
Fenfluramine, sold under the brand name Fintepla, is a serotonergic medication used for the treatment of seizures associated with Dravet syndrome and Lennox–Gastaut syndrome. It was formerly used as an appetite suppressant in the treatment of obesity, but was discontinued for this use due to cardiovascular toxicity before being repurposed for new indications. Fenfluramine was used for weight loss both alone under the brand name Pondimin and in combination with phentermine commonly known as fen-phen.

Chlorphentermine, sold under the brand names Apsedon, Desopimon, and Lucofen, is a serotonergic appetite suppressant of the amphetamine family. Developed in 1962, it is the para-chloro derivative of the better-known appetite suppressant phentermine, which is still in current use.

Norfenfluramine, or 3-trifluoromethylamphetamine, is a never-marketed drug of the amphetamine family and a major active metabolite of the appetite suppressants fenfluramine and benfluorex. The compound is a racemic mixture of two enantiomers with differing activities, dexnorfenfluramine and levonorfenfluramine.

Indanorex (Dietor) is a stimulant drug which was developed in the 1970s. It has appetite suppressant effects and also has antihypoglycemia effects.

MEAI, also known as 5-methoxy-2-aminoindane (5-MeO-AI), is a monoamine releasing agent of the 2-aminoindane group. It specifically acts as a selective serotonin releasing agent (SSRA). The drug is under development for the treatment of alcoholism, cocaine use disorder, metabolic syndrome, and obesity under the developmental code name CMND-100.

para-Chloroamphetamine (PCA), also known as 4-chloroamphetamine (4-CA), is a serotonin–norepinephrine–dopamine releasing agent (SNDRA) and serotonergic neurotoxin of the amphetamine family. It is used in scientific research in the study of the serotonin system, as a serotonin releasing agent (SRA) at lower doses to produce serotonergic effects, and as a serotonergic neurotoxin at higher doses to produce long-lasting depletions of serotonin.

MDAI, also known as 5,6-methylenedioxy-2-aminoindane, is an entactogen drug of the 2-aminoindane group which is related to MDMA and produces similar subjective effects.

A monoamine releasing agent (MRA), or simply monoamine releaser, is a drug that induces the release of one or more monoamine neurotransmitters from the presynaptic neuron into the synapse, leading to an increase in the extracellular concentrations of the neurotransmitters and hence enhanced signaling by those neurotransmitters. The monoamine neurotransmitters include serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine; MRAs can induce the release of one or more of these neurotransmitters.

3-Methoxy-4-methylamphetamine (MMA) is an entactogen and psychedelic drug of the phenethylamine and amphetamine classes. It was first synthesized in 1970 and was encountered as a street drug in Italy in the same decade. MMA was largely forgotten until being reassayed by David E. Nichols as a non-neurotoxic MDMA analogue in 1991, and has subsequently been sold as a designer drug on the internet since the late 2000s.
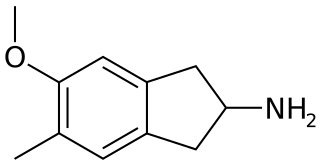
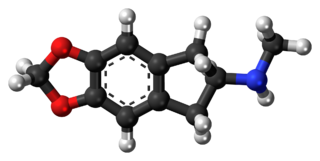
5-Methoxy-6-methyl-2-aminoindane (MMAI) is a drug of the 2-aminoindane group developed in the 1990s by a team led by David E. Nichols at Purdue University. It acts as a less neurotoxic and highly selective serotonin releasing agent (SSRA) and produces entactogenic effects in humans. It has been sold as a designer drug and research chemical online since 2010.
5,6-Methylenedioxy-N-methyl-2-aminoindane (MDMAI), is a drug of the 2-aminoindane group developed in the 1990s by a team led by David E. Nichols at Purdue University. It acts as a non-neurotoxic and highly selective serotonin releasing agent (SSRA) in animals and a putative entactogen in humans.

5-Iodo-2-aminoindane (5-IAI) is an entactogen drug of the 2-aminoindane group. Human anecdotal reports suggest that it is entactogenic but produces little euphoria or stimulation.

2-Aminoindane (2-AI) is an aminoindane and research chemical with applications in neurologic disorders and psychotherapy that has also been sold as a designer drug. It acts as a selective substrate for NET and DAT.

A serotonin releasing agent (SRA) is a type of drug that induces the release of serotonin into the neuronal synaptic cleft. A selective serotonin releasing agent (SSRA) is an SRA with less significant or no efficacy in producing neurotransmitter efflux at other types of monoamine neurons, including dopamine and norepinephrine neurons.

N-Ethyl-5-trifluoromethyl-2-aminoindane (ETAI) is a drug of the 2-aminoindane group with putative entactogenic effects. It functions as a selective serotonin releasing agent (SSRA). ETAI is the aminoindane analogue of fenfluramine and is approximately 50% as neurotoxic in comparison.

para-Iodoamphetamine (PIA), also known as 4-iodoamphetamine (4-IA), is a monoamine releasing agent (MRA) and serotonergic neurotoxin of the amphetamine family related to para-chloroamphetamine (PCA).

3-Methoxyamphetamine (3-MA), also known as meta-methoxyamphetamine (MMA), is a monoamine releasing agent (MRA) of the amphetamine family. It is a positional isomer of para-methoxyamphetamine.

Levofenfluramine (INN), or (−)-3-trifluoromethyl-N-ethylamphetamine, also known as (−)-fenfluramine or (R)-fenfluramine, is a drug of the amphetamine family that, itself (i.e., in enantiopure form), was never marketed. It is the levorotatory enantiomer of fenfluramine, the racemic form of the compound, whereas the dextrorotatory enantiomer is dexfenfluramine. Both fenfluramine and dexfenfluramine are anorectic agents that have been used clinically in the treatment of obesity (and hence, levofenfluramine has been as well since it is a component of fenfluramine). However, they have since been discontinued due to reports of causing cardiovascular conditions such as valvular heart disease and pulmonary hypertension, adverse effects that are likely to be caused by excessive stimulation of 5-HT2B receptors expressed on heart valves.

NM-2-AI, also known as N-methyl-2-aminoindane, is a drug of the 2-aminoindane group that has been sold online as a designer drug. It is a rigid analogue of methamphetamine. NM-2-AI acts as a selective norepinephrine releasing agent, but also has affinity for several monoamine receptors.

A monoamine neurotoxin, or monoaminergic neurotoxin, is a drug that selectively damages or destroys monoaminergic neurons. Monoaminergic neurons are neurons that signal via stimulation by monoamine neurotransmitters including serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine.




















