
Amphetamine is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant that is used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), narcolepsy, and obesity; it is also used to treat binge eating disorder in the form of its inactive prodrug lisdexamfetamine. Amphetamine was discovered as a chemical in 1887 by Lazăr Edeleanu, and then as a drug in the late 1920s. It exists as two enantiomers: levoamphetamine and dextroamphetamine. Amphetamine properly refers to a specific chemical, the racemic free base, which is equal parts of the two enantiomers in their pure amine forms. The term is frequently used informally to refer to any combination of the enantiomers, or to either of them alone. Historically, it has been used to treat nasal congestion and depression. Amphetamine is also used as an athletic performance enhancer and cognitive enhancer, and recreationally as an aphrodisiac and euphoriant. It is a prescription drug in many countries, and unauthorized possession and distribution of amphetamine are often tightly controlled due to the significant health risks associated with recreational use.

Methcathinone is a monoamine alkaloid and psychoactive stimulant, a substituted cathinone. It is used as a recreational drug due to its potent stimulant and euphoric effects and is considered to be addictive, with both physical and psychological withdrawal occurring if its use is discontinued after prolonged or high-dosage administration. It is usually snorted, but can be smoked, injected, or taken orally.

Dextroamphetamine is a potent central nervous system (CNS) stimulant and enantiomer of amphetamine that is primarily prescribed for the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy. It has also been used illicitly to enhance cognitive and athletic performance, as well as an aphrodisiac and euphoriant. Dextroamphetamine is generally regarded as the prototypical stimulant.
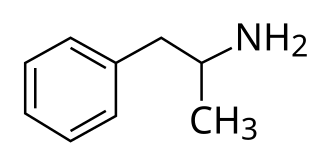
Adderall and Mydayis are trade names for a combination drug containing four salts of amphetamine. The mixture is composed of equal parts racemic amphetamine and dextroamphetamine, which produces a (3:1) ratio between dextroamphetamine and levoamphetamine, the two enantiomers of amphetamine. Both enantiomers are stimulants, but differ enough to give Adderall an effects profile distinct from those of racemic amphetamine or dextroamphetamine, which are marketed as Evekeo and Dexedrine/Zenzedi, respectively. Adderall is used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy. It is also used illicitly as an athletic performance enhancer, cognitive enhancer, appetite suppressant, and recreationally as a euphoriant. It is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant of the phenethylamine class.

2,5-Dimethoxy-4-methylamphetamine is a psychedelic and a substituted amphetamine. It was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin, and later reported in his book PiHKAL: A Chemical Love Story. DOM is classified as a Schedule I substance in the United States, and is similarly controlled in other parts of the world. Internationally, it is a Schedule I drug under the Convention on Psychotropic Substances. It is generally taken orally.

para-Methoxyamphetamine (PMA), also known as 4-methoxyamphetamine (4-MA), is a designer drug of the amphetamine class with serotonergic effects. Unlike other similar drugs of this family, PMA does not produce stimulant, euphoriant, or entactogen effects, and behaves more like an antidepressant in comparison, though it does have some psychedelic properties.
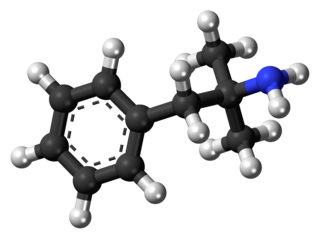
Phentermine, sold under the brand name Adipex-P among others, is a medication used together with diet and exercise to treat obesity. It is available by itself or as the combination phentermine/topiramate. Phentermine is taken by mouth.

Phenmetrazine, sold under the brand name Preludin among others, is a stimulant drug first synthesized in 1952 and originally used as an appetite suppressant, but withdrawn from the market in the 1980s due to widespread misuse. It was initially replaced by its analogue phendimetrazine which functions as a prodrug to phenmetrazine, but now it is rarely prescribed, due to concerns of misuse and addiction. Chemically, phenmetrazine is a substituted amphetamine containing a morpholine ring or a substituted phenylmorpholine.
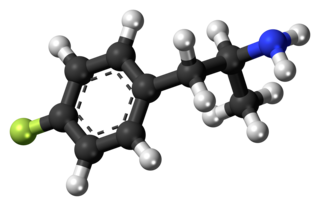
4-Fluoroamphetamine, also known as para-fluoroamphetamine (PFA) is a psychoactive research chemical of the phenethylamine and substituted amphetamine chemical classes. It produces stimulant and entactogenic effects. As a recreational drug, 4-FA is sometimes sold along with related compounds such as 2-fluoroamphetamine and 4-fluoromethamphetamine.

Clobenzorex is a stimulant drug of the amphetamine chemical class used as an appetite suppressant. The drug is legally distributed in Mexico under the trade name Asenlix by Aventis.

Lisdexamfetamine, sold under the brand names Vyvanse and Elvanse among others, is a stimulant medication that is used to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in children and adults and for moderate-to-severe binge eating disorder in adults. Lisdexamfetamine is taken by mouth. Its effects generally begin within two hours and last for up to 14 hours.

para-Methoxy-N-methylamphetamine, chemically known as methyl-MA, 4-methoxy-N-methylamphetamine, and 4-MMA is a stimulant and psychedelic drug closely related to the amphetamine-class serotonergic drug para-methoxyamphetamine (PMA). PMMA is the 4-methoxy analog of methamphetamine. Little is known about the pharmacological properties, metabolism, and toxicity of PMMA; because of its structural similarity to PMA, which has known toxicity in humans, it is thought to have considerable potential to cause harmful side effects or death in overdose. In the early 2010s, a number of deaths in users of the drug MDMA were linked to misrepresented tablets and capsules of PMMA.

Etilamfetamine, also known as N-ethylamphetamine and formerly sold under the brand names Apetinil and Adiparthrol, is a stimulant drug of the amphetamine family. It was invented in the early 20th century and was subsequently used as an anorectic or appetite suppressant in the 1950s, but was not as commonly used as other amphetamines such as amphetamine, methamphetamine, and benzphetamine, and was largely discontinued once newer drugs such as phenmetrazine were introduced.

Levoamphetamine is a stimulant medication which is used in the treatment of certain medical conditions. It was previously marketed by itself under the brand name Cydril, but is now available only in combination with dextroamphetamine in varying ratios under brand names like Adderall and Evekeo. The drug is known to increase wakefulness and concentration in association with decreased appetite and fatigue. Pharmaceuticals that contain levoamphetamine are currently indicated and prescribed for the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), obesity, and narcolepsy in some countries. Levoamphetamine is taken by mouth.
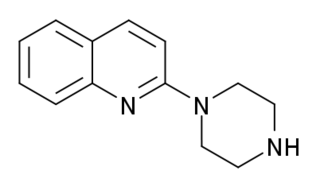
Quipazine, also known as 1-(2-quinolinyl)piperazine, is a serotonergic drug of the arylpiperazine family and an analogue of 1-(2-pyridinyl)piperazine which is used in scientific research. It was first described in the 1960s and was originally intended as an antidepressant but was never developed or marketed for medical use.

2-Aminoindane (2-AI) is an aminoindane and research chemical with applications in neurologic disorders and psychotherapy that has also been sold as a designer drug. It acts as a selective substrate for NET and DAT.

4-Methylamphetamine is a stimulant and anorectic drug of the phenethylamine and amphetamine chemical classes.

4-Methylmethamphetamine (4-MMA), also known as mephedrine, is a putative stimulant and entactogen drug of the amphetamine family. It acts as a serotonin–norepinephrine–dopamine releasing agent (SNDRA). The drug is the β-deketo analogue of mephedrone and the N-methyl analogue of 4-methylamphetamine (4-MA).
Substituted amphetamines, or simply amphetamines, are a class of compounds based upon the amphetamine structure; it includes all derivative compounds which are formed by replacing, or substituting, one or more hydrogen atoms in the amphetamine core structure with substituents. The compounds in this class span a variety of pharmacological subclasses, including stimulants, empathogens, and hallucinogens, among others. Examples of substituted amphetamines are amphetamine (itself), methamphetamine, ephedrine, cathinone, phentermine, mephentermine, tranylcypromine, bupropion, methoxyphenamine, selegiline, amfepramone (diethylpropion), pyrovalerone, MDMA (ecstasy), and DOM (STP).
Amphetamine type stimulants (ATS) are a group of synthetic drugs that are chemical derivatives of the parent compound alpha-methylphenethylamine, also known as amphetamine. Common ATS includes amphetamine, methamphetamine, ephedrine, pseudoephedrine, 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA), 3,4-methylenedioxyamphetamine (MDA) and 3,4-methylenedioxyethylamphetamine (MDEA). ATS when used illicitly has street names including ice, meth, crystal, crank, bennies, and speed. Within the group of amphetamine-type stimulants, there are also prescription drugs including mixed amphetamine salts, dextroamphetamine, and lisdexamfetamine.



















