
Inhalants are a broad range of household and industrial chemicals whose volatile vapors or pressurized gases can be concentrated and breathed in via the nose or mouth to produce intoxication, in a manner not intended by the manufacturer. They are inhaled at room temperature through volatilization or from a pressurized container, and do not include drugs that are sniffed after burning or heating.

A solvent is a substance that dissolves a solute, resulting in a solution. A solvent is usually a liquid but can also be a solid, a gas, or a supercritical fluid. Water is a solvent for polar molecules, and the most common solvent used by living things; all the ions and proteins in a cell are dissolved in water within the cell.

Petrochemicals are the chemical products obtained from petroleum by refining. Some chemical compounds made from petroleum are also obtained from other fossil fuels, such as coal or natural gas, or renewable sources such as maize, palm fruit or sugar cane.

Naphthalene is an organic compound with formula C
10H
8. It is the simplest polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon, and is a white crystalline solid with a characteristic odor that is detectable at concentrations as low as 0.08 ppm by mass. As an aromatic hydrocarbon, naphthalene's structure consists of a fused pair of benzene rings. It is the main ingredient of traditional mothballs.
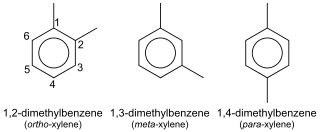
In organic chemistry, xylene or xylol are any of three organic compounds with the formula (CH3)2C6H4. They are derived from the substitution of two hydrogen atoms with methyl groups in a benzene ring; which hydrogens are substituted determines which of three structural isomers results. It is a colorless, flammable, slightly greasy liquid of great industrial value.
Mesitylene or 1,3,5-trimethylbenzene is a derivative of benzene with three methyl substituents positioned symmetrically around the ring. The other two isomeric trimethylbenzenes are 1,2,4-trimethylbenzene (pseudocumene) and 1,2,3-trimethylbenzene (hemimellitene). All three compounds have the formula C6H3(CH3)3, which is commonly abbreviated C6H3Me3. Mesitylene is a colorless liquid with sweet aromatic odor. It is a component of coal tar, which is its traditional source. It is a precursor to diverse fine chemicals. The mesityl group (Mes) is a substituent with the formula C6H2Me3 and is found in various other compounds.

Ethylbenzene is an organic compound with the formula C6H5CH2CH3. It is a highly flammable, colorless liquid with an odor similar to that of gasoline. This monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbon is important in the petrochemical industry as a reaction intermediate in the production of styrene, the precursor to polystyrene, a common plastic material. In 2012, more than 99% of ethylbenzene produced was consumed in the production of styrene.

p-Xylene (para-xylene) is an aromatic hydrocarbon. It is one of the three isomers of dimethylbenzene known collectively as xylenes. The p- stands for para-, indicating that the two methyl groups in p-xylene occupy the diametrically opposite substituent positions 1 and 4. It is in the positions of the two methyl groups, their arene substitution pattern, that it differs from the other isomers, o-xylene and m-xylene. All have the same chemical formula C6H4(CH3)2. All xylene isomers are colorless and highly flammable. The odor threshold of p-xylene is 0.62 parts per million (ppm).

Chlorobenzene (abbreviated PhCl) is an aryl chloride and the simplest of the chlorobenzenes, consisting of a benzene ring substituted with one chlorine atom. Its chemical formula is C6H5Cl. This colorless, flammable liquid is a common solvent and a widely used intermediate in the manufacture of other chemicals.

o-Xylene (ortho-xylene) is an aromatic hydrocarbon with the formula C6H4(CH3)2, with two methyl substituents bonded to adjacent carbon atoms of a benzene ring (the ortho configuration). It is a constitutional isomer of m-xylene and p-xylene, the mixture being called xylene or xylenes. o-Xylene is a colourless slightly oily flammable liquid.

m-Xylene (meta-xylene) is an aromatic hydrocarbon. It is one of the three isomers of dimethylbenzene known collectively as xylenes. The m- stands for meta-, indicating that the two methyl groups in m-xylene occupy positions 1 and 3 on a benzene ring. It is in the positions of the two methyl groups, their arene substitution pattern, that it differs from the other isomers, o-xylene and p-xylene. All have the same chemical formula C6H4(CH3)2. All xylene isomers are colorless and highly flammable.
1,2,4-Trimethylbenzene, also known as pseudocumene, is an organic compound with the chemical formula C6H3(CH3)3. Classified as an aromatic hydrocarbon, it is a flammable colorless liquid with a strong odor. It is nearly insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents. It occurs naturally in coal tar and petroleum (about 3%). It is one of the three isomers of trimethylbenzene.
Methylcyclohexane (cyclohexylmethane) is an organic compound with the molecular formula is CH3C6H11. Classified as saturated hydrocarbon, it is a colourless liquid with a faint odor.

Durene, or 1,2,4,5-tetramethylbenzene, is an organic compound with the formula C6H2(CH3)4. It is a colourless solid with a sweet odor. The compound is classified as an alkylbenzene. It is one of three isomers of tetramethylbenzene, the other two being prehnitene (1,2,3,4-tetramethylbenzene) and isodurene (1,2,3,5-tetramethylbenzene). Durene has an unusually high melting point (79.2 °C), reflecting its high molecular symmetry.

Hexachlorobutadiene, (often abbreviated as "HCBD") Cl2C=C(Cl)C(Cl)=CCl2, is a colorless liquid at room temperature that has an odor similar to that of turpentine. It is a chlorinated aliphatic diene with niche applications but is most commonly used as a solvent for other chlorine-containing compounds. Structurally, it has a 1,3-butadiene core, but fully substituted with chlorine atoms.

Benzene is an organic chemical compound with the molecular formula C6H6. The benzene molecule is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar hexagonal ring with one hydrogen atom attached to each. Because it contains only carbon and hydrogen atoms, benzene is classed as a hydrocarbon.
1,2,3-Trimethylbenzene is an organic compound with the chemical formula C6H3(CH3)3. Classified as an aromatic hydrocarbon, it is a flammable colorless liquid. It is nearly insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents.
In organic chemistry, transalkylation is a chemical reaction involving the transfer of an alkyl group from one organic compound to another. The reaction is used for the transfer of methyl and ethyl groups between benzene rings. This is of particular value in the petrochemical industry to manufacture p-xylene, styrene, and other aromatic compounds. Motivation for using transalkylation reactions is based on a difference in production and demand for benzene, toluene, and xylenes. Transalkylation can convert toluene, which is overproduced, into benzene and xylene, which are under-produced. Zeolites are often used as catalysts in transalkylation reactions.

In the petroleum refining and petrochemical industries, the initialism BTX refers to mixtures of benzene, toluene, and the three xylene isomers, all of which are aromatic hydrocarbons. The xylene isomers are distinguished by the designations ortho –, meta –, and para – as indicated in the adjacent diagram. If ethylbenzene is included, the mixture is sometimes referred to as BTEX.
Petroleum benzine is a hydrocarbon-based solvent mixture that is classified by its physical properties rather than a specific chemical composition. This complicates distinction within the long list of petroleum distillate solvent mixtures: mineral spirits, naphtha, petroleum naptha, white gas, white spirits, turps substitute, mineral turpentine, petroleum ether, ligroin, and Stoddard solvent.






















