 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
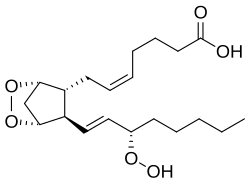
| IUPAC name (5Z)-7-{(1R,4S,5R,6R)-6-[(1E,3S)-3-Hydroperoxy-1-octen-1-yl]-2,3-dioxabicyclo[2.2.1]hept-5-yl}-5-heptenoic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C20H32O6 | |
| Molar mass | 368.470 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Prostaglandin G2 (PGG2) is an organic peroxide belonging to the family of prostaglandins. [1] The compound has been isolated as a solid, although it is usually used in vivo. It quickly converts into prostaglandin H2, a process catalyzed by the enzyme cyclooxygenase (COX).
Prostaglandin G2 is produced from the fatty acid arachidonic acid. The reaction, a double oxygenation, requires the enzyme COX, which inserts two molecules of O2 into the C-H bonds of the substrate acid. [2] [1] [3]