
Ketoprofen is one of the propionic acid class of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) with analgesic and antipyretic effects. It acts by inhibiting the body's production of prostaglandin.

Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) are members of a therapeutic drug class which reduces pain, decreases inflammation, decreases fever, and prevents blood clots. Side effects depend on the specific drug, its dose and duration of use, but largely include an increased risk of gastrointestinal ulcers and bleeds, heart attack, and kidney disease.

Ibuprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that is used to relieve pain, fever, and inflammation. This includes painful menstrual periods, migraines, and rheumatoid arthritis. It may also be used to close a patent ductus arteriosus in a premature baby. It can be taken orally or intravenously. It typically begins working within an hour.

Naproxen, sold under the brand name Aleve among others, is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to treat pain, menstrual cramps, and inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, gout and fever. It is taken orally. It is available in immediate and delayed release formulations. Onset of effects is within an hour and lasts for up to twelve hours. Naproxen is also available in salt form, naproxen sodium, which has better solubility when taken orally.
Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors, also known as coxibs, are a type of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that directly target cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), an enzyme responsible for inflammation and pain. Targeting selectivity for COX-2 reduces the risk of peptic ulceration and is the main feature of celecoxib, rofecoxib, and other members of this drug class.

Indometacin, also known as indomethacin, is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) commonly used as a prescription medication to reduce fever, pain, stiffness, and swelling from inflammation. It works by inhibiting the production of prostaglandins, endogenous signaling molecules known to cause these symptoms. It does this by inhibiting cyclooxygenase, an enzyme that catalyzes the production of prostaglandins.
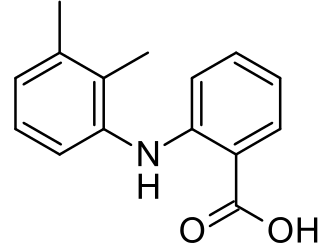
Mefenamic acid is a member of the anthranilic acid derivatives class of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and is used to treat mild to moderate pain.
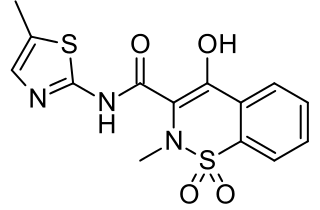
Meloxicam, sold under the brand name Mobic among others, is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to treat pain and inflammation in rheumatic diseases and osteoarthritis. It is taken by mouth or given by injection into a vein. It is recommended that it be used for as short a period as possible and at a low dose.
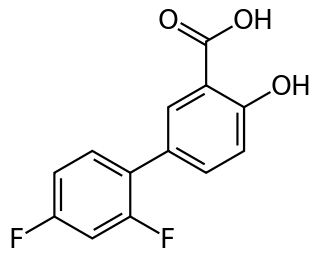
Diflunisal is a salicylic acid derivative with analgesic and anti-inflammatory activity. It was developed by Merck Sharp & Dohme in 1971, as MK647, after showing promise in a research project studying more potent chemical analogs of aspirin. It was first sold under the brand name Dolobid, marketed by Merck & Co., but generic versions are now widely available. It is classed as a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) and is available in 250 mg and 500 mg tablets.

Deracoxib is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) of the coxib class, used in dogs to treat pain associated with osteoarthritis, or to prevent pain following orthopedic or dental surgery. It is available as beef-flavored tablets.

Antimigraine drugs are medications intended to reduce the effects or intensity of migraine headache. They include drugs for the treatment of acute migraine symptoms as well as drugs for the prevention of migraine attacks.

Etofenamate is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used for the treatment of joint and muscular pain. It is available for topical application as a cream, a gel or as a spray.
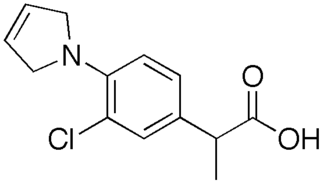
Pirprofen was a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that was brought to market by Ciba-Geigy in 1982 as a treatment for arthritis and pain. Its label was restricted after adverse events arose, including some cases of fatal liver toxicity. Ciba-Geigy voluntarily withdrew the drug from the market worldwide in 1990.

Lornoxicam, also known as chlortenoxicam, is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) of the oxicam class with analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antipyretic properties. It is available in oral and parenteral formulations.

Tenoxicam, sold under the brand name Mobiflex among others, is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). It is used to relieve inflammation, swelling, stiffness, and pain associated with rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, tendinitis, bursitis, and periarthritis of the shoulders or hips.
Floctafenine is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID).
NSAIDhypersensitivity reactions encompass a broad range of allergic or allergic-like symptoms that occur within minutes to hours after ingesting aspirin or other NSAID nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Hypersensitivity drug reactions differ from drug toxicity reactions in that drug toxicity reactions result from the pharmacological action of a drug, are dose-related, and can occur in any treated individual. Hypersensitivity reactions are idiosyncratic reactions to a drug. Although the term NSAID was introduced to signal a comparatively low risk of adverse effects, NSAIDs do evoke a broad range of hypersensitivity syndromes. These syndromes have recently been classified by the European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology Task Force on NSAIDs Hypersensitivity.
Oxycodone/ibuprofen is an oral combination drug formulation of the opioid analgesic oxycodone and the nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) ibuprofen that is used in the treatment of chronic and acute pain. This particular drug is supplied in a fixed dose combination tablet which contains Oxycodone Hydrochloride, USP 5 mg with Ibuprofen, USP 400 mg.
Prostaglandin inhibitors are drugs that inhibit the synthesis of prostaglandin in human body. There are various types of prostaglandins responsible for different physiological reactions such as maintaining the blood flow in stomach and kidney, regulating the contraction of involuntary muscles and blood vessels, and act as a mediator of inflammation and pain. Cyclooxygenase (COX) and Phospholipase A2 are the major enzymes involved in prostaglandin production, and they are the drug targets for prostaglandin inhibitors. There are mainly 2 classes of prostaglandin inhibitors, namely non- steroidal anti- inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and glucocorticoids. In the following sections, the medical uses, side effects, contraindications, toxicity and the pharmacology of these prostaglandin inhibitors will be discussed.















