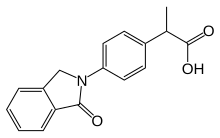
Ibuprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that is used to relieve pain, fever, and inflammation. This includes painful menstrual periods, migraines, and rheumatoid arthritis. It may also be used to close a patent ductus arteriosus in a premature baby. It can be taken orally or intravenously. It typically begins working within an hour.

Spinal muscular atrophies (SMAs) are a genetically and clinically heterogeneous group of rare debilitating disorders characterised by the degeneration of lower motor neurons and subsequent atrophy (wasting) of various muscle groups in the body. While some SMAs lead to early infant death, other diseases of this group permit normal adult life with only mild weakness.

Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) is a rare neuromuscular disorder that results in the loss of motor neurons and progressive muscle wasting. It is usually diagnosed in infancy or early childhood and if left untreated it is the most common genetic cause of infant death. It may also appear later in life and then have a milder course of the disease. The common feature is progressive weakness of voluntary muscles, with arm, leg and respiratory muscles being affected first. Associated problems may include poor head control, difficulties swallowing, scoliosis, and joint contractures.
Gideon Dreyfuss is an American biochemist, the Isaac Norris Professor of Biochemistry and Biophysics at the University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine, and an investigator of the Howard Hughes Medical Institute. He was elected to the National Academy of Sciences in 2012.

Flunarizine, sold under the brand name Sibelium among others, is a drug classified as a calcium antagonist which is used for various indications. It is not available by prescription in the United States or Japan. The drug was discovered at Janssen Pharmaceutica (R14950) in 1968.

Survival of motor neuron or survival motor neuron (SMN) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SMN1 and SMN2 genes.

Survival of motor neuron 1 (SMN1), also known as component of gems 1 or GEMIN1, is a gene that encodes the SMN protein in humans.

Small nuclear ribonucleoprotein Sm D2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SNRPD2 gene. It belongs to the small nuclear ribonucleoprotein core protein family, and is required for pre-mRNA splicing and small nuclear ribonucleoprotein biogenesis. Alternative splicing occurs at this locus and two transcript variants encoding the same protein have been identified.

Gem-associated protein 2 (GEMIN2), also called survival of motor neuron protein-interacting protein 1 (SIP1), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GEMIN2 gene.

Probable ATP-dependent RNA helicase DDX20, also known as DEAD-box helicase 20 and gem-associated protein 3 (GEMIN3), is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DDX20 gene.

Baculoviral IAP repeat-containing protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NAIP gene.

Chondrolectin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CHODL gene. Mouse chondrolectin is encoded by Chodl.

Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as motor neurone disease (MND) or Lou Gehrig's disease (LGD), is a rare, terminal neurodegenerative disorder that results in the progressive loss of both upper and lower motor neurons that normally control voluntary muscle contraction. ALS is the most common form of the motor neuron diseases. ALS often presents in its early stages with gradual muscle stiffness, twitches, weakness, and wasting. Motor neuron loss typically continues until the abilities to eat, speak, move, and, lastly, breathe are all lost. While only 15% of people with ALS also fully develop frontotemporal dementia, an estimated 50% face at least some minor difficulties with thinking and behavior. Depending on which of the aforementioned symptoms develops first, ALS is classified as limb-onset or bulbar-onset.

Survival of motor neuron 2 (SMN2) is a gene that encodes the SMN protein in humans.
Congenital distal spinal muscular atrophy (cDSMA), also known as distal hereditary motor neuropathytype VIII (dHMN8), is a hereditary medical condition characterized by muscle wasting (atrophy), particularly of distal muscles in legs and hands, and by early-onset contractures of the hip, knee, and ankle. Affected individuals often have shorter lower limbs relative to the trunk and upper limbs. The condition is a result of a loss of anterior horn cells localized to lumbar and cervical regions of the spinal cord early in infancy, which in turn is caused by a mutation of the TRPV4 gene. The disorder is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. Arm muscle and function, as well as cardiac and respiratory functions are typically well preserved.

Neurodegenerative diseases are a heterogeneous group of complex disorders linked by the degeneration of neurons in either the peripheral nervous system or the central nervous system. Their underlying causes are extremely variable and complicated by various genetic and/or environmental factors. These diseases cause progressive deterioration of the neuron resulting in decreased signal transduction and in some cases even neuronal death. Peripheral nervous system diseases may be further categorized by the type of nerve cell affected by the disorder. Effective treatment of these diseases is often prevented by lack of understanding of the underlying molecular and genetic pathology. Epigenetic therapy is being investigated as a method of correcting the expression levels of misregulated genes in neurodegenerative diseases.

Nusinersen, marketed as Spinraza, is a medication used in treating spinal muscular atrophy (SMA), a rare neuromuscular disorder. In December 2016, it became the first approved drug used in treating this disorder.

Branaplam is a pyridazine derivative that is being studied as an experimental drug. It was originally developed by Novartis to treat spinal muscular atrophy (SMA); since 2020 it was being developed to treat Huntington's disease but the trial ended in 2023 due to toxicity concerns.

Risdiplam, sold under the brand name Evrysdi, is a medication used to treat spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) and the first oral medication approved to treat this disease.
Ravindra N. Singh is an Indian American scientist, inventor and academic. He is a professor in the Department of Biomedical Sciences of the College of Veterinary Medicine at Iowa State University.