Toxicogenomics is a subdiscipline of pharmacology that deals with the collection, interpretation, and storage of information about gene and protein activity within a particular cell or tissue of an organism in response to exposure to toxic substances. Toxicogenomics combines toxicology with genomics or other high-throughput molecular profiling technologies such as transcriptomics, proteomics and metabolomics. Toxicogenomics endeavors to elucidate the molecular mechanisms evolved in the expression of toxicity, and to derive molecular expression patterns that predict toxicity or the genetic susceptibility to it.

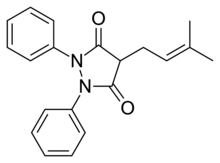
5-MeO-DPT, also known as 5-methoxy-N,N-dipropyltryptamine, is a psychedelic and entheogenic designer drug of the tryptamine family related to dipropyltryptamine (DPT) and 5-MeO-DMT.
Toluene toxicity refers to the harmful effects caused by toluene on the body.
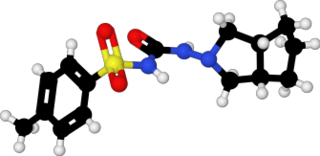
Gliclazide, sold under the brand name Diamicron among others, is a sulfonylurea type of anti-diabetic medication, used to treat type 2 diabetes. It is used when dietary changes, exercise, and weight loss are not enough. It is taken by mouth.
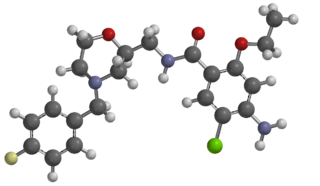
Mosapride is a gastroprokinetic agent that acts as a selective 5HT4 agonist. The major active metabolite of mosapride, known as M1, additionally acts as a 5HT3 antagonist, which accelerates emptying throughout the whole of the gastrointestinal tract in humans, and is used for the treatment of gastritis, gastroesophageal reflux disease, functional dyspepsia and irritable bowel syndrome. It is recommended to be taken on an empty stomach (i.e. at least one hour before food or two hours after food).

PRC200-SS is an experimental drug of the triple reuptake inhibitor class that was investigated by the Mayo Clinic.

Methysticin is one of the six major kavalactones found in the kava plant. Research suggests that methysticin and the related compound dihydromethysticin have CYP1A1 inducing effects which may be responsible for their toxicity. Additionally, methysticin has been shown to potentiate GABAA receptor activity, contributing to the overall anxiolytic profile of the kava plant.
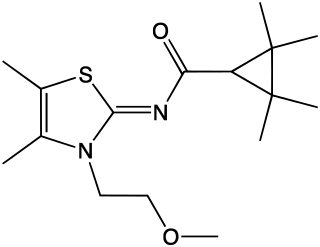
A-836,339 is a drug developed by Abbott Laboratories that acts as a potent cannabinoid receptor full agonist. It is selective for CB2, with Ki values of 0.64 nM at CB2 vs 270 nM at the psychoactive CB1 receptor, but while it exhibits selective analgesic, anti-inflammatory and anti-hyperalgesic effects at low doses, its high efficacy at both targets results in typical cannabis-like effects appearing at higher doses, despite its low binding affinity for CB1. In 2012 A-836,339 was detected via X-ray crystallography in a "dubious product" sold in Japan, though the product was described as a white powder, not herbal incense, it was suggested to be for human consumption.

Acetylfentanyl is an opioid analgesic drug that is an analog of fentanyl. Studies have estimated acetylfentanyl to be 15 times more potent than morphine, which would mean that despite being somewhat weaker than fentanyl, it is nevertheless still several times stronger than pure heroin. It has never been licensed for medical use and instead has only been sold on the illicit drug market. Acetylfentanyl was discovered at the same time as fentanyl itself and had only rarely been encountered on the illicit market in the late 1980s. However, in 2013, Canadian police seized 3 kilograms of acetylfentanyl. As a μ-opioid receptor agonist, acetylfentanyl may serve as a direct substitute for oxycodone, heroin or other opioids. Common side effects of fentanyl analogs are similar to those of fentanyl itself, which include itching, nausea, and potentially fatal respiratory depression. Fentanyl analogs have killed hundreds of people throughout Europe and the former Soviet republics since the most recent resurgence in use began in Estonia in the early 2000s, and novel derivatives continue to appear.

25-C-NBOH is a derivative of the phenethylamine derived hallucinogen 2C-C which has been sold as a designer drug. It has similar serotonin receptor affinity to the better-known compound 25C-NBOMe.

25N-NBOMe is a derivative of the hallucinogen 2C-N. The pharmacological properties of 25N-NBOMe have not been described in the scientific literature, but it is believed to act in a similar manner to related compounds such as 25I-NBOMe and 25C-NBOMe, which are potent agonists at the 5HT2A receptor. 25N-NBOMe has been sold as a street drug and has only been described in the literature in terms of identification by forensic analysis.

THJ-2201 is an indazole-based synthetic cannabinoid that presumably acts as a potent agonist of the CB1 receptor and has been sold online as a designer drug.
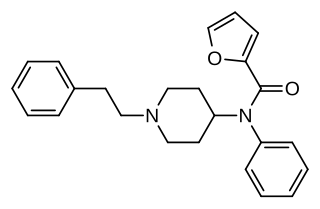
Furanylfentanyl (Fu-F) is an opioid analgesic that is an analog of fentanyl and has been sold as a designer drug. It has an ED50 value of 0.02 mg/kg in mice. This makes it approximately one fifth as potent as fentanyl.
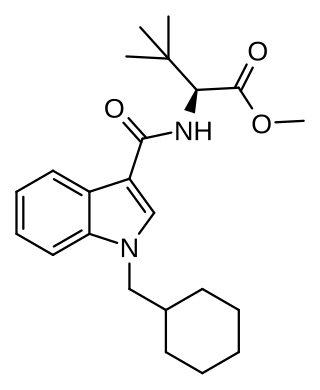
'MDMB-CHMICAa' is an indole-based synthetic cannabinoid that is a potent agonist of the CB1 receptor and has been sold online as a designer drug. While MDMB-CHMICA was initially sold under the name "MMB-CHMINACA", the compound corresponding to this code name (i.e. the isopropyl instead of t-butyl analogue of MDMB-CHMINACA) has been identified on the designer drug market in 2015 as AMB-CHMINACA.
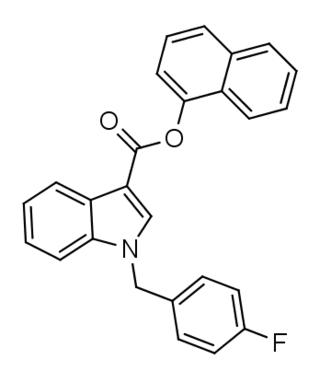
FDU-PB-22 is a derivative of JWH-018 that is presumed to be a potent agonist of the CB1 receptor, and has been sold online as a designer drug.
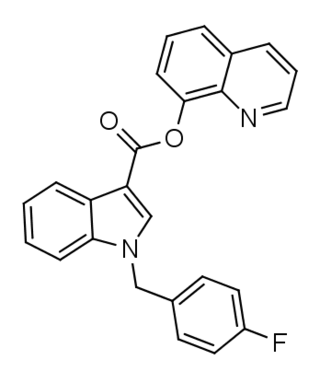
FUB-PB-22 (QUFUBIC) is an indole-based synthetic cannabinoid that is a potent agonist of the CB1 receptor and has been sold online as a designer drug.
4'-Methoxy-α-pyrrolidinopentiophenone is a stimulant drug of the cathinone class that has been sold online as a designer drug.

Methoxmetamine is a dissociative anesthetic of the arylcyclohexylamine class that is closely related to methoxetamine and methoxyketamine, and has been sold online as a designer drug.

25iP-NBOMe is a derivative of the phenethylamine hallucinogen 2C-iP, which acts as a highly potent agonist for the human 5-HT2A receptor.

25E-NBOH is a derivative of the phenethylamine derived hallucinogen 2C-E. It was first developed by Martin Hansen at the University of Copenhagen in 2010 as a brain imaging agent, but has subsequently been sold as a designer drug, first being identified in Brazil in 2018 on seized blotter paper, as well as in Slovenia and France. It acts as a potent serotonin receptor agonist with similar affinity to better-known compounds such as 25I-NBOMe at 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors.