Related Research Articles

Hepatitis is inflammation of the liver tissue. Some people or animals with hepatitis have no symptoms, whereas others develop yellow discoloration of the skin and whites of the eyes (jaundice), poor appetite, vomiting, tiredness, abdominal pain, and diarrhea. Hepatitis is acute if it resolves within six months, and chronic if it lasts longer than six months. Acute hepatitis can resolve on its own, progress to chronic hepatitis, or (rarely) result in acute liver failure. Chronic hepatitis may progress to scarring of the liver (cirrhosis), liver failure, and liver cancer.

Hepatitis C is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV) that primarily affects the liver; it is a type of viral hepatitis. During the initial infection period, people often have mild or no symptoms. Early symptoms can include fever, dark urine, abdominal pain, and yellow tinged skin. The virus persists in the liver, becoming chronic, in about 70% of those initially infected. Early on, chronic infection typically has no symptoms. Over many years however, it often leads to liver disease and occasionally cirrhosis. In some cases, those with cirrhosis will develop serious complications such as liver failure, liver cancer, or dilated blood vessels in the esophagus and stomach.
Hepatitis D is a type of viral hepatitis caused by the hepatitis delta virus (HDV). HDV is one of five known hepatitis viruses: A, B, C, D, and E. HDV is considered to be a satellite because it can propagate only in the presence of the hepatitis B virus (HBV). Transmission of HDV can occur either via simultaneous infection with HBV (coinfection) or superimposed on chronic hepatitis B or hepatitis B carrier state (superinfection).

Hepatotoxicity implies chemical-driven liver damage. Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is a cause of acute and chronic liver disease caused specifically by medications and the most common reason for a drug to be withdrawn from the market after approval.
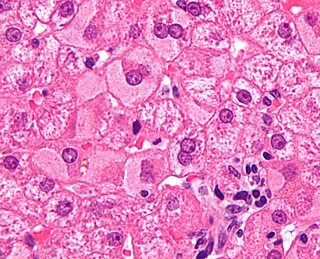
Viral hepatitis is liver inflammation due to a viral infection. It may present in acute form as a recent infection with relatively rapid onset, or in chronic form, typically progressing from a long-lasting asymptomatic condition up to a decompensated hepatic disease and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).

Alcoholic hepatitis is hepatitis due to excessive intake of alcohol. Patients typically have a history of at least 10 years of heavy alcohol intake, typically 8–10 drinks per day. It is usually found in association with fatty liver, an early stage of alcoholic liver disease, and may contribute to the progression of fibrosis, leading to cirrhosis. Symptoms may present acutely after a large amount of alcoholic intake in a short time period, or after years of excess alcohol intake. Signs and symptoms of alcoholic hepatitis include jaundice, ascites, fatigue and hepatic encephalopathy. Mild cases are self-limiting, but severe cases have a high risk of death. Severity in alcoholic hepatitis is determined several clinical prediction models such as the Maddrey's Discriminant Function and the MELD score.

Autoimmune hepatitis, formerly known as lupoid hepatitis, plasma cell hepatitis, or autoimmune chronic active hepatitis, is a chronic, autoimmune disease of the liver that occurs when the body's immune system attacks liver cells, causing the liver to be inflamed. Common initial symptoms may include fatigue, nausea, muscle aches, or weight loss or signs of acute liver inflammation including fever, jaundice, and right upper quadrant abdominal pain. Individuals with autoimmune hepatitis often have no initial symptoms and the disease may be detected by abnormal liver function tests and increased protein levels during routine bloodwork or the observation of an abnormal-looking liver during abdominal surgery.

Liver disease, or hepatic disease, is any of many diseases of the liver. If long-lasting it is termed chronic liver disease. Although the diseases differ in detail, liver diseases often have features in common.

Acute liver failure is the appearance of severe complications rapidly after the first signs of liver disease, and indicates that the liver has sustained severe damage. The complications are hepatic encephalopathy and impaired protein synthesis. The 1993 classification defines hyperacute as within 1 week, acute as 8–28 days, and subacute as 4–12 weeks; both the speed with which the disease develops and the underlying cause strongly affect outcomes.

Phenobarbital, also known as phenobarbitone or phenobarb, sold under the brand name Luminal among others, is a medication of the barbiturate type. It is recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO) for the treatment of certain types of epilepsy in developing countries. In the developed world, it is commonly used to treat seizures in young children, while other medications are generally used in older children and adults. It is also used for veterinary purposes. It may be administered by slow intravenous infusion, intramuscularly (IM), or orally. Subcutaneous administration is not recommended. The IV or IM may be used to treat status epilepticus if other drugs fail to achieve satisfactory results. Phenobarbital is occasionally used to treat insomnia, anxiety, and benzodiazepine withdrawal, and prior to surgery as an anxiolytic and to induce sedation. It usually begins working within five minutes when used intravenously and half an hour when administered orally. Its effects last for between four hours and two days.

Flucloxacillin, also known as floxacillin, is an antibiotic used to treat skin infections, external ear infections, infections of leg ulcers, diabetic foot infections, and infection of bone. It may be used together with other medications to treat pneumonia, and endocarditis. It may also be used prior to surgery to prevent Staphylococcus infections. It is not effective against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). It is taken by mouth or given by injection into a vein or muscle.
Acute fatty liver of pregnancy is a rare life-threatening complication of pregnancy that occurs in the third trimester or the immediate period after delivery. It is thought to be caused by a disordered metabolism of fatty acids by mitochondria in the fetus, caused by long-chain 3-hydroxyacyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase deficiency. This leads to decreased metabolism of long chain fatty acids by the feto-placental unit, causing subsequent rise in hepatotoxic fatty acids in maternal plasma. The condition was previously thought to be universally fatal, but aggressive treatment by stabilizing the mother with intravenous fluids and blood products in anticipation of early delivery has improved prognosis.
The King's College Criteria or the King's College Hospital criteria were devised in 1989 to determine if there were any early indices of poor prognosis in patients with acute liver failure. Acute liver failure is defined as the onset of encephalopathy or coagulopathy within 26 weeks of a patient diagnosed with liver disease. Patients with hepatitis B acquired at birth, Wilson's disease and autoimmune hepatitis are included if their disease was identified within the past 26 weeks. These patients are very ill, and have a very high risk of dying of their illness without adequate treatment which may include liver transplantation. It is important that physicians find ways of identifying patients with acute liver failure early in their course who will do poorly, and may require liver transplantation. The King's College Criteria have consistently shown excellent operating characteristics for determining prognosis in these patients. As liver transplantation becomes a more accessible option for patients with acute liver failure, the King's College Criteria serve a role in determining which patients may require transplantation.
Hy's law is a rule of thumb that a patient is at high risk of a fatal drug-induced liver injury if given a medication that causes hepatocellular injury with jaundice. The law is based on observations by Hy Zimmerman, a major scholar of drug-induced liver injury. Some have suggested the principle be called a hypothesis or observation.
In medicine, the presence of elevated transaminases, commonly the transaminases alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate transaminase (AST), may be an indicator of liver dysfunction. Other terms include transaminasemia, and elevatedliver enzymes. Normal ranges for both ALT and AST vary by gender, age, and geography and are roughly 8-40 U/L. Mild transaminesemia refers to levels up to 250 U/L. Drug-induced increases such as that found with the use of anti-tuberculosis agents such as isoniazid are limited typically to below 100 U/L for either ALT or AST. Muscle sources of the enzymes, such as intense exercise, are unrelated to liver function and can markedly increase AST and ALT. Cirrhosis of the liver or fulminant liver failure secondary to hepatitis commonly reach values for both ALT and AST in the >1000 U/L range; however, many people with liver disease have normal transaminases. Elevated transaminases that persist less than six months are termed "acute" in nature, and those values that persist for six months or more are termed "chronic" in nature.

Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the Hepatitis B virus (HBV) that affects the liver; it is a type of viral hepatitis. It can cause both acute and chronic infection.

Cirrhosis, also known as liver cirrhosis or hepatic cirrhosis, and end-stage liver disease, is a condition of the liver in which the normal functioning tissue, or parenchyma, is replaced with scar tissue (fibrosis) and regenerative nodules as a result of chronic liver disease. Damage to the liver leads to repair of liver tissue and subsequent formation of scar tissue. Over time, scar tissue and nodules of regenerating hepatocytes can replace the parenchyma, causing increased resistance to blood flow in the liver's capillaries—the hepatic sinusoids—and consequently portal hypertension, as well as impairment in other aspects of liver function. The disease typically develops slowly over months or years.
The AST/ALT ratio or De Ritis ratio is the ratio between the concentrations of two enzymes, aspartate transaminase (AST) and alanine transaminase, aka alanine aminotransferase (ALT), in the blood of a human or animal. It is used as one of several liver function tests, and measured with a blood test. It is sometimes useful in medical diagnosis for elevated transaminases to differentiate between causes of liver damage, or hepatotoxicity.
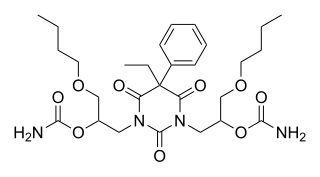
Difebarbamate (INN) is a tranquilizer of the barbiturate and carbamate families which is used in Europe as a component of a combination drug formulation referred to as tetrabamate.
A liver support system or diachysis is a type of therapeutic device to assist in performing the functions of the liver. Such systems focus either on removing the accumulating toxins, or providing additional replacement of the metabolic functions of the liver through the inclusion of hepatocytes to the device. A diachysis machine is used for acute care i.e. emergency care, as opposed to a dialysis machine which are typically used over the longer term. These systems are being trialed to help people with acute liver failure (ALF) or acute-on-chronic liver failure.
References
- ↑ Index nominum 2000: international drug directory. Taylor & Francis US. 2000. pp. 333 & 427. ISBN 978-3-88763-075-1 . Retrieved 26 November 2011.
- ↑ Chitturi S, Farrell GC (19 October 2011). "Drug-Induced Liver Disease". In Schiff ER, Maddrey WC, Sorrell MF (eds.). Schiff's Diseases of the Liver. John Wiley and Sons. pp. 703–783. doi:10.1002/9781119950509.ch27. ISBN 978-1-119-95048-6 . Retrieved 26 November 2011.
- 1 2 Binder D, Jost R, Flury R, Salomon F (May 1995). "[Acute liver failure following tetrabamate]". Schweizerische Medizinische Wochenschrift (in German). 125 (19): 965–969. PMID 7761807.
- 1 2 Consolidated list of products whose consumption and/or sale have been banned, withdrawn, severely restricted or not approved by governments. United Nations Publications. 2003. p. 259. ISBN 978-92-1-130230-1 . Retrieved 26 November 2011.[ permanent dead link ]
- ↑ Horsmans Y, Lannes D, Pessayre D, Larrey D (December 1994). "Possible association between poor metabolism of mephenytoin and hepatotoxicity caused by Atrium, a fixed combination preparation containing phenobarbital, febarbamate and difebarbamate". Journal of Hepatology. 21 (6): 1075–1079. doi:10.1016/s0168-8278(05)80620-8. PMID 7699230.
- 1 2 "Severe hepatitis due to Atrium". Prescrire International. 10 (55): 150. October 2001. PMID 11824432.