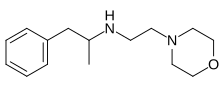
Ephedrine is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant that is often used to prevent low blood pressure during anesthesia. It has also been used for asthma, narcolepsy, and obesity but is not the preferred treatment. It is of unclear benefit in nasal congestion. It can be taken by mouth or by injection into a muscle, vein, or just under the skin. Onset with intravenous use is fast, while injection into a muscle can take 20 minutes, and by mouth can take an hour for effect. When given by injection it lasts about an hour and when taken by mouth it can last up to four hours.
An international nonproprietary name (INN) is an official generic and nonproprietary name given to a pharmaceutical drug or an active ingredient. INNs are intended to make communication more precise by providing a unique standard name for each active ingredient, to avoid prescribing errors. The INN system has been coordinated by the World Health Organization (WHO) since 1953.

Dimethoxybromoamphetamine (DOB), also known as brolamfetamine (INN) and bromo-DMA, is a psychedelic drug and substituted amphetamine of the phenethylamine class of compounds. DOB was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin in 1967. Its synthesis and effects are documented in Shulgin's book PiHKAL: A Chemical Love Story.
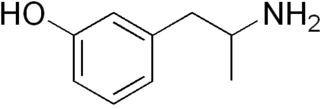
3-Hydroxyamphetamine, also known as meta-hydroxyamphetamine, and α-methyl-meta-tyramine, is an antihypotensive or sympathomimetic agent of the amphetamine family that is marketed in certain European countries.
Substituted amphetamines are a class of compounds based upon the amphetamine structure; it includes all derivative compounds which are formed by replacing, or substituting, one or more hydrogen atoms in the amphetamine core structure with substituents. The compounds in this class span a variety of pharmacological subclasses, including stimulants, empathogens, and hallucinogens, among others. Examples of substituted amphetamines are amphetamine (itself), methamphetamine, ephedrine, cathinone, phentermine, mephentermine, tranylcypromine, bupropion, methoxyphenamine, selegiline, amfepramone (diethylpropion), pyrovalerone, MDMA (ecstasy), and DOM (STP).

Fenbutrazate (INN), also known as phenbutrazate (BAN), is a psychostimulant used as an appetite suppressant under the trade names Cafilon, Filon, and Sabacid in Europe, Japan, and Hong Kong. It is a derivative of phenmetrazine and may function as a prodrug due to its similarity to phendimetrazine.

Aloracetam (INN) is a drug described as a nootropic which is closely related to, but technically not of, the racetam family of compounds. It was studied by Aventis for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease, but was never marketed.

Nisobamate is a tranquilizer of the carbamate family which was never marketed.
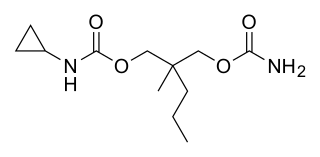
Lorbamate is a muscle relaxant and tranquilizer of the carbamate family which was never marketed.

Tetrabarbital is a barbiturate derivative used as a hypnotic.

Formetorex (INN), also known as formetamide or N-formylamphetamine, is a substituted amphetamine described as an anorectic which does not appear to have ever been marketed.

Berefrine, also known as burefrine, is a sympathomimetic and mydriatic agent that was never marketed. It is an oxazolidine prodrug of phenylephrine, and hence, an α1-adrenergic receptor agonist.
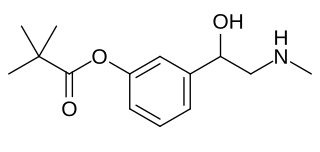
Pivenfrine (INN), also known as pivalylphenylephrine, is a sympathomimetic and mydriatic agent.

Picilorex is an anorectic which is no longer marketed. It is a monoamine reuptake inhibitor, a stimulant as well as a derivate of Pyrrolidine.

Acridorex is an amphetamine which was investigated as an anorectic but does not appear to have ever been marketed.

Oxifentorex (INN) is an amphetamine described as an anorectic which does not appear to have ever been marketed.

Fenisorex is an amphetamine-like anorectic drug which does not appear to have ever been marketed.

Flucetorex (INN) is an amphetamine. It was investigated as an anorectic, but does not appear to have been marketed. It is related to fenfluramine.
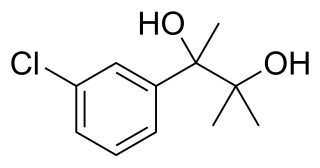
Metaglycodol (INN) is a drug described as a tranquilizer which was never marketed.

Pipoxizine is a first-generation antihistamine as well as serotonin antagonist of the diphenylmethylpiperazine group related to hydroxyzine. It was investigated as a bronchodilator but was never marketed.