A ligament is the fibrous connective tissue that connects bones to other bones. It also connects flight feathers to bones, in dinosaurs and birds. All 30,000 species of amniotes have ligaments.
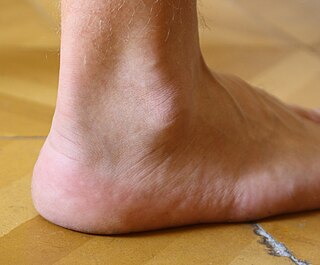
The ankle, the talocrural region or the jumping bone (informal) is the area where the foot and the leg meet. The ankle includes three joints: the ankle joint proper or talocrural joint, the subtalar joint, and the inferior tibiofibular joint. The movements produced at this joint are dorsiflexion and plantarflexion of the foot. In common usage, the term ankle refers exclusively to the ankle region. In medical terminology, "ankle" can refer broadly to the region or specifically to the talocrural joint.
A sprain is a soft tissue injury of the ligaments within a joint, often caused by a sudden movement abruptly forcing the joint to exceed its functional range of motion. Ligaments are tough, inelastic fibers made of collagen that connect two or more bones to form a joint and are important for joint stability and proprioception, which is the body's sense of limb position and movement. Sprains may be mild, moderate, or severe, with the latter two classes involving some degree of tearing of the ligament. Sprains can occur at any joint but most commonly occur in the ankle, knee, or wrist. An equivalent injury to a muscle or tendon is known as a strain.

The Maisonneuve fracture is a spiral fracture of the proximal third of the fibula associated with a tear of the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis and the interosseous membrane. There is an associated fracture of the medial malleolus or rupture of the deep deltoid ligament of the ankle. This type of injury can be difficult to detect.

A joint dislocation, also called luxation, occurs when there is an abnormal separation in the joint, where two or more bones meet. A partial dislocation is referred to as a subluxation. Dislocations are often caused by sudden trauma to the joint like an impact or fall. A joint dislocation can cause damage to the surrounding ligaments, tendons, muscles, and nerves. Dislocations can occur in any major joint or minor joint. The most common joint dislocation is a shoulder dislocation.

An ankle fracture is a break of one or more of the bones that make up the ankle joint. Symptoms may include pain, swelling, bruising, and an inability to walk on the injured leg. Complications may include an associated high ankle sprain, compartment syndrome, stiffness, malunion, and post-traumatic arthritis.

Hypermobility, also known as double-jointedness, describes joints that stretch farther than normal. For example, some hypermobile people can bend their thumbs backwards to their wrists and bend their knee joints backwards, put their leg behind the head or perform other contortionist "tricks". It can affect one or more joints throughout the body.
The knee examination, in medicine and physiotherapy, is performed as part of a physical examination, or when a patient presents with knee pain or a history that suggests a pathology of the knee joint.

The superior tibiofibular articulation is an arthrodial joint between the lateral condyle of tibia and the head of the fibula.

The triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) is formed by the triangular fibrocartilage discus (TFC), the radioulnar ligaments (RULs) and the ulnocarpal ligaments (UCLs).
Joint stability refers to the resistance offered by various musculoskeletal tissues that surround a skeletal joint. Several subsystems ensure the stability of a joint. These are the passive, active and neural subsystems. It is believed that one or more of the subsystems must have failed if joint instability occurs, usually a torn or overstretched ligament. Instability of joints can cause unhealthy ranges of movement in your joints, which can result in the joints fracturing.

Pellegrini–Stieda syndrome refers to the ossification of the superior part of the medial collateral ligament of the knee. It is a common incidental finding on knee radiographs. It is named for the Italian surgeon A. Pellegrini and the German surgeon A. Stieda (1869–1945). While the eponym is credited to Pellegrini and Stieda, the condition was first discovered by Köhler in 1903, before any namesakes. Pellegrini-Stieda combines the aforementioned radiographic findings and concomitant medial knee joint pain or restricted range of motion.

Genu recurvatum is a deformity in the knee joint, so that the knee bends backwards. In this deformity, excessive extension occurs in the tibiofemoral joint. Genu recurvatum is also called knee hyperextension and back knee. This deformity is more common in women and people with familial ligamentous laxity. Hyperextension of the knee may be mild, moderate or severe.
Anterior interval release (AIR) is a type of arthroscopic knee surgery performed to alleviate pain and associated symptoms caused by scar tissue accumulation in the anterior region of the knee, behind and under the knee cap, in a condition called arthrofibrosis. In normal, asymptomatic knees, this anterior compartment of the knee comprises mobile, scar-free tissues such as the infrapatellar (Hoffa's) fat pad. With progression, scar tissue leads to closure of the anterior interval, tethering the patella tendon and causing pain, loss of range of motion, damage to knee cartilage, and/or pain, among other symptoms.

The term sacroiliac joint dysfunction refers to abnormal motion in the sacroiliac joint, either too much motion or too little motion, that causes pain in this region.
Posterolateral corner injuries of the knee are injuries to a complex area formed by the interaction of multiple structures. Injuries to the posterolateral corner can be debilitating to the person and require recognition and treatment to avoid long term consequences. Injuries to the PLC often occur in combination with other ligamentous injuries to the knee; most commonly the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and posterior cruciate ligament (PCL). As with any injury, an understanding of the anatomy and functional interactions of the posterolateral corner is important to diagnosing and treating the injury.

Medial knee injuries are the most common type of knee injury. The medial ligament complex of the knee consists of:
Craniocervical instability (CCI) is a medical condition characterized by excessive movement of the vertebra at the atlanto-occipital joint and the atlanto-axial joint located between the skull and the top two vertebra, known as C1 and C2. The condition can cause neural injury and compression of nearby structures, including the brain stem, spinal cord, vagus nerve, and vertebral artery, resulting in a constellation of symptoms.
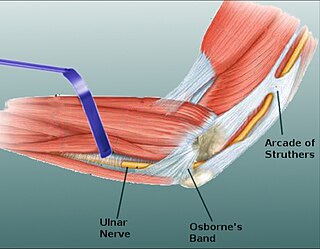
Osborne's ligament, also Osborne's band, Osborne's fascia, Osborne's arcade, arcuate ligament of Osborne, or the cubital tunnel retinaculum, refers to either the connective tissue which spans the humeral and ulnar heads of the flexor carpi ulnaris (FCU) or another distinct tissue located between the olecranon process of the ulna and the medial epicondyle of the humerus. It is named after Geoffrey Vaughan Osborne, a British orthopedic surgeon, who described the eponymous tissue in 1957.

Sinus tarsi syndrome is the clinical disorder of pain and tenderness in the sinus tarsi, which is a lateral tunnel in the foot at the junction of the hindfoot and the midfoot, between the ankle and the heel. Most of the time, sinus tarsi syndrome onsets after ankle sprains, however there can be other causes. There are a variety of treatments, divided into conservative treatments such as physical and orthotic therapy, and more invasive ones such as cortisone injections. The condition is somewhat poorly understood and is subject to heavy debate in the medical community.













