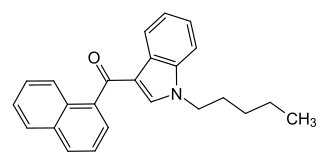
JWH-018 (1-pentyl-3-(1-naphthoyl)indole, NA-PIMO or AM-678) is an analgesic chemical from the naphthoylindole family that acts as a full agonist at both the CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptors, with some selectivity for CB2. It produces effects in animals similar to those of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), a cannabinoid naturally present in cannabis, leading to its use as synthetic cannabinoid products that, in some countries, are sold legally as "incense blends".

JWH-250 or (1-pentyl-3-(2-methoxyphenylacetyl)indole) is an analgesic chemical from the phenylacetylindole family that acts as a cannabinoid agonist at both the CB1 and CB2 receptors, with a Ki of 11 nM at CB1 and 33 nM at CB2. Unlike many of the older JWH series compounds, this compound does not have a naphthalene ring, instead occupying this position with a 2'-methoxy-phenylacetyl group, making JWH-250 a representative member of a new class of cannabinoid ligands. Other 2'-substituted analogues such as the methyl, chloro and bromo compounds are also active and somewhat more potent.

AM-694 (1-(5-fluoropentyl)-3-(2-iodobenzoyl)indole) is a designer drug that acts as a potent and selective agonist for the cannabinoid receptor CB1. It is used in scientific research for mapping the distribution of CB1 receptors.

JWH-007 is an analgesic chemical from the naphthoylindole family, which acts as a cannabinoid agonist at both the CB1 and CB2 receptors. It was first reported in 1994 by a group including the noted cannabinoid chemist John W. Huffman. It was the most active of the first group of N-alkyl naphoylindoles discovered by the team led by John W Huffman, several years after the family was initially described with the discovery of the N-morpholinylethyl compounds pravadoline (WIN 48,098), JWH-200 (WIN 55,225) and WIN 55,212-2 by the Sterling Winthrop group. Several other N-alkyl substituents were found to be active by Huffman's team including the n-butyl, n-hexyl, 2-heptyl, and cyclohexylethyl groups, but it was subsequently determined that the 2-methyl group on the indole ring is not required for CB1 binding, and tends to increase affinity for CB2 instead. Consequently, the 2-desmethyl derivative of JWH-007, JWH-018, has slightly higher binding affinity for CB1, with an optimum binding of 9.00 nM at CB1 and 2.94 nM at CB2, and JWH-007 displayed optimum binding of 9.50 nM at CB1 and 2.94 nM at CB2.
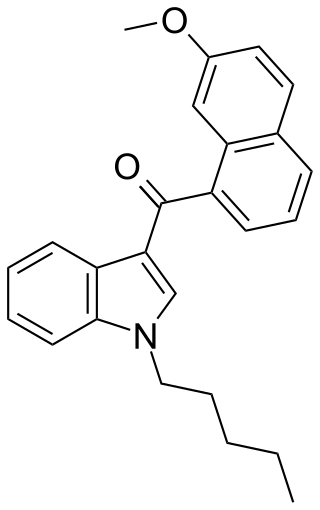
JWH-164 is a synthetic cannabinoid receptor agonist from the naphthoylindole family. It has approximately equal affinity for the CB1 and CB2 receptors, with a Ki of 6.6 nM at CB1 and 6.9 nM at CB2. JWH-164 is a positional isomer of the related compound JWH-081, but with a methoxy group at the 7-position of the naphthyl ring, rather than the 4-position as in JWH-081. Its potency is intermediate between that of JWH-081 and its ring unsubstituted derivative JWH-018, demonstrating that substitution of the naphthyl 7-position can also result in increased cannabinoid receptor binding affinity.

AM-2201 is a recreational designer drug that acts as a potent but nonselective full agonist for the cannabinoid receptor. It is part of the AM series of cannabinoids discovered by Alexandros Makriyannis at Northeastern University.

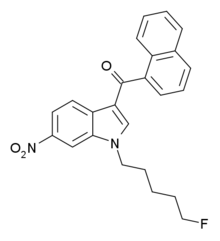
AM-1221 is a drug that acts as a potent and selective agonist for the cannabinoid receptor CB2, with a Ki of 0.28 nM at CB2 and 52.3 nM at the CB1 receptor, giving it around 180 times selectivity for CB2. The 2-methyl and 6-nitro groups on the indole ring both tend to increase CB2 affinity while generally reducing affinity at CB1, explaining the high CB2 selectivity of AM-1221. However, despite this relatively high selectivity for CB2, its CB1 affinity is still too strong to make it useful as a truly selective CB2 agonist, so the related compound AM-1241 is generally preferred for research purposes.

AM-679 (part of the AM cannabinoid series) is a drug that acts as a moderately potent agonist for the cannabinoid receptors, with a Ki of 13.5 nM at CB1 and 49.5 nM at CB2. AM-679 was one of the first 3-(2-iodobenzoyl)indole derivatives that was found to have significant cannabinoid receptor affinity, and while AM-679 itself has only modest affinity for these receptors, it was subsequently used as a base to develop several more specialised cannabinoid ligands that are now widely used in research, including the potent CB1 agonists AM-694 and AM-2233, and the selective CB2 agonist AM-1241. AM-679 was first identified as having been sold as a cannabinoid designer drug in Hungary in 2011, along with another novel compound 1-pentyl-3-(1-adamantoyl)indole.

AM-2233 is a drug that acts as a highly potent full agonist for the cannabinoid receptors, with a Ki of 1.8 nM at CB1 and 2.2 nM at CB2 as the active (R) enantiomer. It was developed as a selective radioligand for the cannabinoid receptors and has been used as its 131I derivative for mapping the distribution of the CB1 receptor in the brain. AM-2233 was found to fully substitute for THC in rats, with a potency lower than that of JWH-018 but higher than WIN 55,212-2.

AM-1248 is a drug that acts as a moderately potent agonist for both the cannabinoid receptors CB1 and CB2, but with some dispute between sources over its exact potency and selectivity. Replacing the 3-(1-naphthoyl) group found in many indole derived cannabinoid ligands, with an adamantoyl group, generally confers significant CB2 selectivity, but reasonable CB1 affinity and selectivity is retained when an N-methylpiperidin-2-ylmethyl substitution is used at the indole 1-position. The related compound 1-pentyl-3-(1-adamantoyl)indole was identified as having been sold as a cannabinoid designer drug in Hungary in 2011, along with another synthetic cannabinoid AM-679.

AM-2232 (1-(4-cyanobutyl)-3-(naphthalen-1-oyl)indole) is a drug that acts as a potent but unselective agonist for the cannabinoid receptors, with a Ki of 0.28 nM at CB1 and 1.48 nM at CB2.

AM-1220 is a drug that acts as a potent and moderately selective agonist for the cannabinoid receptor CB1, with around 19 times selectivity for CB1 over the related CB2 receptor. It was originally invented in the early 1990s by a team led by Thomas D'Ambra at Sterling Winthrop, but has subsequently been researched by many others, most notably the team led by Alexandros Makriyannis at the University of Connecticut. The (piperidin-2-yl)methyl side chain of AM-1220 contains a stereocenter, so there are two enantiomers with quite different potency, the (R)-enantiomer having a Ki of 0.27 nM at CB1 while the (S)-enantiomer has a much weaker Ki of 217 nM.

AB-001 (1-pentyl-3-(1-adamantoyl)indole) is a designer drug that was found as an ingredient in synthetic cannabis smoking blends in Ireland in 2010 and Hungary and Germany in 2011. It is unclear who AB-001 was originally developed by, but it is structurally related to compounds such as AM-1248 and its corresponding 1-(tetrahydropyran-4-ylmethyl) analogue, which are known to be potent cannabinoid agonists with moderate to a high selectivity for CB2 over CB1. The first published synthesis and pharmacological evaluation of AB-001 revealed that it acts as a full agonist at CB1 (EC50 = 35 nM) and CB2 receptors (EC50 = 48 nM). However, AB-001 was found to possess only weak cannabimimetic effects in rats at doses up to 30 mg/kg, making it less potent than the carboxamide analogue APICA, which possesses potent cannabimimetic activity at doses of 3 mg/kg.

UR-144 (TMCP-018, KM-X1, MN-001, YX-17) is a drug invented by Abbott Laboratories, that acts as a selective full agonist of the peripheral cannabinoid receptor CB2, but with much lower affinity for the psychoactive CB1 receptor.

JWH-047 is a selective cannabinoid ligand that binds to both CB1 and CB2. It has a bindining affinity of Ki = 0.9 nM for the CB2 subtype, and more than 65 times selectivity over the CB1.
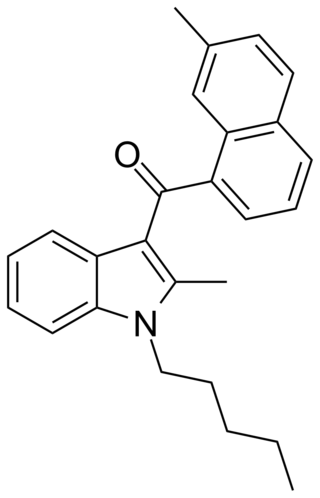
JWH-048 is a selective cannabinoid ligand, with a bindining affinity of Ki = 0.5 ± 0.1 nM for the CB2 subtype, and more than 22 times selectivity over the CB1.

STS-135 (N-(adamantan-1-yl)-1-(5-fluoropentyl)-1H-indole-3-carboxamide, also called 5F-APICA) is a designer drug offered by online vendors as a cannabimimetic agent. The structure of STS-135 appears to use an understanding of structure-activity relationships within the indole class of cannabimimetics, although its design origins are unclear. STS-135 is the terminally-fluorinated analogue of SDB-001, just as AM-2201 is the terminally-fluorinated analogue of JWH-018, and XLR-11 is the terminally-fluorinated analogue of UR-144. STS-135 acts a potent cannabinoid receptor agonist in vitro, with an EC50 of 51 nM for human CB2 receptors, and 13 nM for human CB1 receptors. STS-135 produces bradycardia and hypothermia in rats at doses of 1–10 mg/kg, suggesting cannabinoid-like activity.
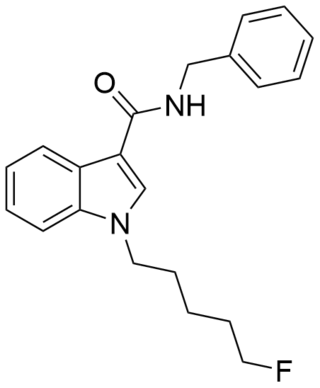
5F-SDB-006 is a drug that acts as a potent agonist for the cannabinoid receptors, with an EC50 of 50 nM for human CB1 receptors, and 123 nM for human CB2 receptors. It was discovered during research into the related compound APICA which had been sold illicitly as "2NE1". 5F-SDB-006 is the terminally fluorinated analog of SDB-006, just as STS-135 is the terminally fluorinated analog of APICA. Given the known metabolic liberation (and presence as an impurity) of amantadine in the related compound APINACA, it is suspected that metabolic hydrolysis of the amide group of 5F-SDB-006 may release benzylamine.

SDB-005 is an indazole-based synthetic cannabinoid that has been sold online as a designer drug. It is presumed to be an agonist of the CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptors. SDB-005 is the indazole core analog of PB-22 where the 8-hydroxyquinoline has also been replaced with a naphthalene group.