Amphetamine is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant that is used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), narcolepsy, and obesity. Amphetamine was discovered in 1887 and exists as two enantiomers: levoamphetamine and dextroamphetamine. Amphetamine properly refers to a specific chemical, the racemic free base, which is equal parts of the two enantiomers in their pure amine forms. The term is frequently used informally to refer to any combination of the enantiomers, or to either of them alone. Historically, it has been used to treat nasal congestion and depression. Amphetamine is also used as an athletic performance enhancer and cognitive enhancer, and recreationally as an aphrodisiac and euphoriant. It is a prescription drug in many countries, and unauthorized possession and distribution of amphetamine are often tightly controlled due to the significant health risks associated with recreational use.

Stimulants is an overarching term that covers many drugs including those that increase the activity of the central nervous system and the body, drugs that are pleasurable and invigorating, or drugs that have sympathomimetic effects. Stimulants are widely used throughout the world as prescription medicines as well as without a prescription as performance-enhancing or recreational drugs. Among narcotics, stimulants produce a noticeable crash or comedown at the end of their effects. The most frequently prescribed stimulants as of 2013 were lisdexamfetamine (Vyvanse), methylphenidate (Ritalin), and amphetamine (Adderall). It was estimated in 2015 that the percentage of the world population that had used cocaine during a year was 0.4%. For the category "amphetamines and prescription stimulants" the value was 0.7%, and for MDMA 0.4%.

Ephedrine is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant that is often used to prevent low blood pressure during anesthesia. It has also been used for asthma, narcolepsy, and obesity but is not the preferred treatment. It is of unclear benefit in nasal congestion. It can be taken by mouth or by injection into a muscle, vein, or just under the skin. Onset with intravenous use is fast, while injection into a muscle can take 20 minutes, and by mouth can take an hour for effect. When given by injection it lasts about an hour and when taken by mouth it can last up to four hours.

Phenylpropanolamine (PPA) is a sympathomimetic agent which is used as a decongestant and appetite suppressant. It was commonly used in prescription and over-the-counter cough and cold preparations. In veterinary medicine, it is used to control urinary incontinence in dogs.

Adderall and Mydayis are trade names for a combination drug called mixed amphetamine salts containing four salts of amphetamine. The mixture is composed of equal parts racemic amphetamine and dextroamphetamine, which produces a (3:1) ratio between dextroamphetamine and levoamphetamine, the two enantiomers of amphetamine. Both enantiomers are stimulants, but differ enough to give Adderall an effects profile distinct from those of racemic amphetamine or dextroamphetamine, which are marketed as Evekeo and Dexedrine/Zenzedi, respectively. Adderall is used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy. It is also used illicitly as an athletic performance enhancer, cognitive enhancer, appetite suppressant, and recreationally as a euphoriant. It is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant of the phenethylamine class.

Phenylacetone, also known as phenyl-2-propanone, is an organic compound with the chemical formula C6H5CH2COCH3. It is a colorless oil that is soluble in organic solvents. It is a mono-substituted benzene derivative, consisting of an acetone attached to a phenyl group. As such, its systematic IUPAC name is 1-phenyl-2-propanone.
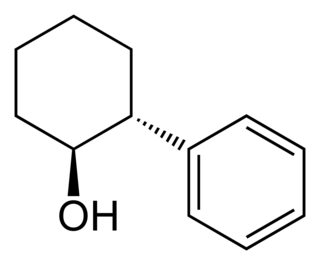
trans-2-Phenyl-1-cyclohexanol is an organic compound. The two enantiomers of this compound are used in organic chemistry as chiral auxiliaries.

4-Methylaminorex is a stimulant drug of the 2-amino-5-aryloxazoline class that was first synthesized in 1960 by McNeil Laboratories. It is also known by its street name "U4Euh" ("Euphoria"). It is banned in many countries as a stimulant.

Ethylone, also known as 3,4-methylenedioxy-N-ethylcathinone, is a recreational designer drug classified as an entactogen, stimulant, and psychedelic of the phenethylamine, amphetamine, and cathinone chemical classes. It is the β-keto analogue of MDEA ("Eve"). Ethylone has only a short history of human use and is reported to be less potent than its relative methylone. In the United States, it began to be found in cathinone products in late 2011.

Mivacurium chloride is a short-duration non-depolarizing neuromuscular-blocking drug or skeletal muscle relaxant in the category of non-depolarizing neuromuscular-blocking drugs, used adjunctively in anesthesia to facilitate endotracheal intubation and to provide skeletal muscle relaxation during surgery or mechanical ventilation.

Resmethrin is a pyrethroid insecticide with many uses, including control of the adult mosquito population.

Cyclopentamine is a sympathomimetic alkylamine, classified as a vasoconstrictor. Cyclopentamine was indicated in the past as an over-the-counter (OTC) medication for use as a nasal decongestant, notably in Europe and Australia, but has now been largely discontinued.
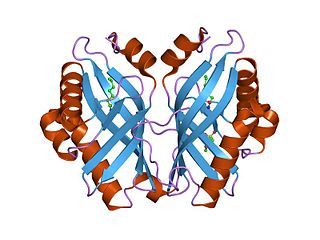
In enzymology, a limonene-1,2-epoxide hydrolase (EC 3.3.2.8) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
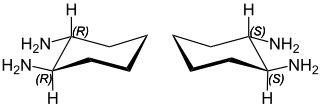
trans-1,2-Diaminocyclohexane is an organic compound with the formula C6H10(NH2)2. This diamine is a building block for C2-symmetric ligands that are useful in asymmetric catalysis.

2-Aminotetralin (2-AT), also known as 1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalen-2-amine (THN), is a stimulant drug with a chemical structure consisting of a tetralin group combined with an amine.
Substituted amphetamines are a class of compounds based upon the amphetamine structure; it includes all derivative compounds which are formed by replacing, or substituting, one or more hydrogen atoms in the amphetamine core structure with substituents. The compounds in this class span a variety of pharmacological subclasses, including stimulants, empathogens, and hallucinogens, among others. Examples of substituted amphetamines are amphetamine (itself), methamphetamine, ephedrine, cathinone, phentermine, mephentermine, tranylcypromine, bupropion, methoxyphenamine, selegiline, amfepramone (diethylpropion), pyrovalerone, MDMA (ecstasy), and DOM (STP).

4-Substituted-2,5-dimethoxyamphetamines (DOx) is a chemical class of substituted amphetamine derivatives featuring methoxy groups at the 2- and 5- positions of the phenyl ring, and a substituent such as alkyl or halogen at the 4- position of the phenyl ring. Most compounds of this class are potent and long-lasting psychedelic drugs, and act as highly selective 5-HT2A, 5-HT2B, and 5-HT2C receptor partial agonists. A few bulkier derivatives such as DOAM have similarly high binding affinity for 5-HT2 receptors but instead act as antagonists, and so do not produce psychedelic effects though they retain amphetamine-like stimulant effects.
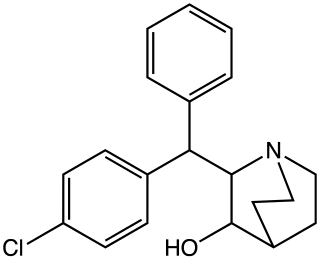
AL-1095, is a centrally acting stimulant drug with comparable effects to amphetamine, developed by Bristol in the 1970s.
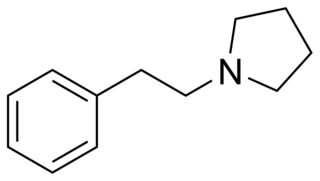
1-(2-Phenylethyl)pyrrolidine (PEP) is a chemical compound. It is an analogue of 2-phenylethylamine where the amine has been replaced by a pyrrolidine ring.
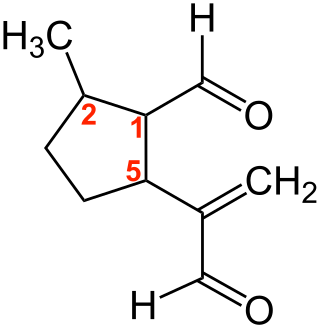
Dolichodial is a natural chemical compound with two aldehyde groups, which belongs to the group of iridoids.