 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
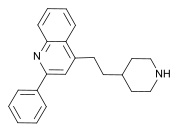
| Formula | C22H24N2 |
| Molar mass | 316.448 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Pipequaline (INN; development code PK-8165) is an anxiolytic drug that was never marketed. [1] It possesses a novel chemical structure that is not closely related to other drugs of this type. The drug has a similar pharmacological profile to the benzodiazepine family of drugs, but with mainly anxiolytic properties and very little sedative, amnestic or anticonvulsant effects, and so is classified as a nonbenzodiazepine anxiolytic. [2] [3] [4]
Pipequaline acts as a non-selective GABAA receptor partial agonist. [5] [6] [7] While its profile of anxiolytic effects without sedation would appear to have potential medical applications, pipequaline has never been developed for medical use and is currently only used in scientific research.