Related Research Articles

Arthritis is a term often used to mean any disorder that affects joints. Symptoms generally include joint pain and stiffness. Other symptoms may include redness, warmth, swelling, and decreased range of motion of the affected joints. In some types of arthritis, other organs are also affected. Onset can be gradual or sudden.
Interstitial cystitis (IC), a type of bladder pain syndrome (BPS), is chronic pain in the bladder and pelvic floor of unknown cause. It is the urologic chronic pelvic pain syndrome of women. Symptoms include feeling the need to urinate right away, needing to urinate often, and pain with sex. IC/BPS is associated with depression and lower quality of life. Many of those affected also have irritable bowel syndrome and fibromyalgia.

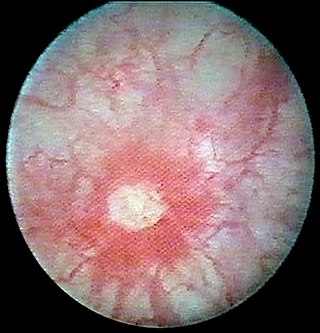
Conjunctivitis, also known as pink eye, is inflammation of the outermost layer of the white part of the eye and the inner surface of the eyelid. It makes the eye appear pink or reddish. Pain, burning, scratchiness, or itchiness may occur. The affected eye may have increased tears or be "stuck shut" in the morning. Swelling of the white part of the eye may also occur. Itching is more common in cases due to allergies. Conjunctivitis can affect one or both eyes.

Myalgia is the medical term for muscle pain. Myalgia is a symptom of many diseases. The most common cause of acute myalgia is the overuse of a muscle or group of muscles; another likely cause is viral infection, especially when there has been no trauma.

Back pain is pain felt in the back. It may be classified as neck pain (cervical), middle back pain (thoracic), lower back pain (lumbar) or coccydynia based on the segment affected. The lumbar area is the most common area affected. An episode of back pain may be acute, subacute or chronic depending on the duration. The pain may be characterized as a dull ache, shooting or piercing pain or a burning sensation. Discomfort can radiate to the arms and hands as well as the legs or feet, and may include numbness or weakness in the legs and arms.

Tietze syndrome is a benign inflammation of one or more of the costal cartilages. It was first described in 1921 by German surgeon Alexander Tietze and was subsequently named after him. The condition is characterized by tenderness and painful swelling of the anterior (front) chest wall at the costochondral, sternocostal, or sternoclavicular junctions. Tietze syndrome affects the true ribs and has a predilection for the 2nd and 3rd ribs, commonly affecting only a single joint.

Laryngitis is inflammation of the larynx. Symptoms often include a hoarse voice and may include fever, cough, pain in the front of the neck, and trouble swallowing. Typically, these last under two weeks.

Acute septic arthritis, infectious arthritis, suppurative arthritis, pyogenic arthritis, osteomyelitis, or joint infection is the invasion of a joint by an infectious agent resulting in joint inflammation. Generally speaking, symptoms typically include redness, heat and pain in a single joint associated with a decreased ability to move the joint. Onset is usually rapid. Other symptoms may include fever, weakness and headache. Occasionally, more than one joint may be involved, especially in neonates, younger children and immunocompromised individuals. In neonates, infants during the first year of life, and toddlers, the signs and symptoms of septic arthritis can be deceptive and mimic other infectious and non-infectious disorders.

Costochondritis, also known as chest wall pain syndrome or costosternal syndrome, is a benign inflammation of the upper costochondral and sternocostal joints. 90% of patients are affected in multiple ribs on a single side, typically at the 2nd to 5th ribs. Chest pain, the primary symptom of costochondritis, is considered a symptom of a medical emergency, making costochondritis a common presentation in the emergency department. One study found costochondritis was responsible for 30% of patients with chest pain in an emergency department setting.

Polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR) is a syndrome experienced as pain or stiffness, usually in the neck, shoulders, upper arms, and hips, but which may occur all over the body. The pain can be sudden or can occur gradually over a period. Most people with PMR wake up in the morning with pain in their muscles; however, cases have occurred in which the person has developed the pain during the evenings or has pain and stiffness all day long.

Pneumonitis describes general inflammation of lung tissue. Possible causative agents include radiation therapy of the chest, exposure to medications used during chemo-therapy, the inhalation of debris, aspiration, herbicides or fluorocarbons and some systemic diseases. If unresolved, continued inflammation can result in irreparable damage such as pulmonary fibrosis.
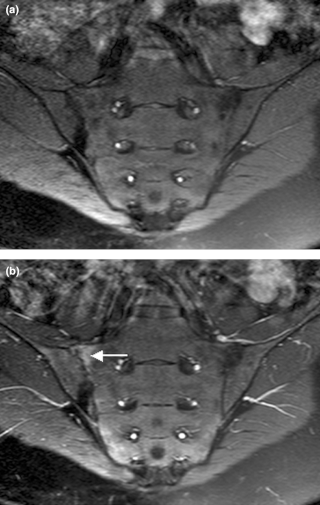
Sacroiliitis is inflammation within the sacroiliac joint. It is a feature of spondyloarthropathies, such as axial spondyloarthritis, psoriatic arthritis, reactive arthritis or arthritis related to inflammatory bowel diseases, including ulcerative colitis or Crohn's disease. It is also the most common presentation of arthritis from brucellosis.
Eosinophilic pneumonia is a disease in which an eosinophil, a type of white blood cell, accumulates in the lungs. These cells cause disruption of the normal air spaces (alveoli) where oxygen is extracted from the atmosphere. Several different kinds of eosinophilic pneumonia exist and can occur in any age group. The most common symptoms include cough, fever, difficulty breathing, and sweating at night. Eosinophilic pneumonia is diagnosed by a combination of characteristic symptoms, findings on a physical examination by a health provider, and the results of blood tests and X-rays. Prognosis is excellent once most eosinophilic pneumonia is recognized and treatment with corticosteroids is begun.
Felty's syndrome (FS), also called Felty syndrome, is a rare autoimmune disease characterized by the triad of rheumatoid arthritis, enlargement of the spleen and low neutrophil count. The condition is more common in those aged 50–70 years, specifically more prevalent in females than males, and more so in Caucasians than those of African descent. It is a deforming disease that causes many complications for the individual.

Transient synovitis of hip is a self-limiting condition in which there is an inflammation of the inner lining of the capsule of the hip joint. The term irritable hip refers to the syndrome of acute hip pain, joint stiffness, limp or non-weightbearing, indicative of an underlying condition such as transient synovitis or orthopedic infections. In everyday clinical practice however, irritable hip is commonly used as a synonym for transient synovitis. It should not be confused with sciatica, a condition describing hip and lower back pain much more common to adults than transient synovitis but with similar signs and symptoms.

Subacute thyroiditis refers to a temporal classification of the different forms of thyroiditis based on onset of symptoms. The temporal classification of thyroiditis includes presentation of symptoms in an acute, subacute, or chronic manner. There are also other classification systems for thyroiditis based on factors such as clinical symptoms and underlying etiology.
Greater trochanteric pain syndrome (GTPS), a form of bursitis, is inflammation of the trochanteric bursa, a part of the hip.
Serum sickness in humans is a reaction to proteins in antiserum derived from a non-human animal source, occurring 5–10 days after exposure. Symptoms often include a rash, joint pain, fever, and lymphadenopathy. It is a type of hypersensitivity, specifically immune complex hypersensitivity. The term serum sickness–like reaction (SSLR) is occasionally used to refer to similar illnesses that arise from the introduction of certain non-protein substances, such as penicillin.
Cerebral vasculitis is vasculitis involving the brain and occasionally the spinal cord. It affects all of the vessels: very small blood vessels (capillaries), medium-size blood vessels, or large blood vessels. If blood flow in a vessel with vasculitis is reduced or stopped, the parts of the body that receive blood from that vessel begins to die. It may produce a wide range of neurological symptoms, such as headache, skin rashes, feeling very tired, joint pains, difficulty moving or coordinating part of the body, changes in sensation, and alterations in perception, thought or behavior, as well as the phenomena of a mass lesion in the brain leading to coma and herniation. Some of its signs and symptoms may resemble multiple sclerosis. 10% have associated bleeding in the brain.

An antiarthritic is any drug used to relieve or prevent arthritic symptoms, such as joint pain or joint stiffness. Depending on the antiarthritic drug class, it is used for managing pain, reducing inflammation or acting as an immunosuppressant. These drugs are typically given orally, topically or through administration by injection. The choice of antiarthritic medication is often determined by the nature of arthritis, the severity of symptoms as well as other factors, such as the tolerability of side effects.
References
- ↑ "Arthralgia Definition". MedicineNet.com. Archived from the original on 11 October 2007. Retrieved 2007-09-20.
- 1 2 3 Joe G. Hardin. "Arthralgia". Clinical Methods - The History, Physical, and Laboratory Examinations. Retrieved 2007-09-20.
- ↑ James R Philp. "Allergic Drug Reactions - Systemic Allergic Drug Reactions". Clinical Methods - The History, Physical, and Laboratory Examinations. Retrieved 2007-09-20.
- ↑ "MeSH" . Retrieved 2007-12-23.
- ↑ Joe G. Hardin. "Table 161.1. Some Common Regional Rheumatic Syndromes". Clinical Methods - The History, Physical, and Laboratory Examinations. Retrieved 2007-09-20.
- ↑ Loris McVittie. "Information from CDC and FDA on the Safety of Gardasil Vaccine". supplement to your biologics license application (BLA) for Human Papillomavirus Quadrivalent (Types 6, 11, 16 and 18) Vaccine, Recombinant (GARDASIL), to include arthralgia, myalgia, asthenia, fatigue, and malaise in the Adverse Reactions section of the package insert. Retrieved 2008-07-21.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 Table 6-8 in: Elizabeth D Agabegi; Agabegi, Steven S. (2008). Step-Up to Medicine (Step-Up Series) . Hagerstwon, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 978-0-7817-7153-5.
- ↑ Diagnosis lag time of median 4 weeks, and median diagnosis lag time of 18 weeks, taken from: Chan, K. W.; Felson, D. T.; Yood, R. A.; Walker, A. M. (1994). "The lag time between onset of symptoms and diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis". Arthritis and Rheumatism. 37 (6): 814–820. doi:10.1002/art.1780370606. PMID 8003053.
- ↑ Doria, A.; Zen, M.; Canova, M.; Bettio, S.; Bassi, N.; Nalotto, L.; Rampudda, M.; Ghirardello, A.; Iaccarino, L. (2010). "SLE diagnosis and treatment: When early is early". Autoimmunity Reviews. 10 (1): 55–60. doi:10.1016/j.autrev.2010.08.014. PMID 20813207.
- ↑ "Ehlers-Danlos syndrome - Symptoms and causes" . Retrieved 10 February 2018.
- 1 2 Page 740 (upper right of page) in: Schaider, Jeffrey; Wolfson, Allan B.; Hendey, Gregory W.; Ling, Louis; Rosen, Carlo L. (2009). Harwood-Nuss' Clinical Practice of Emergency Medicine (Clinical Practice of Emergency Medicine (Harwood-Nuss)). Hagerstwon, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 978-0-7817-8943-1.
- ↑ Passier, Anneke; van Puijenbroek, Eugene (November 2005). "Mirtazapine-induced arthralgia". British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 60 (5): 570–572. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2125.2005.02481.x. PMC 1884949 . PMID 16236049.
- ↑ "Henoch-Schonlein purpura (video)". Khan Academy. Retrieved 2020-06-06.
- ↑ "Table 159mptomatic Extraarticular Features of the Connective Tissue Diseases and the Spondyloarthropathies". Clinical Methods - The History, Physical, and Laboratory Examinations. Retrieved 2007-09-20.
- ↑ "Pain Management". Arthritis Action UK. Arthritis Action. Archived from the original on 13 February 2016. Retrieved 16 October 2015.