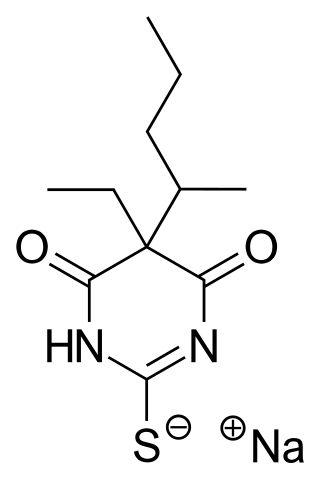
Sodium thiopental, also known as Sodium Pentothal, thiopental, thiopentone, or Trapanal, is a rapid-onset short-acting barbiturate general anesthetic. It is the thiobarbiturate analog of pentobarbital, and an analog of thiobarbital. Sodium thiopental was a core medicine in the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines, but was supplanted by propofol. Despite this, thiopental is listed as an acceptable alternative to propofol, depending on local availability and cost of these agents. It was previously the first of three drugs administered during most lethal injections in the United States, but the US manufacturer Hospira stopped manufacturing the drug in 2011 and the European Union banned the export of the drug for this purpose. Although thiopental abuse carries a dependency risk, its recreational use is rare.

Cyclopropane is the cycloalkane with the molecular formula (CH2)3, consisting of three methylene groups (CH2) linked to each other to form a ring. The small size of the ring creates substantial ring strain in the structure. Cyclopropane itself is mainly of theoretical interest but many of its derivatives - cyclopropanes - are of commercial or biological significance.
Sulfur dyes are the most commonly used dyes manufactured for cotton in terms of volume. They are inexpensive, generally have good wash-fastness, and are easy to apply. Sulfur dyes are predominantly black, brown, and dark blue. Red sulfur dyes are unknown, although a pink or lighter scarlet color is available.

An anesthetic or anaesthetic is a drug used to induce anesthesia — in other words, to result in a temporary loss of sensation or awareness. They may be divided into two broad classes: general anesthetics, which result in a reversible loss of consciousness, and local anesthetics, which cause a reversible loss of sensation for a limited region of the body without necessarily affecting consciousness.
Pentobarbital (US) or pentobarbitone is a short-acting barbiturate typically used as a sedative, a preanesthetic, and to control convulsions in emergencies. It can also be used for short-term treatment of insomnia but has been largely replaced by the benzodiazepine family of drugs.

Monocalcium phosphate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ca(H2PO4)2 ("AMCP" or "CMP-A" for anhydrous monocalcium phosphate). It is commonly found as the monohydrate ("MCP" or "MCP-M"), Ca(H2PO4)2·H2O. Both salts are colourless solids. They are used mainly as superphosphate fertilizers and are also popular leavening agents.
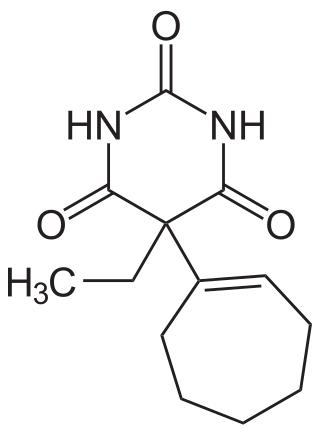
Heptabarb, also known as heptabarbitone (BAN) or heptabarbital, is a sedative and hypnotic drug of the barbiturate family. It was used in Europe for the treatment of insomnia from the 1950s onwards, but has since been discontinued.

Sodium hydrosulfide is the chemical compound with the formula NaSH. This compound is the product of the half-neutralization of hydrogen sulfide with sodium hydroxide (NaOH). NaSH and sodium sulfide are used industrially, often for similar purposes. Solid NaSH is colorless. The solid has an odor of H2S owing to hydrolysis by atmospheric moisture. In contrast with sodium sulfide, which is insoluble in organic solvents, NaSH, being a 1:1 electrolyte, is more soluble.

Molten salt is salt which is solid at standard temperature and pressure but liquified due to elevated temperature. A salt that is liquid even at standard temperature and pressure is usually called a room-temperature ionic liquid, and molten salts are technically a class of ionic liquids.
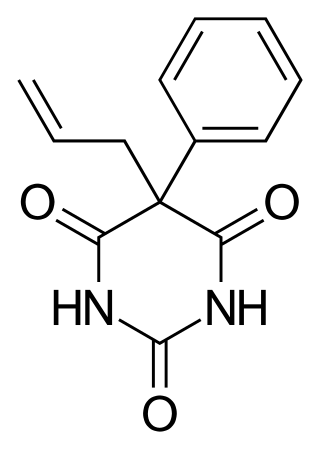
Alphenal, also known as 5-allyl-5-phenylbarbituric acid, is a barbiturate derivative developed in the 1920s. It has primarily anticonvulsant properties, and was used occasionally for the treatment of epilepsy or convulsions, although not as commonly, as better known barbiturates such as phenobarbital.

Cyclopentobarbital sodium is a barbiturate derivative invented in the 1940s. It has sedative and anticonvulsant properties, and was used primarily as an anaesthetic in veterinary medicine. Cyclopal is considered similar in effects to phenobarbital but lasts almost three times as long, and is considered a long-acting barbiturate with a fairly slow onset of action.
Isopropyl alcohol is a colorless, flammable organic compound with a pungent alcoholic odor. As an isopropyl group linked to a hydroxyl group it is the simplest example of a secondary alcohol, where the alcohol carbon atom is attached to two other carbon atoms. It is a structural isomer of propan-1-ol and ethyl methyl ether. They all have the formula C3H8O.

Barbiturates are a class of depressant drugs that are chemically derived from barbituric acid. They are effective when used medically as anxiolytics, hypnotics, and anticonvulsants, but have physical and psychological addiction potential as well as overdose potential among other possible adverse effects. They have been used recreationally for their anti-anxiety and sedative effects, and are thus controlled in most countries due to the risks associated with such use.
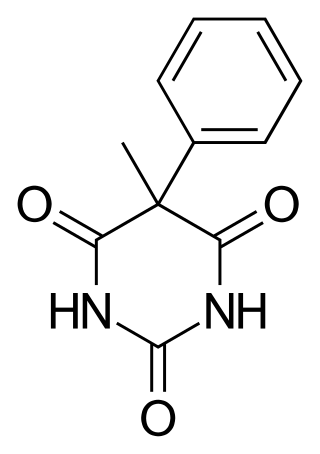
Heptobarbital (Rutonal), also known as phenylmethylbarbituric acid is a barbiturate derivative. It has often been confused with methylphenobarbital because both drugs contain a methylphenyl moiety and are overall very similar in structure.

Thiotetrabarbital is a drug which is a short-acting barbiturate derivative that is used as an anesthetic. It has been used in veterinary medicine.
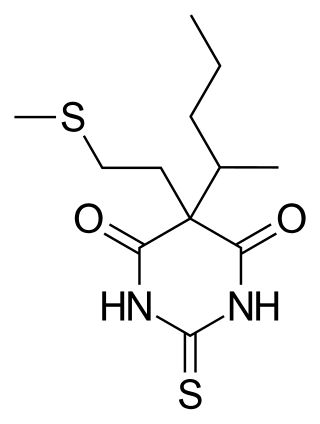
Methitural, or methitural sodium, also known as methioturiate, is a barbiturate derivative which was marketed in the 1950s in Europe as an ultra-short-acting intravenous anesthetic.

Propylbarbital, also known as 5,5-dipropylbarbituric acid, is a barbiturate derivative used as a hypnotic drug.
Sodium tetrasulfide is an inorganic compound with the formula Na2S4. It is a yellow-orange solid that dissolves via hydrolysis in water. It is a precursor to some specialty polymers and intermediates in prototypes of the sodium-sulfur battery.
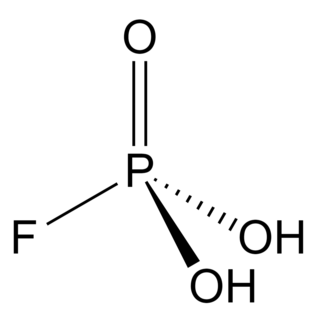
Fluorophosphoric acid is the inorganic compound with the formula H2PO3F. It is a colorless viscous liquid that solidifies to a rigid glass upon cooling at −78 °C (−108 °F).















