In biochemistry, denaturation is a process in which proteins or nucleic acids lose folded structure present in their native state due to various factors, including application of some external stress or compound, such as a strong acid or base, a concentrated inorganic salt, an organic solvent, agitation and radiation, or heat. If proteins in a living cell are denatured, this results in disruption of cell activity and possibly cell death. Protein denaturation is also a consequence of cell death. Denatured proteins can exhibit a wide range of characteristics, from conformational change and loss of solubility or dissociation of cofactors to aggregation due to the exposure of hydrophobic groups. The loss of solubility as a result of denaturation is called coagulation. Denatured proteins lose their 3D structure, and therefore, cannot function.

Protein tertiary structure is the three-dimensional shape of a protein. The tertiary structure will have a single polypeptide chain "backbone" with one or more protein secondary structures, the protein domains. Amino acid side chains and the backbone may interact and bond in a number of ways. The interactions and bonds of side chains within a particular protein determine its tertiary structure. The protein tertiary structure is defined by its atomic coordinates. These coordinates may refer either to a protein domain or to the entire tertiary structure. A number of these structures may bind to each other, forming a quaternary structure.

Hypochlorous acid is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula ClOH, also written as HClO, HOCl, or ClHO. Its structure is H−O−Cl. It is an acid that forms when chlorine dissolves in water, and itself partially dissociates, forming a hypochlorite anion, ClO−. HClO and ClO− are oxidizers, and the primary disinfection agents of chlorine solutions. HClO cannot be isolated from these solutions due to rapid equilibration with its precursor, chlorine.

Prostacyclin (also called prostaglandin I2 or PGI2) is a prostaglandin member of the eicosanoid family of lipid molecules. It inhibits platelet activation and is also an effective vasodilator.
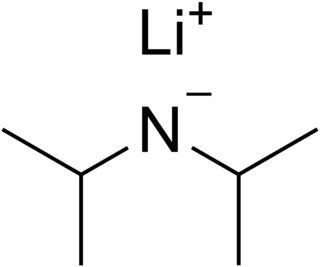
Lithium diisopropylamide is a chemical compound with the molecular formula LiN(CH 2)2. It is used as a strong base and has been widely utilized due to its good solubility in non-polar organic solvents and non-nucleophilic nature. It is a colorless solid, but is usually generated and observed only in solution. It was first prepared by Hamell and Levine in 1950 along with several other hindered lithium diorganylamides to effect the deprotonation of esters at the α position without attack of the carbonyl group.
Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA; also icosapentaenoic acid) is an omega−3 fatty acid. In physiological literature, it is given the name 20:5(n−3). It also has the trivial name timnodonic acid. In chemical structure, EPA is a carboxylic acid with a 20-carbon chain and five cis double bonds; the first double bond is located at the third carbon from the omega end.
In computer science, object composition and object aggregation are closely related ways to combine objects or data types into more complex ones. In conversation, the distinction between composition and aggregation is often ignored. Common kinds of compositions are objects used in object-oriented programming, tagged unions, sets, sequences, and various graph structures. Object compositions relate to, but are not the same as, data structures.
Disintegrins are a family of small proteins from viper venoms that function as potent inhibitors of both platelet aggregation and integrin-dependent cell adhesion.

Alpha sheet is an atypical secondary structure in proteins, first proposed by Linus Pauling and Robert Corey in 1951. The hydrogen bonding pattern in an alpha sheet is similar to that of a beta sheet, but the orientation of the carbonyl and amino groups in the peptide bond units is distinctive; in a single strand, all the carbonyl groups are oriented in the same direction on one side of the pleat, and all the amino groups are oriented in the same direction on the opposite side of the sheet. Thus the alpha sheet accumulates an inherent separation of electrostatic charge, with one edge of the sheet exposing negatively charged carbonyl groups and the opposite edge exposing positively charged amino groups. Unlike the alpha helix and beta sheet, the alpha sheet configuration does not require all component amino acid residues to lie within a single region of dihedral angles; instead, the alpha sheet contains residues of alternating dihedrals in the traditional right-handed (αR) and left-handed (αL) helical regions of Ramachandran space. Although the alpha sheet is only rarely observed in natural protein structures, it has been speculated to play a role in amyloid disease and it was found to be a stable form for amyloidogenic proteins in molecular dynamics simulations. Alpha sheets have also been observed in X-ray crystallography structures of designed peptides.
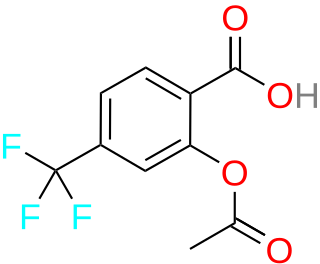
Triflusal is a platelet aggregation inhibitor that was discovered and developed in the Uriach Laboratories, and commercialised in Spain since 1981. Currently, it is available in 25 countries in Europe, Asia, Africa and America. It is a derivative of acetylsalicylic acid in which a hydrogen atom on the benzene ring has been replaced by a trifluoromethyl group. Trade names include Disgren, Grendis, Aflen and Triflux.

Cloricromen is a platelet aggregation inhibitor. Coronary vasodilator.

Etamsylate is an antihemorrhagic agent which is believed to work by increasing resistance in the endothelium of capillaries and promoting platelet adhesion. It also inhibits biosynthesis and action of those prostaglandins which cause platelet disaggregation, vasodilation and increased capillary permeability.

Lysophosphatidic acid receptor 1 also known as LPA1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LPAR1 gene. LPA1 is a G protein-coupled receptor that binds the lipid signaling molecule lysophosphatidic acid (LPA).

Aspirin causes several different effects in the body, mainly the reduction of inflammation, analgesia, the prevention of clotting, and the reduction of fever. Much of this is believed to be due to decreased production of prostaglandins and TXA2. Aspirin's ability to suppress the production of prostaglandins and thromboxanes is due to its irreversible inactivation of the cyclooxygenase (COX) enzyme. Cyclooxygenase is required for prostaglandin and thromboxane synthesis. Aspirin acts as an acetylating agent where an acetyl group is covalently attached to a serine residue in the active site of the COX enzyme. This makes aspirin different from other NSAIDs, which are reversible inhibitors; aspirin creates an allosteric change in the structure of the COX enzyme. However, other effects of aspirin, such as uncoupling oxidative phosphorylation in mitochondria, and the modulation of signaling through NF-κB, are also being investigated. Some of its effects are like those of salicylic acid, which is not an acetylating agent.

In molecular biology, protein aggregation is a phenomenon in which intrinsically-disordered or mis-folded proteins aggregate either intra- or extracellularly. Protein aggregates have been implicated in a wide variety of diseases known as amyloidoses, including ALS, Alzheimer's, Parkinson's and prion disease.
Viral neuraminidase is a type of neuraminidase found on the surface of influenza viruses that enables the virus to be released from the host cell. Neuraminidases are enzymes that cleave sialic acid groups from glycoproteins. Viral neuraminidase was discovered by Alfred Gottschalk at the Walter and Eliza Hall Institute in 1957. Neuraminidase inhibitors are antiviral agents that inhibit influenza viral neuraminidase activity and are of major importance in the control of influenza.

Oenin is an anthocyanin. It is the 3-glucoside of malvidin. It is one of the red pigments found in the skin of purple grapes and in wine.

Asim K. Duttaroy is an Indian-born American medical scientist who, since 2001, has worked as a Professor at the Faculty of Medicine, University of Oslo, Norway. He was born in Gopinagar (Gangnapur), Nadia district, West Bengal, India.
Poxytrins or dihydroxy-E,Z,E-polyunsaturated fatty acids (dihydroxy-E,Z,E-PUFAs) are PUFA metabolites that possess two hydroxyl residues and three in-series conjugated double bonds in an E,Z,E cis–trans configuration. Poxytrins have platelet-inhibiting properties that are not found in isomers with three conjugated double bonds presenting in a different geometry. The unique E,Z,E configuration in poxytrins may prove to be relevant in treating human conditions and diseases that involve pathological platelet activation.

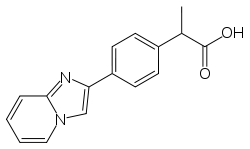
The profens are a class of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Profens are also known as 2-arylpropionic acids to reflect their chemical structure. The most common example of a profen is ibuprofen, which has been sold under the brand name Profen among others.