A heterocyclic compound or ring structure is a cyclic compound that has atoms of at least two different elements as members of its ring(s). Heterocyclic chemistry is the branch of organic chemistry dealing with the synthesis, properties, and applications of these heterocycles.

The Povarov reaction is an organic reaction described as a formal cycloaddition between an aromatic imine and an alkene. The imine in this organic reaction is a condensation reaction product from an aniline type compound and a benzaldehyde type compound. The alkene must be electron rich which means that functional groups attached to the alkene must be able to donate electrons. Such alkenes are enol ethers and enamines. The reaction product in the original Povarov reaction is a quinoline. Because the reactions can be carried out with the three components premixed in one reactor it is an example of a multi-component reaction.

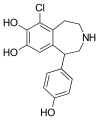
Fenoldopam mesylate (Corlopam) is a drug and synthetic benzazepine derivative which acts as a selective D1 receptor partial agonist. Fenoldopam is used as an antihypertensive agent. It was approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in September 1997.
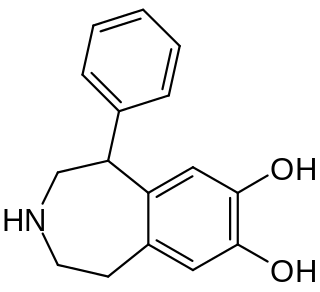
SKF-38,393 is a synthetic compound of the benzazepine chemical class which acts as a selective D1/D5 receptor partial agonist. It has stimulant and anorectic effects.

SKF-82,958 is a synthetic compound of the benzazepine class that acts as a D1/D5 receptor full agonist. SKF-82,958 and similar D1-like-selective full agonists like SKF-81,297 and 6-Br-APB produce characteristic anorectic effects, hyperactivity and self-administration in animals, with a similar but not identical profile to that of dopaminergic stimulants such as amphetamine. SKF-82,958 was also subsequently found to act as an agonist of ERα with negligible activity at ERβ, making it a subtype-selective estrogen.

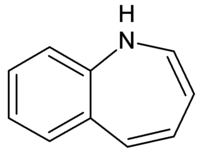
Azepines are unsaturated heterocycles of seven atoms, with a nitrogen replacing a carbon at one position.

The benzhydryl compounds are a group of organic compounds whose parent structures include diphenylmethane, with any number of attached substituents, including bridges. This group typically excludes compounds in which either benzene is fused to another ring or includes a heteroatom, or where the methane connects to three or four benzenes.

Dibenzazepine (iminostilbene) is a chemical compound with two benzene rings fused to an azepine group.

Dopamine receptor D1, also known as DRD1, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DRD1 gene.
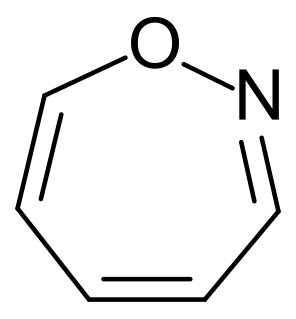
Oxazepines are a family of unsaturated heterocycles containing seven atoms, with a nitrogen replacing a carbon at one position and with an oxygen replacing a carbon at one position.

Lorcaserin, marketed under the brand name Belviq is a weight-loss drug developed by Arena Pharmaceuticals. It reduces appetite by activating a type of serotonin receptor known as the 5-HT2C receptor in a region of the brain called the hypothalamus, which is known to control appetite. It was removed from the market in the United States in 2020 due to its increased risk of cancer.

SKF-83,959 is a synthetic benzazepine derivative used in scientific research which acts as an agonist at the D1-D2 dopamine receptor. It behaves as a full agonist at the D1 protomer and a high-affinity partial agonist at the D2 protomer. It was further shown to act as an allosteric modulator of the sigma-1 receptor. SKF-83,959 is a racemate that consists of the R-(+)- and S-(−)-enantiomers MCL 202 and MCL 201, respectively. SKF-83,959 inhibits sodium channels as well as delayed rectifier potassium channels.

6-Br-APB is a synthetic compound that acts as a selective D1 agonist, with the (R)-enantiomer being a potent full agonist, while the (S) enantiomer retains its D1 selectivity but is a weak partial agonist. (R)-6-Br-APB and similar D1-selective full agonists like SKF-81,297 and SKF-82,958 produce characteristic anorectic effects, stereotyped behaviour and self-administration in animals, with a similar but not identical profile to that of dopaminergic stimulants such as amphetamine.

SKF-81,297 is a synthetic drug of the benzazepine chemical class that acts as a selective dopamine D1/D5 receptor full agonist, and produces a characteristic stimulant-like pattern of anorexia, hyperactivity and self-administration in animals. This profile is shared with several related drugs such as 6-Br-APB and SKF-82,958, but not with certain other D1 full agonists such as A-77,636, reflecting functional selectivity of D1 activation. Newer findings reveal that SKF-81,297 additionally acts as a partial agonist at D1-D2 receptor heteromers.

SKF-89,145 is a drug which acts as a dopamine agonist selective for the D1 subtype. The N-desmethyl derivative SKF-89,626 is also a selective D1 agonist with similar potency and selectivity to SKF 89,145.

Corey lactone 4-phenylbenzoate is a synthetic intermediate used in the manufacture of some prostaglandin derivatives. It has been used as a false name by some designer drug manufacturers as a label to sell substituted cathinone derivatives after the banning of mephedrone and related drugs in some jurisdictions - but there is no evidence to suggest that Corey lactone 4-phenylbenzoate has any stimulant effects in its own right.
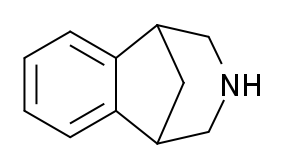
2,3,4,5-Tetrahydro-1,5-methano-1H-3-benzazepine is a drug originally researched as a potential opioid analgesic, but was found to be inactive in this assay, and relatively toxic to mice. Subsequently it was found to possess activity as an agonist at nicotinic acetylcholine receptors during the course of work that ultimately led to the discovery of the anti-smoking drug varenicline.

Anilopam is an opioid analgesic of the benzazepine class which was developed by Pentwell in the 1960s but was never marketed.

Trepipam (INN) is a dopamine receptor agonist of the benzazepine group that was never marketed.
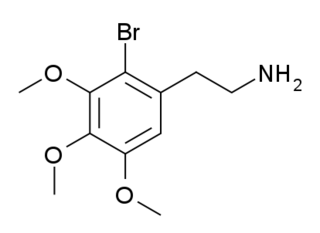
2-Bromomescaline (2-Br-M) is a derivative of the phenethylamine hallucinogen mescaline which has an unusual 2-bromo substitution. It is an agonist for serotonin receptors, with a binding affinity of 215 nM at 5-HT1A, 513 nM at 5-HT2A and 379 nM at 5-HT2C, so while it is around ten times more tightly binding than mescaline at 5-HT1A and 5-HT2A receptors, it is over twenty times more potent at 5-HT2C.