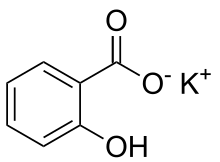
Salicylic acid is an organic compound with the formula HOC6H4COOH. A colorless (or, white), bitter-tasting solid, it is a precursor to and a metabolite of aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid). It is a plant hormone, and has been listed by the EPA Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) Chemical Substance Inventory as an experimental teratogen. The name is from Latin salix for willow tree, from which it was initially identified and derived. It is an ingredient in some anti-acne products. Salts and esters of salicylic acid are known as salicylates.

Rubbing alcohol is either an isopropyl alcohol or an ethanol-based liquid, with isopropyl alcohol products being the most widely available. The comparable British Pharmacopoeia (BP) is surgical spirit. Rubbing alcohol is denatured and undrinkable even if it is ethanol-based, due to the bitterants added.

Sulfites or sulphites are compounds that contain the sulfite ion, SO2−
3. The sulfite ion is the conjugate base of bisulfite. Although its acid is elusive, its salts are widely used.

Methyl salicylate (oil of wintergreen or wintergreen oil) is an organic compound with the formula C8H8O3. It is the methyl ester of salicylic acid. It is a colorless, viscous liquid with a sweet, fruity odor reminiscent of root beer (in which it is used as a flavoring), but often associatively called "minty", as it is an ingredient in mint candies. It is produced by many species of plants, particularly wintergreens. It is also produced synthetically, used as a fragrance and as a flavoring agent.
ATC code N02Analgesics is a therapeutic subgroup of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System, a system of alphanumeric codes developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) for the classification of drugs and other medical products. Subgroup N02 is part of the anatomical group N Nervous system.
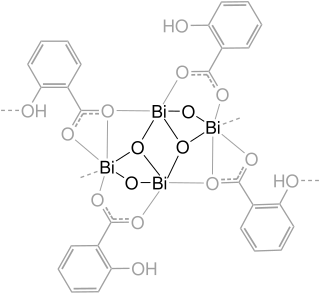
Bismuth subsalicylate, sold generically as pink bismuth and under brand names including Pepto-Bismol, Pepti-Calm and BisBacter, is a medication used to treat temporary discomfort of the stomach and gastrointestinal tract, such as nausea, heartburn, indigestion, upset stomach, and diarrhea.

Wintergreen is a group of aromatic plants. The term wintergreen once commonly referred to plants that remain green throughout the winter. The term evergreen is now more commonly used for this characteristic.
The Kolbe–Schmitt reaction or Kolbe process is a carboxylation chemical reaction that proceeds by treating phenol with sodium hydroxide to form sodium phenoxide, then heating sodium phenoxide with carbon dioxide under pressure, then treating the product with sulfuric acid. The final product is an aromatic hydroxy acid which is also known as salicylic acid.
Salicylate testing is a category of drug testing that is focused on detecting salicylates such as acetysalicylic acid for either biochemical or medical purposes.
A pyrotechnic composition is a substance or mixture of substances designed to produce an effect by heat, light, sound, gas/smoke or a combination of these, as a result of non-detonative self-sustaining exothermic chemical reactions. Pyrotechnic substances do not rely on oxygen from external sources to sustain the reaction.

Salicylate sensitivity is any adverse effect that occurs when a usual amount of salicylate is ingested. People with salicylate intolerance are unable to consume a normal amount of salicylate without adverse effects.

Magnesium salicylate is a common analgesic and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to treat mild to moderate musculoskeletal pain such as in tendons and muscles. It is also used to treat joint pain like arthritis, general back pain, and headaches.

Copper benzoate is the chemical compounds with the formula Cu(C6H5CO2)2(H2O)x. These coordination complexes are derived from the cupric ion and the conjugate base of benzoic acid. Many derivatives are known with diverse ancillary ligands. This compound has found some use as a source of blue light in fireworks.

Phenyl salicylate, or salol, is the organic compound with the formula C6H5O2C6H4OH. It is a white solid. It is occasionally used in sunscreens and as an antiseptic.
Sodium salicylate is a sodium salt of salicylic acid. It can be prepared from sodium phenolate and carbon dioxide under higher temperature and pressure. Historically, it has been synthesized by refluxing methyl salicylate with an excess of sodium hydroxide.

High anion gap metabolic acidosis is a form of metabolic acidosis characterized by a high anion gap. Metabolic acidosis occurs when the body produces too much acid, or when the kidneys are not removing enough acid from the body. Several types of metabolic acidosis occur, grouped by their influence on the anion gap.

Salicylate poisoning, also known as aspirin poisoning, is the acute or chronic poisoning with a salicylate such as aspirin. The classic symptoms are ringing in the ears, nausea, abdominal pain, and a fast breathing rate. Early on, these may be subtle, while larger doses may result in fever. Complications can include swelling of the brain or lungs, seizures, low blood sugar, or cardiac arrest.

The Poison Prevention Packaging Act of 1970 (PPPA); was signed into law by U.S. President Richard Nixon on December 30, 1970. It was enacted by the 91st United States Congress. This law required the use of child-resistant packaging for prescription drugs, over-the-counter (OTC) drugs, household chemicals, and other hazardous materials that could be considered dangerous for children.
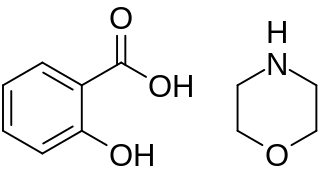
Morpholine salicylate is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug.