of the environment by "(1) strengthening the registration process by shifting the burden of proof to the chemical manufacturer, (2) enforcing compliance against banned and unregistered products, and (3) promulgating the regulatory framework missing from the original law".

Bromethalin is a neurotoxic rodenticide that damages the central nervous system.

Cytochrome P450 2A6 is a member of the cytochrome P450 mixed-function oxidase system, which is involved in the metabolism of xenobiotics in the body. CYP2A6 is the primary enzyme responsible for the oxidation of nicotine and cotinine. It is also involved in the metabolism of several pharmaceuticals, carcinogens, and a number of coumarin-type alkaloids. CYP2A6 is the only enzyme in the human body that appreciably catalyzes the 7-hydroxylation of coumarin, such that the formation of the product of this reaction, 7-hydroxycoumarin, is used as a probe for CYP2A6 activity.

Aluminium phosphide is a highly toxic inorganic compound with the chemical formula AlP, used as a wide band gap semiconductor and a fumigant. This colorless solid is generally sold as a grey-green-yellow powder due to the presence of impurities arising from hydrolysis and oxidation.

Zinc phosphide (Zn3P2) is an inorganic chemical compound. It is a grey solid, although commercial samples are often dark or even black. It is used as a rodenticide. Zn3P2 is a II-V semiconductor with a direct band gap of 1.5 eV and may have applications in photovoltaic cells. A second compound exists in the zinc-phosphorus system, zinc diphosphide (ZnP2).

4-Hydroxycoumarins belong to a class of vitamin K antagonist (VKA) anticoagulant drug molecules derived from coumarin by adding a hydroxy group at the 4 position to obtain 4-hydroxycoumarin, then adding a large aromatic substituent at the 3-position. The large 3-position substituent is required for anticoagulant activity.

Brodifacoum is a highly lethal 4-hydroxycoumarin vitamin K antagonist anticoagulant poison. In recent years, it has become one of the world's most widely used pesticides. It is typically used as a rodenticide, but is also used to control larger pests such as possum.

Diphenadione is a vitamin K antagonist that has anticoagulant effects and is used as a rodenticide against rats, mice, voles, ground squirrels and other rodents. The chemical compound is an anti-coagulant with active half-life longer than warfarin and other synthetic 1,3-indandione anticoagulants.

Bromadiolone is a potent anticoagulant rodenticide. It is a second-generation 4-hydroxycoumarin derivative and vitamin K antagonist, often called a "super-warfarin" for its added potency and tendency to accumulate in the liver of the poisoned organism. When first introduced to the UK market in 1980, it was effective against rodent populations that had become resistant to first generation anticoagulants.

Vitamin K antagonists (VKA) are a group of substances that reduce blood clotting by reducing the action of vitamin K. The term "vitamin K antagonist" is technically a misnomer, as the drugs do not directly antagonise the action of vitamin K in the pharmacological sense, but rather the recycling of vitamin K.

1,3-Difluoro-2-propanol is a metabolic poison which disrupts the citric acid cycle and is used as a rodenticide, similar to sodium fluoroacetate. It is the main ingredient in the rodenticide product Gliftor which was widely used in the former USSR and still approved in China.
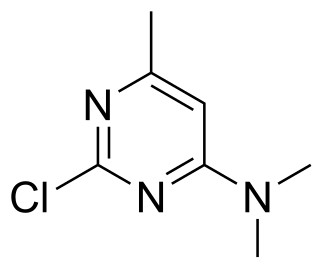
Crimidine is a convulsant poison used as a rodenticide. Crimidine was originally known by its product name, Castrix. It was originally produced in the 1940s by the conglomerate, IG Farben. It is classified as an extremely hazardous substance in the United States as defined in Section 302 of the U.S. Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act, and is subject to strict reporting requirements by facilities which produce, store, or use it in significant quantities. It is also no longer used in the United States as a rodenticide, but is still used to this day in other countries.

4-Hydroxycoumarin is a coumarin derivative with a hydroxy group at the 4-position.
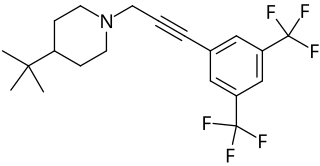
Flupropadine is a rodenticide. Originally made by May and Baker and tested on farms in the United Kingdom it was withdrawn from use by 1994. Flupropadine has a delayed action, and so rodents can have multiple feeds from the bait before being killed.



















