| |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Valmid, Valamin |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Elimination half-life | 2.5 hours |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.355 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C9H13NO2 |
| Molar mass | 167.208 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
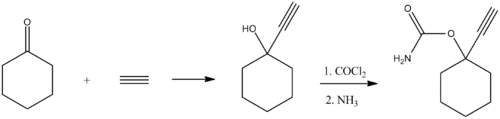
Ethinamate, marketed as Valmid in the United States and Valamin in Australia, [2] is a central nervous system depressant of the carbamate drug class. It was formerly prescribed as a hypnotic for the short-term treatment of insomnia. The drug has a rapid onset of action, a short elimination half-life of around 2.5 hours, and a correspondingly brief duration of effect. Prolonged use leads to drug tolerance, drug dependence, and diminished efficacy after seven days of continuous use. [3]