
The prostaglandins (PG) are a group of physiologically active lipid compounds called eicosanoids having diverse hormone-like effects in animals. Prostaglandins have been found in almost every tissue in humans and other animals. They are derived enzymatically from the fatty acid arachidonic acid. Every prostaglandin contains 20 carbon atoms, including a 5-carbon ring. They are a subclass of eicosanoids and of the prostanoid class of fatty acid derivatives.
Prostaglandin analogues are a class of drugs that bind to a prostaglandin receptor.

Progestogens, also sometimes written progestagens or gestagens, are a class of natural or synthetic steroid hormones that bind to and activate the progesterone receptor (PR). Progesterone is the major and most important progestogen in the body. The progestogens are named for their function in maintaining pregnancy, although they are also present at other phases of the estrous and menstrual cycles.

Prostacyclin (also called prostaglandin I2 or PGI2) is a prostaglandin member of the eicosanoid family of lipid molecules. It inhibits platelet activation and is also an effective vasodilator.
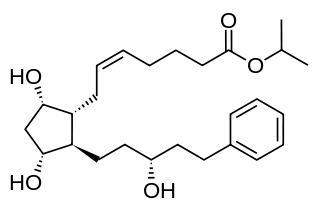
Latanoprost, sold under the brand name Xalatan among others, is a medication used to treat increased pressure inside the eye. This includes ocular hypertension and open angle glaucoma. It is applied as eye drops to the eyes. Onset of effects is usually within four hours, and they last for up to a day.
Luteolysis is the structural and functional degradation of the corpus luteum (CL), which occurs at the end of the luteal phase of both the estrous and menstrual cycles in the absence of pregnancy.

Brimonidine is a medication used to treat open-angle glaucoma, ocular hypertension, and rosacea. In rosacea it improves the redness. It is used as eye drops or applied to the skin.

Carboprost is a synthetic prostaglandin analogue of PGF2α with oxytocic properties.

Bimatoprost, sold under the brand name Lumigan among others, is a medication used to treat high pressure inside the eye including glaucoma. Specifically it is used for open angle glaucoma when other agents are not sufficient. It may also be used to increase the size of the eyelashes. It is used as an eye drop and effects generally occur within four hours.

Travoprost, sold under the brand name Travatan among others, is a medication used to treat high pressure inside the eye including glaucoma. Specifically it is used for open angle glaucoma when other agents are not sufficient. It is used as an eye drop. Effects generally occur within two hours.
In chemical nomenclature, nor- is a prefix to name a structural analog that can be derived from a parent compound by the removal of one carbon atom along with the accompanying hydrogen atoms. The nor-compound can be derived by removal of a CH
3, CH
2, or CH group, or of a C atom. The "nor-" prefix also includes the elimination of a methylene bridge in a cyclic parent compound, followed by ring contraction.. The terms desmethyl- or demethyl- are synonyms of "nor-".
Most of the eicosanoid receptors are integral membrane protein G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) that bind and respond to eicosanoid signaling molecules. Eicosanoids are rapidly metabolized to inactive products and therefore are short-lived. Accordingly, the eicosanoid-receptor interaction is typically limited to a local interaction: cells, upon stimulation, metabolize arachidonic acid to an eicosanoid which then binds cognate receptors on either its parent cell or on nearby cells to trigger functional responses within a restricted tissue area, e.g. an inflammatory response to an invading pathogen. In some cases, however, the synthesized eicosanoid travels through the blood to trigger systemic or coordinated tissue responses, e.g. prostaglandin (PG) E2 released locally travels to the hypothalamus to trigger a febrile reaction. An example of a non-GPCR receptor that binds many eicosanoids is the PPAR-γ nuclear receptor.
Prostaglandin receptors or prostanoid receptors represent a sub-class of cell surface membrane receptors that are regarded as the primary receptors for one or more of the classical, naturally occurring prostanoids viz., prostaglandin D2,, PGE2, PGF2alpha, prostacyclin (PGI2), thromboxane A2 (TXA2), and PGH2. They are named based on the prostanoid to which they preferentially bind and respond, e.g. the receptor responsive to PGI2 at lower concentrations than any other prostanoid is named the Prostacyclin receptor (IP). One exception to this rule is the receptor for thromboxane A2 (TP) which binds and responds to PGH2 and TXA2 equally well.

Prostaglandin EP3 receptor (53kDa), also known as EP3, is a prostaglandin receptor for prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) encoded by the human gene PTGER3; it is one of four identified EP receptors, the others being EP1, EP2, and EP4, all of which bind with and mediate cellular responses to PGE2 and also, but generally with lesser affinity and responsiveness, certain other prostanoids (see Prostaglandin receptors). EP has been implicated in various physiological and pathological responses.

Prostaglandin F receptor (FP) is a receptor belonging to the prostaglandin (PG) group of receptors. FP binds to and mediates the biological actions of Prostaglandin F2α (PGF2α). It is encoded in humans by the PTGFR gene.

Prostaglandin F2α, pharmaceutically termed carboprost is a naturally occurring prostaglandin used in medicine to induce labor and as an abortifacient. Prostaglandin is also used to treat uterine infections in domestic animals.

Aescin or escin is a mixture of saponins with anti-inflammatory, vasoconstrictor and vasoprotective effects found in Aesculus hippocastanum. Aescin is the main active component in horse chestnut, and is responsible for most of its medicinal properties. The main active compound of aescin is β-aescin, although the mixture also contains various other components including α-aescin, protoescigenin, barringtogenol, cryptoescin and benzopyrones.
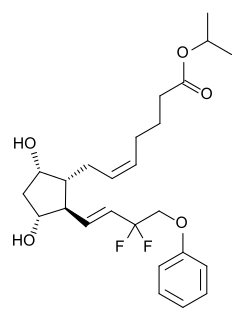
Tafluprost is a prostaglandin analogue. It is used topically to control the progression of open-angle glaucoma and in the management of ocular hypertension, alone or in combination with other medication. It reduces intraocular pressure by increasing the outflow of aqueous fluid from the eyes.

Cloprostenol is a synthetic analogue of prostaglandin F2α (PGF2α). It is a potent luteolytic agent; this means that, within hours of administration, it causes the corpus luteum to stop production of progesterone, and to reduce in size over several days. This effect is used in animals to induce estrus and to cause abortion.
In enzymology, a prostaglandin-F synthase (PGFS; EC 1.1.1.188) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction:













