
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) are members of a therapeutic drug class which reduces pain, decreases inflammation, decreases fever, and prevents blood clots. Side effects depend on the specific drug, its dose and duration of use, but largely include an increased risk of gastrointestinal ulcers and bleeds, heart attack, and kidney disease.

Peptic ulcer disease is a break in the inner lining of the stomach, the first part of the small intestine, or sometimes the lower esophagus. An ulcer in the stomach is called a gastric ulcer, while one in the first part of the intestines is a duodenal ulcer. The most common symptoms of a duodenal ulcer are waking at night with upper abdominal pain, and upper abdominal pain that improves with eating. With a gastric ulcer, the pain may worsen with eating. The pain is often described as a burning or dull ache. Other symptoms include belching, vomiting, weight loss, or poor appetite. About a third of older people with peptic ulcers have no symptoms. Complications may include bleeding, perforation, and blockage of the stomach. Bleeding occurs in as many as 15% of cases.

Ibuprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that is used to relieve pain, fever, and inflammation. This includes painful menstrual periods, migraines, and rheumatoid arthritis. It may also be used to close a patent ductus arteriosus in a premature baby. It can be taken orally or intravenously. It typically begins working within an hour.

Diclofenac, sold under the brand name Voltaren among others, is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to treat pain and inflammatory diseases such as gout. It can be taken orally, inserted rectally as a suppository, injected intramuscularly, injected intravenously, applied to the skin topically, or through eye drops. Improvements in pain last up to eight hours. It is also available as the fixed-dose combination diclofenac/misoprostol (Arthrotec) to help protect the stomach.

Famotidine, sold under the brand name Pepcid among others, is a histamine H2 receptor antagonist medication that decreases stomach acid production. It is used to treat peptic ulcer disease, gastroesophageal reflux disease, and Zollinger-Ellison syndrome. It is taken by mouth or by injection into a vein. It begins working within an hour.

A lipoxin (LX or Lx), an acronym for lipoxygenase interaction product, is a bioactive autacoid metabolite of arachidonic acid made by various cell types. They are categorized as nonclassic eicosanoids and members of the specialized pro-resolving mediators (SPMs) family of polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) metabolites. Like other SPMs, LXs form during, and then act to resolve, inflammatory responses. Initially, two lipoxins were identified, lipoxin A4 (LXA4) and LXB4, but more recent studies have identified epimers of these two LXs: the epi-lipoxins, 15-epi-LXA4 and 15-epi-LXB4 respectively.
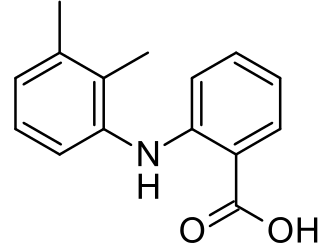
Mefenamic acid is a member of the anthranilic acid derivatives class of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and is used to treat mild to moderate pain.
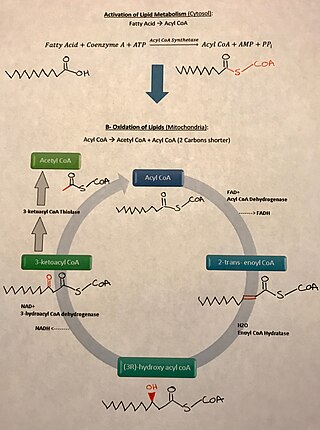
There is a wide variety of fatty acids found in nature. Two classes of fatty acids are considered essential, the omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids. Essential fatty acids are necessary for humans but cannot be synthesized by the body and must therefore be obtained from food. Omega-3 and omega-6 are used in some cellular signaling pathways and are involved in mediating inflammation, protein synthesis, and metabolic pathways in the human body.

Loteprednol is a topical corticosteroid used to treat inflammations of the eye. It is marketed by Bausch and Lomb as Lotemax and Loterex.

Lenabasum (also known as ajulemic acid, 1',1'-dimethylheptyl-delta-8-tetrahydrocannabinol-11-oic acid, DMH-D8-THC-11-OIC, AB-III-56, HU-239, IP-751, CPL 7075, CT-3, JBT-101, Anabasum, and Resunab) is a synthetic cannabinoid that shows anti-fibrotic and anti-inflammatory effects in pre-clinical studies without causing a subjective "high". Although its design was inspired by a metabolite of delta-9-THC known as delta-9-THC-11-oic acid, lenabasum is an analog of the delta-8-THC metabolite delta-8-THC-11-oic acid. It is being developed for the treatment of inflammatory and fibrotic conditions such as systemic sclerosis, dermatomyositis and cystic fibrosis. It does not share the anti-emetic effects of some other cannabinoids, but may be useful for treating chronic inflammatory conditions where inflammation fails to resolve. Side effects include dry mouth, tiredness, and dizziness. The mechanism of action is through activation of the CB2 receptor leading to production of specialized proresolving eicosanoids such as lipoxin A4 and prostaglandin J2. Studies in animals at doses up to 40 mg/kg show minimal psychoactivity of lenabasum, compared to that produced by tetrahydrocannabinol. Lenabasum is being developed by Corbus Pharmaceuticals (formerly JB Therapeutics) for the treatment of orphan chronic life-threatening inflammatory diseases. Development since been discontinued.
Cyclopentenone prostaglandins are a subset of prostaglandins (PGs) or prostanoids that has 15-deoxy-Δ12,14-prostaglandin J2 (15-d-Δ12,14-PGJ2), Δ12-PGJ2, and PGJ2 as its most prominent members but also including PGA2, PGA1, and, while not classified as such, other PGs. 15-d-Δ12,14-PGJ2, Δ12-PGJ2, and PGJ2 share a common mono-unsaturated cyclopentenone structure as well as a set of similar biological activities including the ability to suppress inflammation responses and the growth as well as survival of cells, particularly those of cancerous or neurological origin. Consequently, these three cyclopentenone-PGs and the two epoxyisoprostanes are suggested to be models for the development of novel anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer drugs. The cyclopenentone prostaglandins are structurally and functionally related to a subset of isoprostanes viz., two cyclopentenone isoprostanes, 5,6-epoxyisoprostane E2 and 5,6-epoxisoprostane A2.
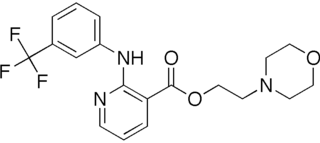
Morniflumate is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID).

Dexibuprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). It is the active dextrorotatory enantiomer of ibuprofen. Most ibuprofen formulations contain a racemic mixture of both isomers.
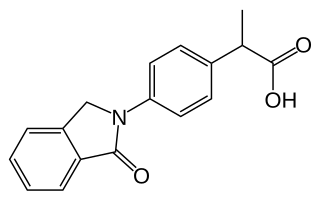
Indoprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). It was withdrawn worldwide in the 1980s after postmarketing reports of severe gastrointestinal bleeding.

ALOX15 is, like other lipoxygenases, a seminal enzyme in the metabolism of polyunsaturated fatty acids to a wide range of physiologically and pathologically important products. ▼ Gene Function

N-formyl peptide receptor 2 (FPR2) is a G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) located on the surface of many cell types of various animal species. The human receptor protein is encoded by the FPR2 gene and is activated to regulate cell function by binding any one of a wide variety of ligands including not only certain N-Formylmethionine-containing oligopeptides such as N-Formylmethionine-leucyl-phenylalanine (FMLP) but also the polyunsaturated fatty acid metabolite of arachidonic acid, lipoxin A4 (LXA4). Because of its interaction with lipoxin A4, FPR2 is also commonly named the ALX/FPR2 or just ALX receptor.

Salsalate is a medication that belongs to the salicylate and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) classes.

Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid is a precursor of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), an active component of cannabis.
Specialized pro-resolving mediators are a large and growing class of cell signaling molecules formed in cells by the metabolism of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) by one or a combination of lipoxygenase, cyclooxygenase, and cytochrome P450 monooxygenase enzymes. Pre-clinical studies, primarily in animal models and human tissues, implicate SPM in orchestrating the resolution of inflammation. Prominent members include the resolvins and protectins.

Glucametacin is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug used for the treatment of mild or moderate pain associated with rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, and other rheumatological disorders. It has analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects.


















