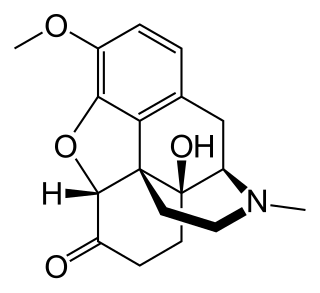
Oxycodone, sold under the brand name Roxicodone and OxyContin among others, is a semi-synthetic opioid used medically for the treatment of moderate to severe pain. It is highly addictive and is a commonly abused drug. It is usually taken by mouth, and is available in immediate-release and controlled-release formulations. Onset of pain relief typically begins within fifteen minutes and lasts for up to six hours with the immediate-release formulation. In the United Kingdom, it is available by injection. Combination products are also available with paracetamol (acetaminophen), ibuprofen, naloxone, naltrexone, and aspirin.

Dihydrocodeine is a semi-synthetic opioid analgesic prescribed for pain or severe dyspnea, or as an antitussive, either alone or compounded with paracetamol (acetaminophen) or aspirin. It was developed in Germany in 1908 and first marketed in 1911.

A natural product is a natural compound or substance produced by a living organism—that is, found in nature. In the broadest sense, natural products include any substance produced by life. Natural products can also be prepared by chemical synthesis and have played a central role in the development of the field of organic chemistry by providing challenging synthetic targets. The term natural product has also been extended for commercial purposes to refer to cosmetics, dietary supplements, and foods produced from natural sources without added artificial ingredients.
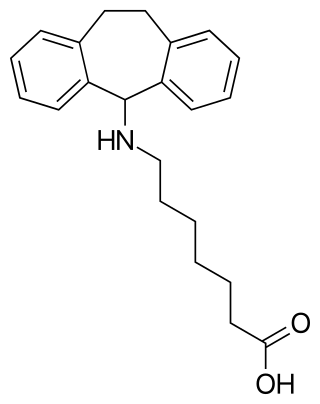
Amineptine, formerly sold under the brand name Survector among others, is an atypical antidepressant of the tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) family. It acts as a selective and mixed dopamine reuptake inhibitor and releasing agent, and to a lesser extent as a norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor.

Metamizole or dipyrone is a painkiller, spasm reliever, and fever reliever drug. It is most commonly given by mouth or by intravenous infusion. It belongs to the ampyrone sulfonate family of medicines and was patented in 1922. Metamizole is marketed under various trade names. It was first used medically in Germany under the brand name "Novalgin", later becoming widely known in Slavic nations and India under the name "Analgin".
Pyrazolone is 5-membered heterocycle containing two adjacent nitrogen atoms. It can be viewed as a derivative of pyrazole possessing an additional carbonyl (C=O) group. Compounds containing this functional group are useful commercially in analgesics and dyes.

Lofepramine, sold under the brand names Gamanil, Lomont, and Tymelyt among others, is a tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) which is used to treat depression. The TCAs are so named as they share the common property of having three rings in their chemical structure. Like most TCAs lofepramine is believed to work in relieving depression by increasing concentrations of the neurotransmitters norepinephrine and serotonin in the synapse, by inhibiting their reuptake. It is usually considered a third-generation TCA, as unlike the first- and second-generation TCAs it is relatively safe in overdose and has milder and less frequent side effects.

Desmetramadol, also known as O-desmethyltramadol (O-DSMT), is an opioid analgesic and the main active metabolite of tramadol. Tramadol is demethylated by the liver enzyme CYP2D6 to desmetramadol in the same way as codeine, and so similarly to the variation in effects seen with codeine, individuals who have a less active form of CYP2D6 will tend to have reduced analgesic effects from tramadol. Because desmetramadol itself does not need to be metabolized to induce an analgesic effect, it can be used in individuals with CYP2D6 inactivating mutations.

Bornaprine is a synthetic anticholinergic medication that is primarily used to treat Parkinson's disease. Additionally, bornaprine has been used to treat other disorders, including hyperhidrosis.

Tilidine, sold under the brand name Valoron among others, is a synthetic opioid analgesic, used mainly in Belgium, Bulgaria, Germany, Albania, Luxembourg, South Africa, and Switzerland for the treatment of moderate to severe pain, both acute and chronic. Its onset of pain relief after oral administration is about 10–15 minutes and peak relief from pain occurs about 25–50 minutes after administration.
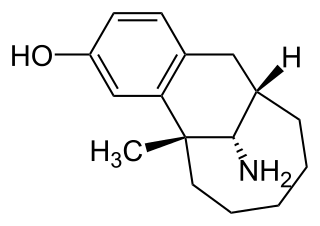
Dezocine, sold under the brand name Dalgan, is an atypical opioid analgesic which is used in the treatment of pain. It is used by intravenous infusion and intramuscular injection.

Nefopam, sold under the brand name Acupan among others, is a centrally acting, non-opioid painkilling medication, with central stimulant and sympathomimetic properties that is primarily used to treat moderate to severe pain.

Flupirtine is an aminopyridine that functions as a centrally acting non-opioid analgesic that was originally used as an analgesic for acute and chronic pain but in 2013 due to issues with liver toxicity, the European Medicines Agency restricted its use to acute pain, for no more than two weeks, and only for people who cannot use other painkillers. In March 2018, marketing authorisations for flupirtine were withdrawn following a European Medicines Agency recommendation based on the finding that the restrictions introduced in 2013 had not been sufficiently followed in clinical practice, and cases of serious liver injury still occurred including liver failure.
An equianalgesic chart is a conversion chart that lists equivalent doses of analgesics. Equianalgesic charts are used for calculation of an equivalent dose between different analgesics. Tables of this general type are also available for NSAIDs, benzodiazepines, depressants, stimulants, anticholinergics and others.
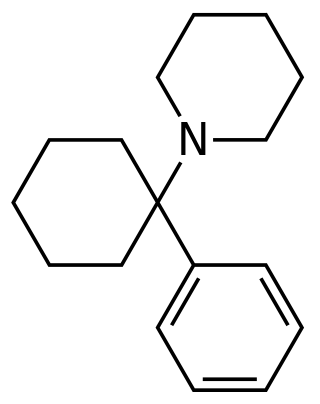
Arylcyclohexylamines, also known as arylcyclohexamines or arylcyclohexanamines, are a chemical class of pharmaceutical, designer, and experimental drugs.
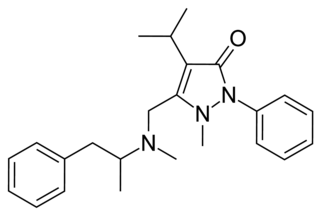
Famprofazone is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agent (NSAID) of the pyrazolone series which is available over-the-counter in some countries such as Taiwan. It has analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and antipyretic effects. Famprofazone has been known to produce methamphetamine as an active metabolite, with 15–20% of an oral dose being converted to it. As a result, famprofazone has occasionally been implicated in causing positives on drug tests for amphetamines.

MT-45 (IC-6) is an opioid analgesic drug invented in the 1970s by Dainippon Pharmaceutical Co. It is chemically a 1-substituted-4-(1,2-diphenylethyl) piperazine derivative, which is structurally unrelated to most other opioid drugs. Racemic MT-45 has around 80% the potency of morphine, with almost all opioid activity residing in the (S) enantiomer. It has been used as a lead compound from which a large family of potent opioid drugs have been developed, including full agonists, partial agonists, and antagonists at the three main opioid receptor subtypes. Fluorinated derivatives of MT-45 such as 2F-MT-45 are significantly more potent as μ-opioid receptor agonists, and one of its main metabolites 1,2-diphenylethylpiperazine also blocks NMDA receptors.
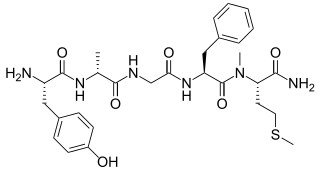
Metkefamide (INN; LY-127,623), or metkephamid acetate (USAN), but most frequently referred to simply as metkephamid, is a synthetic opioid pentapeptide and derivative of [Met]enkephalin with the amino acid sequence Tyr-D-Ala-Gly-Phe-(N-Me)-Met-NH2. It behaves as a potent agonist of the δ- and μ-opioid receptors with roughly equipotent affinity, and also has similarly high affinity as well as subtype-selectivity for the κ3-opioid receptor.

Difenamizole (INN; brand name Pasalin; former developmental code name AP-14) is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) and analgesic of the pyrazolone group related to metamizole. It has monoaminergic properties, including inhibition of monoamine oxidase, augmentation of pargyline-induced elevation of striatal dopamine levels, inhibition of K+-induced striatal dopamine release, and inhibition of the reuptake of dopamine.
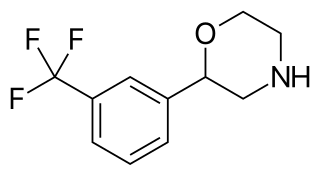
Flumexadol (INN) is a drug described and researched as a non-opioid analgesic which was never marketed. It has been found to act as an agonist of the serotonin 5-HT1A and 5-HT2C receptors and, to a much lesser extent, of the 5-HT2A receptor. According to Nilsson (2006) in a paper on 5-HT2C receptor agonists as potential anorectics, "The (+)-enantiomer of this compound showed [...] affinity for the 5-HT2C receptor (Ki) 25 nM) [...] and was 40-fold selective over the 5-HT2A receptor in receptor binding studies. The racemic version [...], also known as 1841 CERM, was originally reported to possess analgesic properties while no association with 5-HT2C receptor activity was mentioned." It is implied that flumexadol might be employable as an anorectic in addition to analgesic. Though flumexadol itself has never been approved for medical use, oxaflozane is a prodrug of the compound that was formerly used clinically in France as an antidepressant and anxiolytic agent.


















