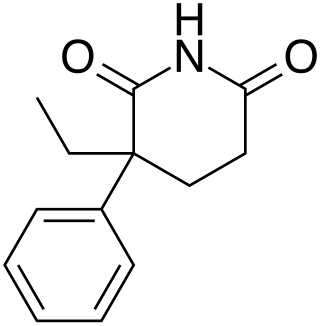
Glutethimide is a hypnotic sedative that was introduced by Ciba in 1954 as a safe alternative to barbiturates to treat insomnia. Before long, however, it had become clear that glutethimide was just as likely to cause addiction and caused similar withdrawal symptoms. Doriden was the brand-name version. Current production levels in the United States point to its use only in small-scale research. Manufacturing of the drug was discontinued in the US in 1993 and discontinued in several eastern European countries in 2006.
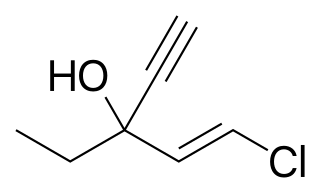
Ethchlorvynol is a GABA-ergic sedative and hypnotic/soporific medication first developed by Pfizer in the 1950s. In the United States it was sold by Abbott Laboratories under the trade name Placidyl. Placidyl was available in 200 mg, 500 mg, and 750 mg strength gel filled capsules. While the 500 mg and 750 mg strength capsules were for use in reducing sleep latency, the 200 mg strength capsules were intended to be used to re-induce sleep in case of early awakening. Abbott discontinued production in 1999, due to it being replaced by the benzodiazepine family and its widespread abuse, after which Placidyl was available for about a year in the United States. Although, theoretically, ethchlorvynol could be manufactured for sale in the United States by another pharmaceutical company, no pharmaceutical company has chosen to do so. Individuals with a valid prescription for the substance may legally transport a reasonable amount of ethclorvynol with them into the United States.

Piperonal, also known as heliotropin, is an organic compound which is commonly found in fragrances and flavors. The molecule is structurally related to other aromatic aldehydes such as benzaldehyde and vanillin.
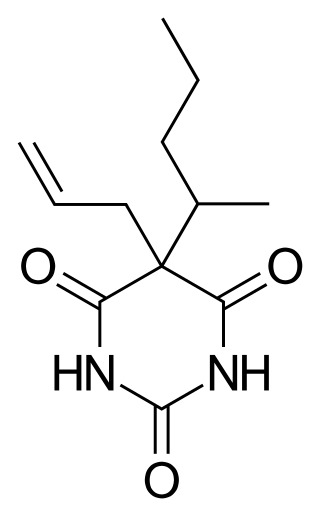
Secobarbital is a short-acting barbiturate derivative drug that was patented in 1934 in the United States. It possesses anaesthetic, anticonvulsant, anxiolytic, sedative, and hypnotic properties. In the United Kingdom, it was known as quinalbarbitone. Secobarbital is considered to be an obsolete sedative-hypnotic, and as a result, it has largely been replaced by the benzodiazepine family. Seconal was widely abused, known on the street as "red devils" or "reds". Among the barbiturates, secobarbital carries a particularly high risk of abuse and addiction, largely responsible for its falling out of use.

Emylcamate is an anxiolytic and muscle relaxant. It was patented in the US in 1961 and advertised for the treatment of anxiety and tension. It was claimed to be superior to meprobamate, which would eventually replace emylcamate.

Phenprobamate is a centrally acting skeletal muscle relaxant, with additional sedative and anticonvulsant effects. Overdose is similar to barbiturates. Its mechanism of action is probably similar to meprobamate. Phenprobamate has been used in humans as an anxiolytic, and is still sometimes used in general anesthesia and for treating muscle cramps and spasticity. Phenprobamate is still used in some European countries, but it has generally been replaced by newer drugs. Phenprobamate is metabolized by oxidative degradation of the carbamate group and ortho-hydroxylation of the benzene ring, and is eliminated in urine by the kidneys.
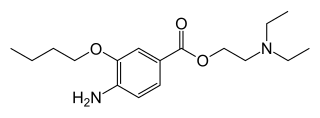
Oxybuprocaine (INN), also known as benoxinate or BNX, is an ester-type local anesthetic, which is used especially in ophthalmology and otolaryngology. Oxybuprocaine is sold by Novartis under the brand names Novesine or Novesin.
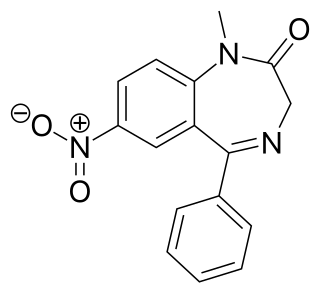
Nimetazepam is an intermediate-acting hypnotic drug which is a benzodiazepine derivative. It was first synthesized by a team at Hoffmann-La Roche in 1964. It possesses powerful hypnotic, anxiolytic, sedative, and skeletal muscle relaxant properties. Nimetazepam is also a particularly potent anticonvulsant. It is marketed in 5 mg tablets known as Erimin, which is the brand name manufactured and marketed by the large Japanese corporation Sumitomo. Japan is the sole manufacturer of nimetazepam in the world. Outside of Japan, Erimin is available in much of East and Southeast Asia and was widely prescribed for the short-term treatment of severe insomnia in patients who have difficulty falling asleep or maintaining sleep. Sumitomo has ceased manufacturing Erimin since November 2015. It is still available as a generic drug or as Lavol.

Cloxazolam is a benzodiazepine derivative that has anxiolytic, sedative, and anticonvulsant properties. It is not widely used; as of August 2018 it was marketed in Belgium, Luxembourg, Portugal, Brazil, and Japan. In 2019, it has been retired from the Belgian market.

Vinylbital, also known as butylvinal, is a sedative hypnotic drug which is a barbiturate derivative. It was developed by Aktiebolaget Pharmacia in the 1950s.

Ethinamate is a short-acting carbamate-derivative sedative-hypnotic medication used to treat insomnia. Regular use leads to drug tolerance, and it is usually not effective for more than 7 days. Prolonged use can lead to dependence.

Methyprylon, or Noludar, is a sedative of the piperidinedione derivative family first developed by Hoffmann-La Roche. This medicine was used for treating insomnia, but is now rarely used as it has been replaced by newer drugs with fewer side effects, such as benzodiazepines.

Promazine, is used as a short-term add-on treatment for psychomotor agitation. Its approved uses in people is limited, but is used as a tranquilizer in veterinary medicine. It has weak antipsychotic effects but is generally not used to treat psychoses.

Dimethylthiambutene (N,N-Dimethyl-1-methyl-3,3-di-2-thienylallylamine, DMTB, trade names Ohton, Aminobutene, Dimethibutin, Kobaton, Takaton, Dimethibutin) is an opioid analgesic drug, most often used in veterinary medicine in Japan and to a lesser extent in other countries in the region and around the world. It is the most prominent and widely used of the thiambutenes, a series of open-chain opioids structurally related to methadone which are also called the thienyl derivative opioids which also includes diethylthiambutene and ethylmethylthiambutene, as well as the non-opioid cough suppressant tipepidine.

Methylpentynol is a tertiary pentynol with hypnotic/sedative and anticonvulsant effects and an exceptionally low therapeutic index. It was discovered by Bayer in 1913 and was used shortly thereafter for the treatment of insomnia, but its use was quickly phased out in response to newer drugs with far more favorable safety profiles.

Chloralodol (Chlorhexadol) is a hypnotic/sedative. It is a Schedule III drug in the USA; however, it is not currently marketed in the United States so it is no longer prescribed.
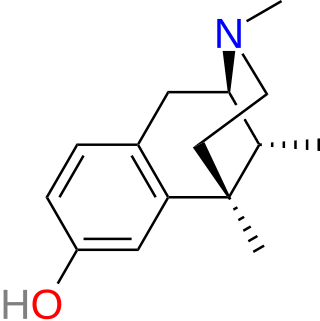
Metazocine is an opioid analgesic related to pentazocine. While metazocine has significant analgesic effects, mediated through a mixed agonist–antagonist action at the mu opioid receptor, its clinical use is limited by dysphoric and hallucinogenic effects which are most likely caused by activity at kappa opioid receptors and/or sigma receptors.

Hydroxydione, as hydroxydione sodium succinate, also known as 21-Hydroxy-5β-pregnane-3,20-dione, is a neuroactive steroid which was formerly used as a general anesthetic, but was discontinued due to incidence of thrombophlebitis in patients. It was introduced in 1957, and was the first neuroactive steroid general anesthetic to be introduced for clinical use, an event which was shortly preceded by the observation in 1954 of the sedative properties of progesterone in mice.

Phenaglycodol is a drug described as a tranquilizer or sedative which has anxiolytic and anticonvulsant properties. It is related pharmacologically to meprobamate, though it is not a carbamate.
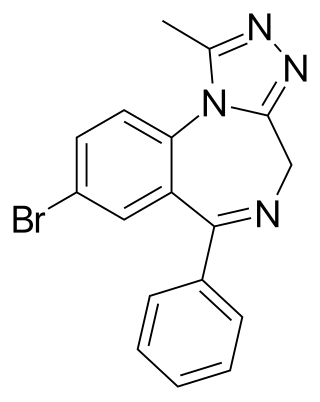
Bromazolam (XLI-268) is a triazolobenzodiazepine (TBZD) which was first synthesised in 1976, but was never marketed. It has subsequently been sold as a designer drug, first being definitively identified by the EMCDDA in Sweden in 2016. It is the bromo instead of chloro analogue of alprazolam and has similar sedative and anxiolytic effects to it and other benzodiazepines. Bromazolam is a non subtype selective agonist at the benzodiazepine site of GABAA receptors, with a binding affinity of 2.81 nM at the α1 subtype, 0.69 nM at α2 and 0.62 nM at α5. The "common" dosage range for users of bromazolam was reported to be 1–2 mg, suggesting its potency is similar to alprazolam.





















