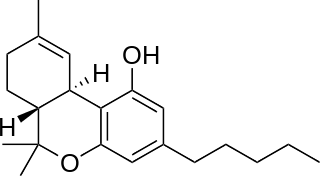
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is a cannabinoid found in cannabis. It is the principal psychoactive constituent of cannabis and one of at least 113 total cannabinoids identified on the plant. Although the chemical formula for THC (C21H30O2) describes multiple isomers, the term THC usually refers to the delta-9-THC isomer with chemical name (−)-trans-Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol. It is a colorless oil.

Medical cannabis, medicinal cannabis or medical marijuana (MMJ) refers to cannabis products and cannabinoid molecules that are prescribed by physicians for their patients. The use of cannabis as medicine has a long history, but has not been as rigorously tested as other medicinal plants due to legal and governmental restrictions, resulting in limited clinical research to define the safety and efficacy of using cannabis to treat diseases.

Cannabinoids are several structural classes of compounds found in the cannabis plant primarily and most animal organisms or as synthetic compounds. The most notable cannabinoid is the phytocannabinoid tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) (delta-9-THC), the primary psychoactive compound in cannabis. Cannabidiol (CBD) is also a major constituent of temperate cannabis plants and a minor constituent in tropical varieties. At least 100 distinct phytocannabinoids have been isolated from cannabis, although only four have been demonstrated to have a biogenetic origin. It was reported in 2020 that phytocannabinoids can be found in other plants such as rhododendron, licorice and liverwort, and earlier in Echinacea.

Cannabidiol (CBD) is a phytocannabinoid, one of 113 identified cannabinoids in cannabis plants, along with tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), and accounts for up to 40% of the plant's extract. Medically, it is an anticonvulsant used to treat multiple forms of epilepsy. It was discovered in 1940 and, as of 2024 clinical research on CBD included studies related to the treatment of anxiety, addiction, psychosis, movement disorders, and pain, but there is insufficient high-quality evidence that CBD is effective for these conditions. CBD is sold as an herbal dietary supplement and promoted with yet unproven claims of particular therapeutic effects.

WIN 55,212-2 is a chemical described as an aminoalkylindole derivative, which produces effects similar to those of cannabinoids such as tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) but has an entirely different chemical structure.

Levonantradol (CP 50,556-1) is a synthetic cannabinoid analog of dronabinol (Marinol) developed by Pfizer in the 1980s. It is around 30 times more potent than THC, and exhibits antiemetic and analgesic effects via activation of CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptors. Levonantradol is not currently used in medicine as dronabinol or nabilone are felt to be more useful for most conditions, however it is widely used in research into the potential therapeutic applications of cannabinoids.

Nabitan (nabutam, benzopyranoperidine, SP-106, Abbott 40656) is a synthetic cannabinoid analog of dronabinol (Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol) and dimethylheptylpyran. It exhibits antiemetic and analgesic effects, most likely by binding to and activating the CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptors, and reduced intraocular pressure in animal tests, making it potentially useful in the treatment of glaucoma.
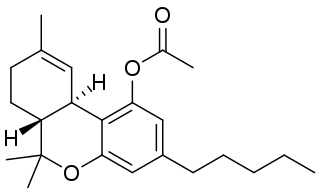
THC-O-acetate is the acetate ester of THC. The term THC-O-acetate and its variations are commonly used for two types of the substance, dependent on which cannabinoid it is synthesized from. The difference between Δ8-THC and Δ9-THC is bond placement on the cyclohexene ring.

Cannabigerol (CBG) is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid and minor constituent of cannabis. It is one of more than 120 identified cannabinoids found in the plant genus Cannabis. The compound is the decarboxylated form of cannabigerolic acid (CBGA), the parent molecule from which other cannabinoids are biosynthesized.

Dimethylheptylpyran (DMHP) is a synthetic cannabinoid and analogue of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC). It was invented in 1949 during attempts to elucidate the structure of Δ9-THC, one of the active components of cannabis. DMHP is a pale yellow, viscous oil which is insoluble in water but dissolves in alcohol or non-polar solvents.

JWH-073, a synthetic cannabinoid, is an analgesic chemical from the naphthoylindole family that acts as a full agonist at both the CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptors. It is somewhat selective for the CB1 subtype, with affinity at this subtype approximately 5× the affinity at CB2. The abbreviation JWH stands for John W. Huffman, one of the inventors of the compound.

JWH-200 (WIN 55,225) is an analgesic chemical from the aminoalkylindole family that acts as a cannabinoid receptor agonist. Its binding affinity, Ki at the CB1 receptor is 42 nM, around the same as that of THC, but its analgesic potency in vivo was higher than that of other analogues with stronger CB1 binding affinity in vitro, around 3 times that of THC but with less sedative effect, most likely reflecting favourable pharmacokinetic characteristics. It was discovered in 1991 by Sterling Drug as a potential analgesic following the earlier identification of related compounds such as pravadoline and WIN 55,212-2.

11-Nor-9-carboxy-Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol, often referred to as 11-nor-9-carboxy-THC or THC-11-oic acid, is the main secondary metabolite of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) which is formed in the body after cannabis is consumed.

JWH-176 is an analgesic drug which acts as a cannabinoid receptor agonist. Its binding affinity at the CB1 receptor is 26.0 nM, making it more potent than THC itself, however JWH-176 is particularly notable in that it is a hydrocarbon containing no heteroatoms. This demonstrates that reasonably high-affinity cannabinoid binding and agonist effects can be produced by compounds with no hydrogen bonding capacity at all, relying merely on Van der Waals and possibly hydrophobic interactions to bind to the receptor. It was discovered by, and named after, John W. Huffman.

AMG-3 (part of the AM cannabinoid series) is an analgesic drug which is a cannabinoid agonist. It is a derivative of Δ8-THC substituted with a dithiolane group on the 3-position side chain. AMG-3 is a potent agonist at both CB1 and CB2 receptors with a Ki of 0.32 nM at CB1 and 0.52 nM at CB2, and its particularly high binding affinity has led to it being used as a template for further structural development of novel cannabinoid drugs. It has sedative and analgesic effects, with analgesia lasting for up to 36 hours after administration.

Cannabichromene (CBC), also called cannabichrome, cannanbichromene, pentylcannabichromene or cannabinochromene, exhibits anti-inflammatory properties in vitro, which may, theoretically, contribute to cannabis analgesic effects. It is a phytocannabinoid, one of the hundreds of cannabinoids found in the Cannabis plant. It bears structural similarity to the other natural cannabinoids, including tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV), cannabidiol (CBD), and cannabinol (CBN), among others. CBC and cannabinols are present in cannabis. It is not scheduled by the Convention on Psychotropic Substances.

Dronabinol, sold under the brand names Marinol and Syndros, is the generic name for the molecule of (−)-trans-Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) in the pharmaceutical context. It has indications as an appetite stimulant, antiemetic, and sleep apnea reliever and is approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) as safe and effective for HIV/AIDS-induced anorexia and chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting.
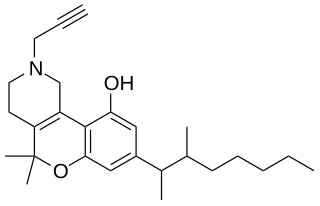
A-40174 (SP-1) is an analgesic drug which acts as a potent cannabinoid receptor agonist, and was developed by Abbott Laboratories in the 1970s. It is a structural analog of dronabinol and dimethylheptylpyran.
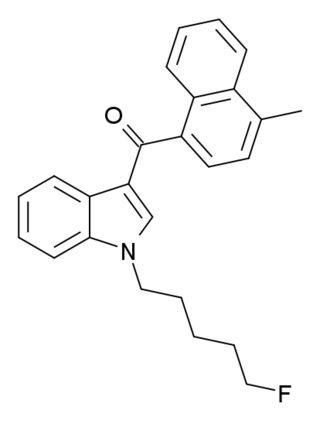
MAM-2201 is a drug that presumably acts as a potent agonist for the cannabinoid receptors. It had never previously been reported in the scientific or patent literature, and was first identified by laboratories in the Netherlands and Germany in June 2011 as an ingredient in synthetic cannabis smoking blends. Like RCS-4 and AB-001, MAM-2201 thus appears to be a novel compound invented by "research chemical" suppliers specifically for grey-market recreational use. Structurally, MAM-2201 is a hybrid of two known cannabinoid compounds JWH-122 and AM-2201, both of which had previously been used as active ingredients in synthetic cannabis blends before being banned in many countries.

11-Hydroxyhexahydrocannabinol is an active metabolite of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and a metabolite of the trace cannabinoid hexahydrocannabinol (HHC).


















