Pemoline, sold under the brand name Cylert among others, is a stimulant medication which has been used in the treatment of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy. It has been discontinued in most countries due to rare but serious problems with liver toxicity. The medication was taken by mouth.

4-Methylaminorex is a stimulant drug of the 2-amino-5-aryloxazoline class that was first synthesized in 1960 by McNeil Laboratories. It is also known by its street name "U4Euh" ("Euphoria"). It is banned in many countries as a stimulant.

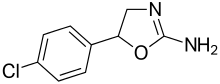
Aminorex is a weight loss (anorectic) stimulant drug. It was withdrawn from the market after it was found to cause pulmonary hypertension. In the U.S., it is an illegal Schedule I drug, meaning it has high abuse potential, no accepted medical use, and a poor safety profile.

Levamisole, sold under the brand name Ergamisol among others, is a medication used to treat parasitic worm infections, specifically ascariasis and hookworm infections. It is taken by mouth.

Fenozolone (Ordinator) was developed by Laboratoires Dausse in the 1960s and is a psychostimulant related to pemoline.

Prolintane is a stimulant and norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitor developed in the 1950s. Being an amphetamine derivative, it is closely related in chemical structure to other drugs such as pyrovalerone, MDPV, and propylhexedrine and it has a similar mechanism of action. Many cases of prolintane abuse have been reported.
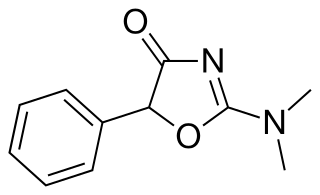
Thozalinone (USAN) is a psychostimulant that has been used as an antidepressant in Europe. It has also been trialed as an anorectic. Thozalinone is described as a "dopaminergic stimulant", and likely acts via inducing the release of dopamine and to a minimal extent norepinephrine; similar to analogue pemoline, it is reportedly devoid of abuse potential unlike other dopaminergic psychostimulants.

Fluminorex is a centrally acting sympathomimetic which is related to other drugs such as aminorex and pemoline. It was developed as an appetite suppressant by McNeil Laboratories in the 1950s.

Cyclazodone is a centrally acting stimulant drug developed by American Cyanamid Company in the 1960s. The drug is related to other drugs such as pemoline and thozalinone. It displayed a favorable therapeutic index and margin of safety in comparison to pemoline and other N-lower-alkyl-substituted pemoline derivatives. The patents concluded that cyclazodone possessed properties efficacious in reducing fatigue and as a potential anorectic. Structural congeners of pemoline have been described as "excitants with unique properties distinguishing them from the sympathomimetic amines" whilst displaying less stimulatory activity and toxicity compared to amphetamine.

The Decree-Law 15/93 of January 22 is a Portuguese drug control law implementing the 1988 United Nations Convention Against Illicit Traffic in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances.
A dopamine releasing agent (DRA) is a type of drug which induces the release of dopamine in the body and/or brain. No selective and robust DRAs are currently known. On the other hand, many releasing agents of both dopamine and norepinephrine and of serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine are known. Serotonin–dopamine releasing agents (SDRAs), for instance 5-chloro-αMT, are much more rare and are not selective for dopamine release but have also been developed. Examples of major NDRAs include the psychostimulants amphetamine and methamphetamine, while an example of an SNDRA is the entactogen methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA). These drugs are frequently used for recreational purposes and encountered as drugs of abuse. Selective DRAs, as well as NDRAs, have medical applications in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
The major drug laws of India are the Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act (1985) and the Prevention of Illicit Trafficking in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act (1988).

4,4'-Dimethylaminorex, sometimes referred to by the street name "Serotoni", is a psychostimulant and entactogen designer drug related to aminorex, 4-methylaminorex, and pemoline. It was first detected in the Netherlands in December 2012, and has been sold as a designer drug around Europe since mid-2013.
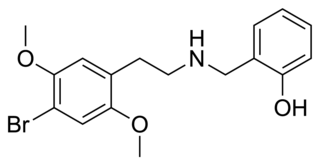
25B-NBOH is a derivative of the phenethylamine derived hallucinogen 2C-B which has been sold as a designer drug. It acts as a potent serotonin receptor agonist with similar affinity to the better-known compound 25B-NBOMe at 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors with pKis values of 8.3 and 9.4, respectively.

Substituted phenylmorpholines, or substituted phenmetrazines alternatively, are chemical derivatives of phenylmorpholine or of the psychostimulant drug phenmetrazine. Most such compounds act as releasers of monoamine neurotransmitters, and have stimulant effects. Some also act as agonists at serotonin receptors, and compounds with an N-propyl substitution act as dopamine receptor agonists. A number of derivatives from this class have been investigated for medical applications, such as for use as anorectics or medications for the treatment of ADHD. Some compounds have also become subject to illicit use as designer drugs.
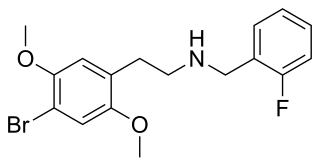
25B-NBF is a derivative of the phenethylamine hallucinogen 2C-B, which acts as a highly potent partial agonist for the human 5-HT2A receptor.
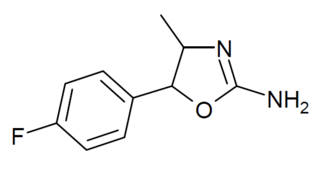
4'-Fluoro-4-methylaminorex is a recreational designer drug from the substituted aminorex family, with stimulant effects. It was first detected in Slovenia in 2018. It was made illegal in Italy in March 2020.

3',4'-Methylenedioxy-4-methylaminorex (MDMAR) is a recreational designer drug from the substituted aminorex family, with monoamine releasing effects.
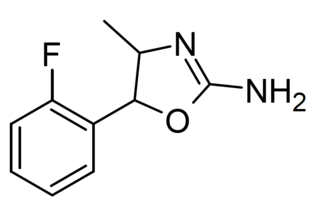
2'-Fluoro-4-methylaminorex is a recreational designer drug from the substituted aminorex family, with stimulant effects, first reported in 2018.