
5-HT receptors, 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors, or serotonin receptors, are a group of G protein-coupled receptor and ligand-gated ion channels found in the central and peripheral nervous systems. They mediate both excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmission. The serotonin receptors are activated by the neurotransmitter serotonin, which acts as their natural ligand.
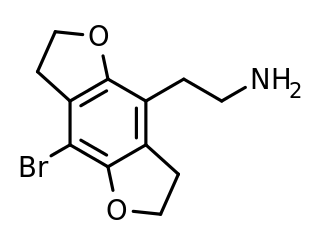
2C-BFLY is a psychedelic phenethylamine and designer drug of the 2C family. It was first synthesized in 1996 by Aaron Monte, Professor of Chemistry at UW-La Crosse.

The 5-HT2A receptor is a subtype of the 5-HT2 receptor that belongs to the serotonin receptor family and is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR). The 5-HT2A receptor is a cell surface receptor, but has several intracellular locations.

A serotonin receptor agonist is an agonist of one or more serotonin receptors. They activate serotonin receptors in a manner similar to that of serotonin, a neurotransmitter and hormone and the endogenous ligand of the serotonin receptors.

Jimscaline (C-(4,5,6-trimethoxyindan-1-yl)methanamine) is a conformationally-restricted derivative of the cactus-derived hallucinogen mescaline, which was discovered in 2006 by a team at Purdue University led by David E. Nichols. It acts as a potent agonist for the 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors with the more active (R)-enantiomer having a Ki of 69 nM at the human 5-HT2A receptor, and around three times the potency of mescaline in drug-substitution experiments in animals. This discovery that the side chain of the phenethylamine hallucinogens could be constrained to give chiral ligands with increased activity then led to the later development of the super-potent benzocyclobutene derivative TCB-2.
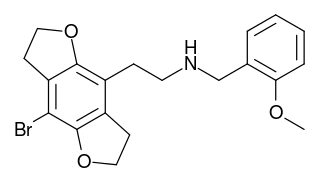
2CBFly-NBOMe is a compound indirectly derived from the phenethylamine hallucinogen 2C-B, and related to benzodifurans like 2C-B-FLY and N-benzylphenethylamines like 25I-NBOMe. It was discovered in 2002, and further researched by Ralf Heim at the Free University of Berlin, and subsequently investigated in more detail by a team at Purdue University led by David E. Nichols. It acts as a potent partial agonist for the 5-HT2A serotonin receptor subtype.

TFMFly is a compound related to psychedelic phenethylamines such as 2C-B-FLY and 2C-TFM. It was first reported in 2005 by a team at Purdue University led by David Nichols. It acts as a potent agonist at the 5HT2A serotonin receptor subtype, and is a chiral compound with the more active (R) enantiomer having a Ki of 0.12 nM at the human 5-HT2A receptor. While the fully aromatic benzodifurans such as Bromo-DragonFLY generally have higher binding affinity than saturated compounds like 2C-B-FLY, the saturated compounds have higher efficacy as agonists.
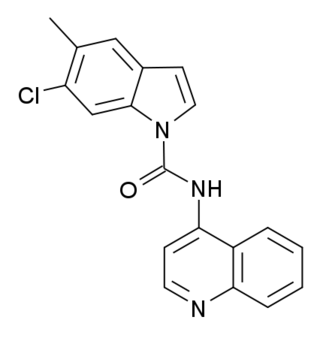
SB-215505 is a drug which acts as a potent and selective antagonist at the serotonin 5-HT2B receptor, with good selectivity over the related 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors. It is used in scientific research into the function of the 5-HT2 family of receptors, especially to study the role of 5-HT2B receptors in the heart, and to distinguish 5-HT2B-mediated responses from those produced by 5-HT2A or 5-HT2C.

25B-NBOMe is a derivative of the phenethylamine psychedelic 2C-B, discovered in 2004 by Ralf Heim at the Free University of Berlin. It acts as a potent full agonist for the 5HT2A receptor. Anecdotal reports from users suggest 25B-NBOMe to be an active hallucinogen at a dose of as little as 250–500 μg, making it a similar potency to other phenethylamine derived hallucinogens such as Bromo-DragonFLY. Duration of effects lasts about 12–16 hours, although the parent compound is rapidly cleared from the blood when used in the radiolabeled form in tracer doses. Recently, Custodio et al. (2019) evaluated the potential involvement of dysregulated dopaminergic system, neuroadaptation, and brain wave changes which may contribute to the rewarding and reinforcing properties of 25B-NBOMe in rodents.

Pruvanserin is a selective 5-HT2A receptor antagonist which was under development by Eli Lilly and Company for the treatment of insomnia. It was in phase II clinical trials in 2008 but appears to have been discontinued as it is no longer in the company's development pipeline. In addition to its sleep-improving properties, pruvanserin has also been shown to have antidepressant, anxiolytic, and working memory-enhancing effects in animal studies.

2CB-Ind is a conformationally-restricted derivative of the phenethylamine hallucinogen 2C-B, discovered in 1974 by Alexander Shulgin. It acts as a moderately potent and selective agonist for the 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors, but unlike the corresponding benzocyclobutene derivative TCB-2 which is considerably more potent than the parent compound 2C-B, 2CB-Ind is several times weaker, with racemic 2CB-Ind having a Ki of 47nM at the human 5-HT2A receptor, only slightly more potent than the mescaline analogue (R)-jimscaline.

25TFM-NBOMe is a derivative of the phenethylamine hallucinogen 2C-TFM, discovered in 2004 by Ralf Heim at the Free University of Berlin. It acts as a potent partial agonist for the 5-HT2A receptor, though its relative potency is disputed, with some studies finding it to be of lower potency than 25I-NBOMe, while others show it to be of similar or higher potency, possibly because of differences in the assay used. 2C-TFM-NB2OMe can be taken to produce psychedelic effects similar to 2C-I-NB2OMe and 2C-D-NB2OMe.

SB-206553 is a drug which acts as a mixed antagonist for the 5-HT2B and 5-HT2C serotonin receptors. It has anxiolytic properties in animal studies and interacts with a range of other drugs. It has also been shown to act as a positive allosteric modulator of α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Modified derivatives of SB-206553 have been used to probe the structure of the 5-HT2B receptor.

The head-twitch response (HTR) is a rapid side-to-side head movement that occurs in mice and rats after the serotonin 5-HT2A receptor is activated. The prefrontal cortex may be the neuroanatomical locus mediating the HTR. Many serotonergic hallucinogens, including lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD), induce the head-twitch response, and so the HTR is used as a behavioral model of hallucinogen effects. However while there is generally a good correlation between compounds that induce head twitch in mice and compounds that are hallucinogenic in humans, it is unclear whether the head twitch response is primarily caused by 5-HT2A receptors, 5-HT2C receptors or both, though recent evidence shows that the HTR is mediated by the 5-HT2A receptor and modulated by the 5-HT2C receptor. Also, the effect can be non-specific, with head twitch responses also produced by some drugs that do not act through 5-HT2 receptors, such as phencyclidine, yohimbine, atropine and cannabinoid receptor antagonists. As well, compounds such as 5-HTP, fenfluramine, 1-Methylpsilocin, Ergometrine, and 3,4-di-methoxyphenethylamine (DMPEA) can also produce head twitch and do stimulate serotonin receptors, but are not hallucinogenic in humans. This means that while the head twitch response can be a useful indicator as to whether a compound is likely to display hallucinogenic activity in humans, the induction of a head twitch response does not necessarily mean that a compound will be hallucinogenic, and caution should be exercised when interpreting such results.

25CN-NBOH is a compound indirectly derived from the phenethylamine series of hallucinogens, which was discovered in 2014 at the University of Copenhagen. This compound is notable as one of the most selective agonist ligands for the 5-HT2A receptor yet discovered, with a pKi of 8.88 at the human 5-HT2A receptor and with 100x selectivity for 5-HT2A over 5-HT2C, and 46x selectivity for 5-HT2A over 5-HT2B. A tritiated version of 25CN-NBOH has also been accessed and used for more detailed investigations of the binding to 5-HT2 receptors and autoradiography.

SB-243213 is a research chemical which acts as a selective inverse agonist for the 5HT2C receptor and has anxiolytic effects. It has better than 100x selectivity for 5-HT2C over all other receptor subtypes tested, and a longer duration of action compared to older 5-HT2C antagonist ligands.
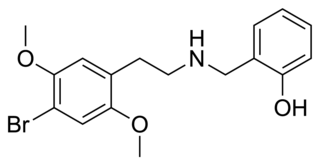
25B-NBOH is a derivative of the phenethylamine derived hallucinogen 2C-B which has been sold as a designer drug. It acts as a potent serotonin receptor agonist with similar affinity to the better-known compound 25B-NBOMe at 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors with pKis values of 8.3 and 9.4, respectively.
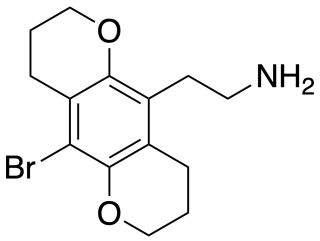
2C-B-BUTTERFLY is a conformationally-restricted derivative of the phenethylamine hallucinogen 2C-B, which was discovered in 1999 by Michael S. Whiteside and Aaron Monte. It is a ring-expanded homologue of the better known compound 2C-B-FLY, and has similar properties as an agonist for serotonin receptors, but with more selectivity for 5-HT2C over 5-HT2A.

The 25-NB (25x-NBx) series, sometimes alternatively referred to as the NBOMe compounds, is a family of serotonergic psychedelics. They are substituted phenethylamines and were derived from the 2C family. They act as selective agonists of the serotonin 5-HT2A receptor. The 25-NB family is unique relative to other classes of psychedelics in that they are, generally speaking, extremely potent and relatively selective for the 5-HT2A receptor. Use of NBOMe series drugs has caused many deaths and hospitalisations since the drugs popularisation in the 2010s. This is primarily due to their high potency, unpredictable pharmacokinetics, and sellers passing off the compounds in the series as LSD.

WAY-163,909 is a drug which acts as a potent and reasonably selective agonist for the serotonin 5-HT2C receptor. It has antipsychotic-like effects in animal models, and has been used to study the role of the 5-HT2C receptor subtype in the action of addictive drugs such as nicotine and methamphetamine.




















